Lab 6
advertisement

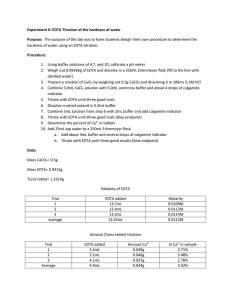
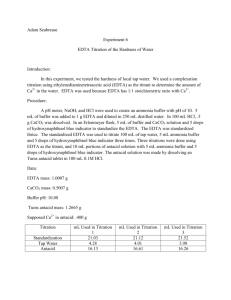
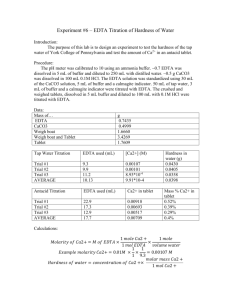
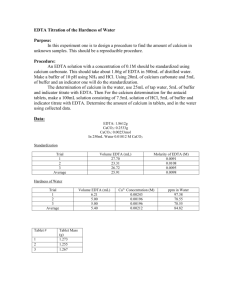
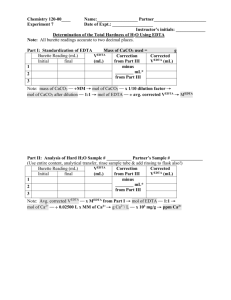
Experiment 6: EDTA Titration of the Hardness of Water Introduction: This experiment was designed to familiarize the student with experimental design by allowing the student to develop his/her own procedure to determine the hardness of tap water. The student was then instructed to extend his/her procedure to determine the calcium content of a commercially-available antacid. Procedure: A pH meter was calibrated, then utilized to measure the pH of a premade ammonia buffer solution. Hydrochloric acid was added to the buffer solution until its pH was approximately 10. Then, 8mL of the buffer solution was combined with 1.8612g EDTA in a 500mL volumetric flask, which was then diluted to the mark with distilled water. A solution of calcium carbonate was prepared by dissolving approximately 0.50g CaCO3 in 0.1M HCl in a 100mL volumetric flask. The flask was then diluted to the mark with 0.1M HCl. An antacid solution was prepared similarly, using approximately 1.2743g of antacid and diluting to 100mL with 0.1M HCl. Three different solutions were titrated using the EDTA solution. The first was 3mL of the CaCO3 solution combined with 5mL of buffer and calmagite indicator. The second was 25mL of tap water combined with 5mL of buffer and calmagite indicator. The third was 3mL of the antacid solution combined with 5mL of buffer and calmagite indicator. All titrations were repeated until 3 good trials were obtained. Data: CaCO3 solution EDTA solution Mass (g) 0.5005 Mass (g) 1.8618 Volume (mL) 100 Volume (mL) 500 Standardization 3mL CaCO3 solution + 5mL buffer + 3 drops indicator Trial Initial Volume (mL) Final Volume (mL) 1 0 16.3 2 0 14.2 3 0 16.7 Tap Water Titration 25mL tap water +5mL buffer + 3 drops indicator Trial Initial Volume (mL) Final Volume (mL) 1 0 3.9 2 0 2.8 3 0 2.8 Tums Titration 3mL Tums solution + 5mL buffer + 3 drops indicator Trial Initial Volume (mL) Final Volume (mL) 1 0 15.00 2 0 14.80 3 0 14.60 Formulas for Calculations: Change in Volume Equation Change in Volume Example Δ𝑉 = 𝑉𝑓 − 𝑉𝑖 Molarity of CaCO3 Equation 𝑀𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 = 𝑔𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 × Molarity of CaCO3 Example 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 ÷ 0.100𝐿𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑛 100.0869𝑔 Molarity of EDTA Equation 𝐿𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 ∗ 𝑀𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 𝐿𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 (because moles of EDTA = moles of Ca2+ = moles of CaCO3) Molarity of Ca2+ in Tap Water Equation ̅𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 𝐿𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 ∗ 𝑀 𝐿𝑡𝑎𝑝 𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 (because moles of EDTA = moles of Ca2+) 𝑀𝐶𝑎2+ = Hardness of Tap Water (ppm) Equation 40.078𝑔 1000𝑚𝑔 × 𝑚𝑜𝑙 1𝑔 (because 1 ppm = 1 mg/L) 𝑝𝑝𝑚𝐶𝑎2+ = 𝑀𝐶𝑎2+ × Claimed % Ca2+ in Tums Equation 0.500𝑔𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 1𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 1𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐶𝑎2+ × × 1𝑡𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒𝑡 100.0869𝑔𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 1𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 40.078𝑔𝐶𝑎2+ × ÷ 𝑔𝑡𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒𝑡 × 100% 1𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐶𝑎2+ Grams Ca2+ in Tums Equation 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 ÷ 0.100𝐿𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑛 100.0869𝑔 0.01000𝑀𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 = 0.00300𝐿𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 ∗ 0.05000𝑀𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 0.01500𝐿𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 Molarity of Ca2+ in Tap Water Example 0.005210𝑀𝐶𝑎2+ = ̅𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 0.00258𝐿𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 ∗ 0.01072𝑀 0.02500𝐿𝑡𝑎𝑝 𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 Hardness of Tap Water (ppm) Example 208.8𝑝𝑝𝑚𝐶𝑎2+ = 0.005210𝑀𝐶𝑎2+ × 40.078𝑔 1000𝑚𝑔 × 𝑚𝑜𝑙 1𝑔 Claimed % Ca2+ in Tums Example 15.74%𝐶𝑎2+ = 0.500𝑔𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 1𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 1𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐶𝑎2+ × × 1𝑡𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒𝑡 100.0869𝑔𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 1𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 40.078𝑔𝐶𝑎2+ × ÷ 1.272𝑔𝑡𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒𝑡 × 100% 1𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐶𝑎2+ Grams Ca2+ in Tums Example 1𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐶𝑎2+ 40.078𝑔𝐶𝑎2+ × 1𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 1𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐶𝑎2+ 100𝑚𝐿𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑛 × 3𝑚𝐿𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑟𝑒𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 (because 3mL were used for each titration) ̅𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 × 𝑔𝐶𝑎2+ = 𝐿𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 × 𝑀 % Ca2+ in Tums Equation ̅𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 × 0.2199𝑔𝐶𝑎2+ = 0.01535𝐿𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 × 0.01072𝑀 × 40.078𝑔𝐶𝑎2+ 100𝑚𝐿𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑛 × 1𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐶𝑎2+ 3𝑚𝐿𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑟𝑒𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 1𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐶𝑎2+ 1𝑚𝑜𝑙𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 % Ca2+ in Tums Example %𝐶𝑎2+ = 𝑔𝐶𝑎2+ × 100% 𝑔𝑡𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒𝑡 % Difference Equation % 𝐷𝑖𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒 = 0.05000𝑀𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 = 0.5005𝑔𝐾𝐼𝑂3 × Molarity of EDTA Example 𝑀𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 = %𝐶𝑎2+ = 16.30mL = 16.91𝑚𝐿 − 0𝑚𝐿 17.29%𝐶𝑎2+ = 0.2199𝑔𝐶𝑎2+ × 100% 1.2720𝑔𝑡𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒𝑡 % Difference Example |𝑡𝑟𝑢𝑒 − 𝑒𝑥𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑙| × 100% 𝑡𝑟𝑢𝑒 9.829% 𝐷𝑖𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒 = |15.74% − 17.29%| × 100% 15.74% Summary of Calculations: Standardization Change in Volume Trial (mL) 1 16.30 2 14.21 3 16.70 Average Trial 1 2 3 Tums Titration Change in Volume (mL) 15.00 14.80 14.60 Average 0.009203658 0.010564763 0.008983212 0.009583878 Tap Water Titration Change in Volume (mL) 3.90 2.80 2.80 Average g Ca2+ % Ca2+ % Difference 0.192051324 0.18949064 0.186929955 0.18949064 15.09837452 14.89706286 14.6957512 14.89706286 5.887789967 7.142619434 8.397448901 7.142619434 Molarity of EDTA Molarity Ca2+ Hardness (ppm) 0.007801021 0.005600733 0.005600733 0.006334162 312.6493161 224.4661757 224.4661757 253.8605558 Molarity of CaCO3 : 0.050486128 M Claimed % Ca2+ in Tums : 15.74025254 % Conclusions: The average calculated hardness of tap water was 208.27ppm. According to accepted standards, this indicates that the tap water was very hard. This can pose certain health risks, and it is important to conduct further experimentation to determine if these results were accurate. The commercially-available antacid analyzed in this experiment was Tums. The manufacturer’s claim is that there are 500mg of calcium carbonate per tablet. This translates to a claimed Ca 2+ percentage of 15.74%. The average experimental Ca2+ percentage was 16.54%. This is very close to the advertised percentage, although slightly higher. This may be due to overshooting the end point of the titration. Overall, the percent difference of the titration was 5.106%, which is acceptable.