Heterotrophic
advertisement

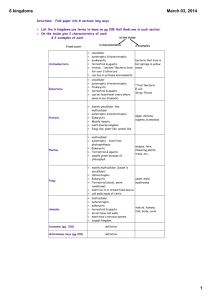
The student will be able to… Identify the basic characteristics of organism, including prokaryotic or eukaryotic, unicellular or multicellular, autotrophic or heterotrophic, and mode of reproduction, that further classify them in the currently recognized Kingdoms. Write these Key Terms in your notes!!!! (words on left) Key Terms to Know • Unicellular – made up of one cell (ex. bacteria) • Multicellular – made up of more than one cell (ex. you) • Prokaryote – cells with an outside membrane only, the organelles inside do not have membranes, no nucleus • Eukaryote – cells with outside membranes and the organelles inside have membranes; ex: nuclear membrane around the nucleus (ex. Plants and animals) • Autotrophic – makes its own food through the process of photosynthesis (ex. - plants) • Heterotrophic – does not make its own food; relies on (eats/digest) others for food (ex.- you) • Modes of Reproduction– Asexual or Sexual Reproduction Here's a simple visual comparison between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell: Two Types of Cells Write these on a foldable with 2 flaps or double bubble map • • • • Prokaryotic Cells No nucleus No membrane-covered organelles Circular DNA Bacteria • • • • Eukaryotic Cells Nucleus Membrane-covered organelles (example: nuclear membrane) Linear DNA All other cells How they are the same: cytoplasm, ribosomes, DNA Despite their differences they perform most of the same kinds of functions in the same way. Classification Hierarchy Domain Did King Philip Come Over For Great Spagetti Kingdom Phylum All organisms Class Order Family Genus Species One type of organism Title: Classification of Living Things (copy this page) Did – Domain (3) Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya King – Kingdom (6) Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protists, Fungus, Plants, Animals Philip – Phylum Come – Class Over – Order For – Family Great – Genus Spaghetti – Species A B E The 6 kingdoms of life are separated mainly by: • How their cells are structured • How organisms attain (get) the energy they need to survive (Write these in your notes) The Kingdom that the organism is assigned to is based on1. Cell type (presence of a nucleus/nuclear membrane) [prokaryotic or eukaryotic] 2. The number of cells in the body (unicellular or multicellular) 3. Its ability to make food or not (autotrophic or heterotrophic) Eukaryotic Single or multi cell Multi-cell Absorbed Move – Cilia/flagellafrom decay Protista Prokaryotic Autotrophic Heterotrophic Fungi Plantae E Animalia Live everywhere Live in extreme conditions Bacteria Archaea B A 6 Kingdoms Use the information on the next several slides to complete the chart Monera has been divided into 2 kingdoms • Archaea (Archaebacteria) • Eubacteria Both are prokaryotic – which means the only membrane is on the outside, the organelles inside don’t have outer walls Archaea or Archaebacteria • • • • • • Prokaryotic (no nuclear membrane) Unicellular Both Autotrophic and Heterotrophic Oldest living organisms on Earth Use flagella to move found in very harsh conditions (such as at the bottom of the sea or in volcanic vents) • Example: halobacteria Eubacteria • • • • • Prokaryotic Unicellular Both Autotrophic and Heterotrophic More complex and common than the archaea It is the eubacteria that most people are talking about when they say bacteria, because they live in more neutral conditions. • Use flagella to move • They can be found everywhere around us – in our bodies, our food, etc. • Bacteria like strep Protista • Eukaryotic – the organelles, like the nucleus, have membranes • Unicellular • Both Autotrophic and Heterotrophic • Have nucleus and other cell structures • Use cilia, flagella or pseudopod to move • Examples: algae, amoeba Fungi • • • • • Eukaryotic Multi-cellular (many cells) Heterotrophic Cannot move Absorb nutrients from other organisms • Examples: mushrooms, yeast, molds Plantae • • • • • Multi-cellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Cannot move Use energy from the sun to make sugars • Examples: trees, flowers, ferns Animalia • • • • • Eukaryotic Multi-cellular Heterotrophic Most can move Get energy by consuming other organisms • Examples: invertebrates, fish, birds, mammals Recap • The Bacteria kingdom is made up of prokaryotic organisms. • This means that their cells lack the structure that eukaryotic cells (our cells for example) have, such as a nucleus and mitochondria. • All the other kingdoms consist of eukaryotic organisms that do have structure to their cells. The differences between these eukaryotic kingdoms (fungi, plants, and animals) are based on how they aquire energy to live. • Plants make their own energy from sunlight by using photosynthesis. (autotrophic) • Animals and fungi are very similar in that they must ingest other organisms in order to get the energy they need (heterotrophic) • The main differences are that: animals are mobile and eat food fungi are immobile and absorb their food (write these in your notes) The protist kingdom, though also eukaryotic, has little rhyme or reason to it. It consists of mostly single-celled organisms that don't really fit in any of the other kingdoms at all. Which is a picture of a Plant? NEXT QUESTION Which is a picture of a Protist? NEXT QUESTION Which is a picture of an Animal? NEXT QUESTION Which is a picture of an Eubacteria? NEXT QUESTION Which is a picture of a Fungus? FINISHED Characteristics Organism A Organism B Number of Cells Multicellular Unicellular Type of Nutrition Autotrophic Heterotrophic Nuclear membrane Present Absent DNA Present Present Based on the information in the chart, which organism belongs to the Kingdom Eubacteria? 1. 2. 3. Parts of a Flower 3 9 5 6 11. Stigma – (F) sticky top Style – (F) slender stalk Pistil – tube grown out of ovary – pollen goes in to 4. Petal – attracts insects 5. Ovary – Female part makes ovules 6. Ovule – (F) holds eggs 7. Sepal – protection/support 8. Filament – (M) stalk 9. Stamen – (M) produces pollen that contains sperm cells 10. Anther – (M) pollen sac 11. Pollen grains – contain sperm cells Pollination occurs when pollen lands on a pistil, sperm cells move down through the ovary, fertilizing the egg cells.