Income Tax

Income
Monday, Jan 13 th
Priorities
• Priority 1
• Essential to life
• Priority 2
• Not essential to life, but important
• Priority 3
• Neither essential, nor important
Needs VS Wants
• In a well developed paragraph, explain how the media turns wants into needs through advertising.
Story
• What sources of income was Rio planning to have as a professional athlete?
• What are some other sources of income that a professional athlete or celebrity could have?
• Rio talked about making 2 million a year, how much money do you think sport figured and celebrities make?
Story
• Does that sound like enough money to meet Rio’s, or another celebrity’s, needs and wants?
• How does Rio’s dream compare with that of a business owner, a professional, a trade-worker, or a student?
Student Sources of Income
• Typical sources of student income include:
• Allowances and gifts
• Wages and tips
• Payments for occasional work
• Income from personal business
• Income from government sources
• Income from investments
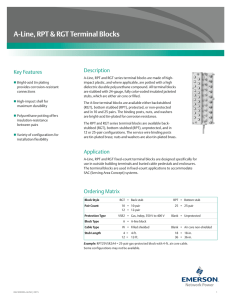
Pay Stub
• General Information: name, employee number, pay period, cheque number, etc.
• Earnings:
• type of earnings (regular, overtime, etc.)
• hours or days worked
• amount earned in a current period
• year-to-date (YTD).
Pay Stub
• Deductions:
• income tax, employment insurance, Canadian Pension Plan
• may also include union dues, medical plan and extended medical coverage, life and disability insurance, savings plans, etc.
• Deductions = automatic payments to government and other organizations that your employer makes on your behalf to pay services or benefits
Pay Stub
• Vacation Pay:
• Employees are entitled to be paid four per cent of their total wages (six per cent after five days) for vacation pay.
• This lets employees take two or three weeks of vacation with pay
• Casual and part-time employees often receive their vacation pay on each paycheque
Pay Stub
• Income Tax:
• a portion of your income that is sent to the Governments of
Canada and BC to pay for federal and provincial government services
• The federal, provincial and territorial governments require you to pay a portion of your income in tax so that the government will have money to operate through the year
Pay Stub
• Income Tax:
• Paid on your total income, minus a number of allowable deductions.
• Eg. Basic personal amount people who have taxable income of less than $10,320 paid no tax
• People who earned more that that could pay between 15 and 29% of their taxable income (federal) and 5.06 to 14.7% (BC)
• Canada has a progressive tax system, meaning that those who have higher earnings pay a higher percentage of their income in taxes
Pay Stub
• Income Tax:
• Not always deducted at the source (by the employer)
• Tax may not be deducted if:
• Your projected income for the year is below the amount of the basic exemption
• You do contract work that is not regular employment
• Whether tax is deducted or not, you are responsible for reporting and paying any income tax you owe
Pay Stub
• Canada Pension Plan (CPP):
• Percentage of gross income paid by employees and employers to provide income when workers retire or become disabled
• Employment Insurance:
• percentage of gross income paid by employees and employers to provide temporary payments if workers become unemployed
Group Work
• Please get into your groups (for your characters):
• Luna, Nikos, Rio, Sienna, Indigo, Quinn, Kane, Gaia
Monthly Income
• Many paycheques are bi-weekly (every two weeks) or semimonthly (twice a month)
• Other types of income may be quarterly (four times a year), annual (once a year), or irregular
Monthly Income
• You can convert income to a monthly amount using the following formulae:
• Semi-monthly income x 2 = monthly income
• Bi-weekly income x 2.17 = monthly income
(the 2.17 comes from 26÷12)
• Quarterly income ÷ 3 = monthly income
• Yearly income ÷ 12 = monthly income
• How would you calculate annual income?
Group Work
• Handout 5-2:
• Use income records to complete the handout
Individually
• Handout 5-3:
• List your own income from various sources (gifts, part-time jobs, allowance, etc.)
• Total your income
• Project your income to determine an anticipated income after deductions over a month and a year.