Carbs and Lipids Review
advertisement
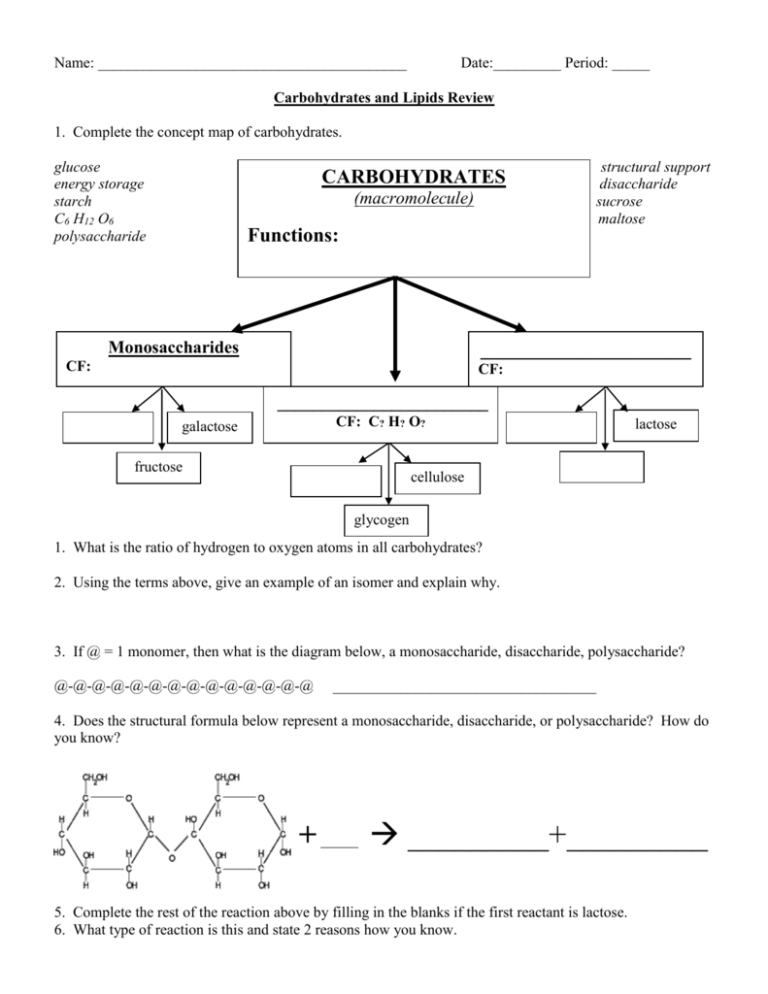
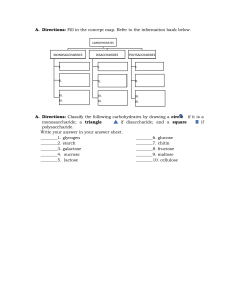
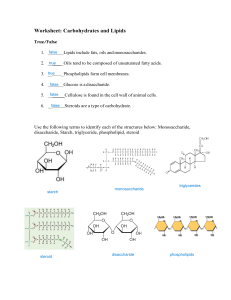
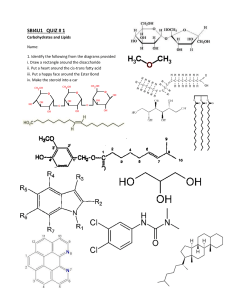
Name: _________________________________________ Date:_________ Period: _____ Carbohydrates and Lipids Review 1. Complete the concept map of carbohydrates. glucose energy storage starch C6 H12 O6 polysaccharide CARBOHYDRATES (macromolecule) structural support disaccharide sucrose maltose Functions: Monosaccharides _____________________ CF: CF: ________________________ CF: C? H? O? galactose fructose lactose cellulose glycogen 1. What is the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms in all carbohydrates? 2. Using the terms above, give an example of an isomer and explain why. 3. If @ = 1 monomer, then what is the diagram below, a monosaccharide, disaccharide, polysaccharide? @-@-@-@-@-@-@-@-@-@-@-@-@-@ ___________________________________ 4. Does the structural formula below represent a monosaccharide, disaccharide, or polysaccharide? How do you know? + _____ _________+_________ 5. Complete the rest of the reaction above by filling in the blanks if the first reactant is lactose. 6. What type of reaction is this and state 2 reasons how you know. 7. Complete the concept map for lipids. triglyceride 3 fatty acids energy storage phospholipid insulation hormones glycerol LIPIDS (macromolecule) Functions: __________________ __________________ carbons are fulfilled with hydrogens; no double bonds Steroids Waxes glycerol lubrication unsaturated structural support phosphate group cell membranes saturated ______________ Found: ________________ carbons not fulfilled with hydrogens; double bonds present 2 fatty acids 8. Is there a set chemical formula for lipids (triglycerides, waxes, steroids, or phospholipids)? 9. Label each of the letters below. A___________________ + B_______________ C _______________________ + D _______ 9. Use the reaction below to answer the following questions. a. What are your reactants in this reaction? b. What are your products in this reaction? c. What type of reaction is this and how do you know? 10. What type of reaction formed this polymer? How do you know?