Experiment 6: EDTA Titration of the Hardness of Water
advertisement

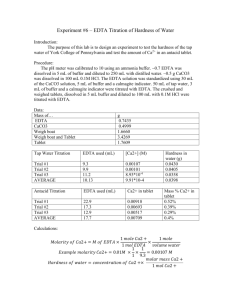
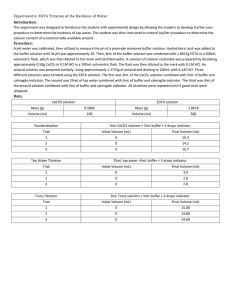
Experiment 6: EDTA Titration of the hardness of water Purpose: The purpose of this lab was to have students design their own procedure to determine the hardness of water using an EDTA titration. Procedure: 1. Using buffer solutions of 4,7, and 10, calibrate a pH meter 2. Weigh out 0.09396g of EDTA and dissolve in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask (fill to the line with distilled water) 3. Prepare a solution of CaCl2 by weighing out 0.5g CaCO3 and dissolving it in 100mL 0.1M HCl 4. Combine 3.0mL CaCl2 solution with 5.0mL ammonia buffer and about 4 drops of calgamite indicator 5. Titrate with EDTA until three good trials 6. Dissolve crushed antacid in 5.0mL buffer 7. Combine 5mL solution from step 6 with 2mL buffer and add calgamite indicator 8. Titrate with EDTA until three good trials (blue endpoint) 9. Determine the percent of Ca2+ in tablets 10. Add 25mL tap water to a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask a. Add about 3mL buffer and several drops of calgamite indicator b. Titrate with EDTA until three good results (blue endpoint) Data: Mass CaCO3= 0.5g Mass EDTA= 0.9313g Tums tablet= 1.3214g Molarity of EDTA Trial 1 2 3 Average EDTA added 13.7mL 13.4mL 13.2mL 13.43mL Molarity 0.0109M 0.0112M 0.0114M 0.0112M Antacid (Tums tablet) titration Trial 1 2 3 Average EDTA added 5.5mL 5.1mL 4.1mL 4.9mL Amount Ca2+ 0.049g 0.046g 0.037g 0.044g % Ca2+ in sample 3.71% 3.48% 2.78% 3.32% Tap water titration Trial 1 2 3 Average Ca2+ concentration 2.28x10-4M 2.78x10-4M 2.96x10-4M 2.67x10-4M EDTA added 5.1mL 6.2mL 6.6mL 5.97mL ppm 9.16 11.1 11.8 10.7 Calculations: Molarity of EDTA: 0.5𝑔 𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 ∗ 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 1 ∗ ∗ 0.003𝐿 𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 ∗ = 0.0109𝑀 100.09𝑔 0.1𝐿 0.0137𝐿 Ca2+ concentration in tap water: 0.0051𝐿 ∗ 0.0112𝑀 𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 ∗ 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐶𝑎2+ 1 ∗ = 2.28 ∗ 10−4 1 𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 0.25𝐿 Hardness of water: 2.28𝑥10 −4 𝑀 𝐶𝑎2+ ∗ 40.07𝑔 𝐶𝑎 1000𝑚𝑔 ∗ = 9.16𝑝𝑝𝑚 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 1𝑔 Tums Tablet Claimed: 0.5𝑔 𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 ∗ 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐶𝑎2+ 40.07𝑔 𝐶𝑎2+ ∗ ∗ = 2.002𝑔 𝐶𝑎2+ 100.09𝑔 𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 2.002𝑔 𝐶𝑎2+ 𝑥100 = 15.15% 1.3214𝑔 𝑡𝑢𝑚𝑠 𝑡𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒𝑡 Tums tablet experimental: 0.0055𝐿 ∗ 0.112𝑀 𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 ∗ 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐶𝑎2+ 40.07𝑔 𝐶𝑎2+ ∗ = 0.049𝑔 𝐶𝑎2+ 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝐸𝐷𝑇𝐴 1𝑚𝑜𝑙 0.049𝑔 𝐶𝑎2+ 𝑥100 = 3.71% 1.3214𝑔 𝑡𝑢𝑚𝑠 𝑡𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒𝑡 Difference: 15.15% − 3.32% = 11.83% 0.2002𝑔 𝐶𝑎2+ − 0.044𝑔 𝐶𝑎2+ = 0.1562𝑔 𝐶𝑎2+ Conclusion: The goal of this lab was to determine the hardness of tap water. According to our experiment results, the average hardness of water was 10.7ppm. The amount of Ca2+ in a Tums tablet was also measured. The claimed amount of calcium in the tablet was 15.15% but the average we calculated after gathering results was only 3.32%. Possible sources of error could have occurred during titration. Our samples containing the tap water and Tums tablets didn’t require a lot of EDTA before the endpoint.