Unit plan Gardens WEB
advertisement
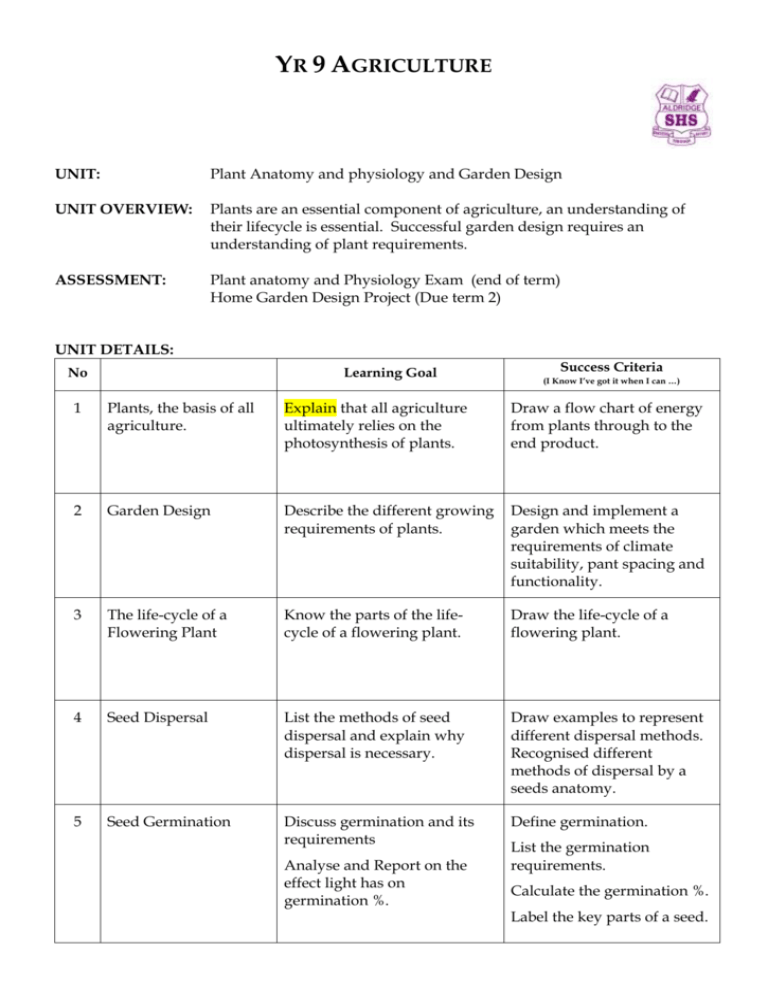
YR 9 AGRICULTURE UNIT: Plant Anatomy and physiology and Garden Design UNIT OVERVIEW: Plants are an essential component of agriculture, an understanding of their lifecycle is essential. Successful garden design requires an understanding of plant requirements. ASSESSMENT: Plant anatomy and Physiology Exam (end of term) Home Garden Design Project (Due term 2) UNIT DETAILS: No Learning Goal Success Criteria (I Know I’ve got it when I can …) 1 Plants, the basis of all agriculture. Explain that all agriculture ultimately relies on the photosynthesis of plants. Draw a flow chart of energy from plants through to the end product. 2 Garden Design Describe the different growing requirements of plants. Design and implement a garden which meets the requirements of climate suitability, pant spacing and functionality. 3 The life-cycle of a Flowering Plant Know the parts of the lifecycle of a flowering plant. Draw the life-cycle of a flowering plant. 4 Seed Dispersal List the methods of seed dispersal and explain why dispersal is necessary. Draw examples to represent different dispersal methods. Recognised different methods of dispersal by a seeds anatomy. 5 Seed Germination Discuss germination and its requirements Define germination. Analyse and Report on the effect light has on germination %. List the germination requirements. Calculate the germination %. Label the key parts of a seed. 6 Vegetative growth List the characteristics of a monocot and a dicot. Identify monocots and dicots from their parts. Describe the process of Photosynthesis. Define photosynthesis using words and symbols. Identify the colours of light used by plants from the spectrum. Explain why plants are green. List the key functions of plant roots and stem; including xylem and phloem. Analyse the effect root pests may have on a plant. List the main colours of the spectrum used by plants. Compare xylem and phloem. 7 Flower and Fruit Formation Identify the key structures and their function in a flower. Label the parts of a flower. 8 Plants have particular requirements which affect when and how they are grown. Define pollination and fertilisation. Compare pollination and fertilisations. Reproduction in plants List and describe the 2 main types of reproduction in plants. 9 Explain why fruit forms poorly in the absence of bees. Describe the procedure for doing tip and semi-hardwood cuttings. Produce cuttings.