Plant Growth & Development
advertisement

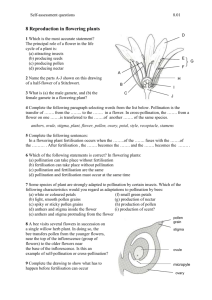
Plant Growth & Development Introduction • There are 6 plant processes that effect growth which are…. – Photosynthesis – Respiration – Absorption – Transpiration – Translocation – Reproduction Use the diagram below to complete the labels on the flower structure worksheet stigma anther style stamen filament ovary ovule petal sepal receptacle stem Flower Structure Pollination Fruit Development Seed Dispersal Germination Test carpel Plant Reproduction Click to Enter Flowers are the reproductive organs of plants Flower Structure Pollination Fertilisation Seed Dispersal Germination Test Pollination The pollen grain contains the male sex cell (gamete) Flower Structure Pollination Fertilisation Seed Dispersal Germination Test What is Pollination? Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma • This is an example of cross-pollination as the pollen travels from one flower to a different flower. This is desirable in plants as it promotes variation. Flower Structure Pollination Fertilisation Seed Dispersal Germination Test Pollen can be carried between flowers by insects or by wind Flower Structure Pollination Fertilisation Seed Dispersal Germination Test Insect-pollinated flowers are adapted to attract insects to them to enable transfer of pollen Pollen has barbs for hooking onto insect fur nectar and a scent present Anthers positioned to rub pollen onto insects Sticky stigma to collect pollen Flower Structure Pollination Brightly colored petals Fertilisation Seed Dispersal Germination Test Wind-pollinated flowers are different in structure because they do not have to attract insects to them but do need to be exposed to the wind. Pollen grains are very small and light. They occur in very large numbers Anthers are exposed to the wind so that pollen can easily be blown away Stigma are feathery to catch pollen carried on wind Petals are small and green as there is no need to attract insects Flower Structure No scent or nectary Pollination Fertilisation Seed Dispersal Germination Test Self-pollination occurs when pollen falls from the anther onto the stigma of the same flower • Click to show animation of selfpollination • Self-pollination is not desirable as it reduces variation Flower Structure Pollination Fertilisation Seed Dispersal Germination Test Flowers will prevent self-pollination by either having stigma above stamen or… Flower Structure Pollination Fertilisation Seed Dispersal Germination Test …by having stamen and stigma mature at different times. Flower Structure Pollination Fertilisation Seed Dispersal Germination Test Click on the icon below to view the summary video on pollination If the hyperlink does not work then copy and paste this url into a new browser window and you can watch the video then, url: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ge3EM8AERV0 Insect pollination (1 minute) Flower Structure Pollination Fertilisation Seed Dispersal Germination Test Fertilization and Fruit Development Flower Structure Pollination Fruit Development Seed Dispersal Germination Test Once pollination occurs a tube grows from the pollen grain down through the style to the ovule stigma style carpel ovary Click to view the animation ovule Note: Petals not shown in order to simplify diagram Flower Structure Pollination Fruit Development Seed Dispersal Germination Test Fertilization occurs when the male gamete fuses with the ovule (the female gamete) Click to view the animation Flower Structure Pollination Fruit Development Seed Dispersal Germination Test Watch this short introductory video to review fertilization (1 minute) If the hyperlink does not work then copy and paste this url into a new browser window and you can watch the video then, url: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pVhH2GPlckE Seed Dispersal Flower Structure Pollination Fruit Development Seed Dispersal Germination Test Watch the video on seed dispersal (lasts just under 10 minutes) If the hyperlink does not work then copy and paste this url into a new browser window and you can watch the video then, url: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zbQ1jWl3AOM After fertilization the petals, stamen and sepals fall off. The ovule turns into a seed, the fertilized egg inside develops into an embryo plant. Cotyledon: Food store Testa: tough seed coat Plumule: Embryo shoot Micropyle: Hole made by pollen tube Radicle: Embryo root Flower Structure Pollination Fruit Development Seed Dispersal Germination Test Embryo plant Seeds need to be dispersed away from the parent plant in order to reduce competition for space, light, nutrients and water. • Seeds can be dispersed by: • • • • Wind Water Mechanical Animals Photosynthesis • Process by which green plants manufacture food. • The beginning of the food chain for all living things on earth. Photosynthesis • Carbon dioxide and water are combined in the presence of light to make sugar and oxygen. • The Formula is…. 6CO2 + 6H2O + 672Kcal C6H12O6 + 6O2 Carbon Dioxide Water Light Glucose Sugar Oxygen Respiration • The process through which plant leaves, stems, and roots consume oxygen and give off carbon dioxide. • Plants produce much more oxygen through photosynthesis then they use through respiration. Photosynthesis vs. Respiration Absorption • The process by which plant roots take in water, air, & nutrients and conduct them to the stem. Transpiration • The process by which plants roots lose water from leaves and stems through evaporation. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mc9gUm1mMzc Translocation • The process by which food and nutrients are moved within a plant from one plant part to another. • Water and minerals move from the roots up to the leaves and food moves from the leaves down to the roots. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r-z7hbCFI2o Translocation http://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=xGCnuXxbZGk Classification of Plants • Vascular plants: Have tube-like structures that carry water, and nutrients throughout the plant. Classification of Plants • Nonvascular plants: Do not have tubelike structures and use other ways to move water and substances. Seedless Plants • Nonvascular plants like moss are only a few cells thick. Each cell absorbs water directly from it environment. • Vascular plants distribute water and nutrients to all plant cells. • Question: Which type of plant can grow larger; nonvascular and vascular? – Vascular can grow bigger and thicker because the vascular tissue distributes the water and nutrients. Seedless Plants • Question: Name parts of a plant. – Roots – Stems – Leaves – Flowers • Question: What do the flowers produce? – Seeds Seedless Plants • Question: Do all plants reproduce from seeds? • Some plants reproduce by spores. Seedless Plants • Question: Can you name a plant that does not have seeds and uses spores to reproduce? –Mosses –Ferns – Video: Seedless plantg Seedless Plants • Ferns and Mosses: – We now know that they do not reproduce by seeds but use spores. Therefore they are alike in that way. – Question: How are they different? • Think vascular, nonvascular Seedless Plants • Peat and Coal: As seedless plants died they compacted and compressed and turned into peat. Over time the peat turned into coal. Seedless Plants • Peat supplies about one third of Ireland’s energy requirements. • Brain Pop: Seedless Plants Seed Plants • Most seed plants have leaves, stems, roots, and vascular tissue. • They also produce seeds. • Question: What is inside a seed? – Embryo and stored food. Video: Seeds 2:00 Seed Plants • Leaves: Where the food making process occurs. – What is the name of that process? • Photosynthesis Seed Plants • Leaf Cell Layers Leaf Cell Layers • Epidermis: Upper and lower surface of a leaf. • Waxy cuticle: coats Epidermis. • Stomata: Opening in leaf to allow; – What gases to enter the leaf? • Carbon dioxide to enter – What gas to exit the leaf? • Oxygen to exit the leaf. Leaf Cell Layers • Guard Cells: Two guard cells surround each stoma to open and close it. • Video: Plant Cells 3:25, Types of plant cells 2:43 Leaf Cell Layers • Just below the epidermis is the palisade layer where most of the food is produced. • Video: Leaves 2:52 Stems • Stems: Materials move between leaves and roots through the vascular tissue in the stem. • Stems support the branches, leaves, and reproductive structures. Video: Stems 3:16 • Question: What is the largest part of a plant? –Roots Roots • Question: What is the purpose of roots? • Transport water and other substances. – Anchor – Support – Store food Video: 1:43 Gymnosperms • Gymnosperms: Vascular plants that produce seeds that are not protected by fruit. • Question: What is an example of this type of plant? – Conifers: Pines, firs, spruces, redwoods. Angiosperms • Angiosperms: A vascular plant that flowers and produces fruit with one or more seeds. • Question: What is an example of an angiosperm? Angiosperms • Life cycle of angiosperms. • Question: What do you call a plant that has a life cycle of one year? Angiosperms • Question: What do you call a plant that continues to survive for many years? – Perennial – Brain Pop: Seed Plants Seed Plant Class Work • Create a list of as many products of seed plants that you can think. – Examples: Potato Chips, oranges. – Video: Sci. of Plants 22