Biochemistry Week 3: Macromolecules

Biochemistry Week 3: Macromolecules
Learning Objective: The main objective of this learning block will be to explore the three main macromolecules used as energy sources in the body, how we get them and their other uses.
Required Readings:
Nelson Biology 12 Text: Chapter 1.2
Learning Goals:
By the end of this learning block we will be able to…
Define hydrocarbons
Identify the functional groups found in biological macromolecules
Explain how the functional groups are related to the bonds created in macromolecules and their purpose in the body
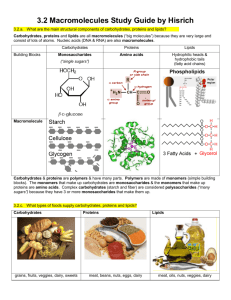
Explain the main properties of carbohydrates
List the three monomers of carbohydrates
Explain how monomers form larger macromolecules and how macromolecules are broken down.
Discuss the role of carbohydrates in the body
Describe the use of lipids in the body and where we derive them from
Explain how we get proteins and what they are used for
Practice Questions:
Organic Chemistry
1) List the elements that must be present for a compound to be considered "organic" and why do we call them organic compounds?
2) Discuss how the special bonding properties of carbon allow organic compounds to be so prevalent in nature.
3) What are "functional groups"?
4) List the main functional groups that we will be considering in biology.
5) What is the importance of functional groups within a biological organism?
Carbohydrates
1) What does it mean for a molecule to be a polymer? What polymers are found in nature?
2) How can simple biological molecules, like a monosaccharide, form a polymer and then how can that polymer be broken down into simple monomers?
3) Discuss how carbohydrates are formed, their chemical composition and uses in nature.
4) Explain, with examples, what an isomer is.
5) How are carbohydrates scientifically named?
6) Explain the process required to link multiple glucose molecules together in order to make chitin.
7) Text questions: pg. 34 #2,3,6-8
Lipids
1) List the four types of fats.
2) What similar chemical composition do all fats have. What is special about fatty acids and glycerol.
3) List some of the properties and uses of fats?
4) How are phospholipids able to form the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane?
5) How are steroids used in the body?
6) Explain how the cell membrane is modified to make it a more effective barrier for a cell than a simple liposome.
7. Practice: pg. 40 # 11-16
Proteins
1) List some of the uses of proteins in nature?
2) State another name for proteins and explain how is this name a better descriptor of the structure of proteins?
3) Describe the four groups in every amino acid.
4) Explain how the increasing levels of structure are achieved in a protein and how these structures affect the role of the protein.
5) Why would a protein commonly found in a cheek cell be less effective in the stomach?
6) How are enzymes vital to biological functions?
Peer Assessment :
With a classmate discuss your work. Together determine which of the above criteria have been met and which have not been met. For any criteria not met, explain why?
Criteria not met
Self Assessment :
Criteria met
Reflect on the above success criteria. Which criteria are you really comfortable with (criteria met) and which criteria require a little more thought / work before you are comfortable (criteria not met)
Criteria met Criteria not met
Self Reflections:
Based on your peer and self assessment, reflect on what changes might need to be made in order for you to maintain or enhance your mastery of the material for the unit test and/or better prepare you to master the new material covered next week