Water = 0°C
advertisement

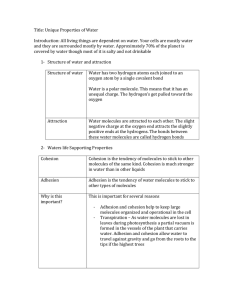
1 Ice = less than 0°C (solid) Water = 0°C – 100 ° C (liquid) Steam = greater than 100 °C (gas) 2 Water consists of an oxygen atom bound to two hydrogen atoms by two single covalent bonds. Oxygen has unpaired & paired electrons which gives it a slightly negative charge while Hydrogen has no unpaired electrons and shares all others with Oxygen This leaves the molecule with positively and negatively charged ends 3 Cohesion Adhesion Capillarity High Specific Heat High Heat of Vaporization Solid water (ice) is less dense than liquid Solvent Transparent 4 Water clings to polar molecules through hydrogen bonding Cohesion refers to attraction to other water molecules, and is responsible for surface tension 5 Adhesion refers to attraction to other substances. Water is adhesive to any substance with which it can form hydrogen bonds. Bluebonnet leaves 6 water evaporates from leaves = transpiration adhesion, cohesion and capillary action roots take up water by capillary action 7 •trees have specialized structures to transport water: xylem and phloem “plumbing” • water molecules are “dragged” from the roots to the top of the tree by capillary action and cohesion: hydrogen bonds help water molecules stick to each other 8 Specific Heat Amount of heat required to change the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1o C. Because of water’s high specific heat, it is used as a coolant in many systems. Car engine with radiator Comanche Peak Nuclear Power Plant Glen Rose, TX 9 A large body of water can absorb a large amount of heat from the sun in daytime and during the summer, while warming only a few degrees. At night and during the winter, the warm water will warm cooler air. Therefore, ocean temperatures and coastal land areas have more stable temperatures than inland areas. The water that dominates the composition of biological organisms moderates changes in temperature better than if composed of a liquid with a lower specific heat. The Earth is over 75% water! 10 Heat of Vaporization Amount of energy required to change 1g of liquid water into a gas (586 calories). large number of hydrogen bonds broken when heat energy is applied 11 Evaporative cooling. As a liquid evaporates, the surface of the liquid that remains behind cools – this is called evaporative cooling. Evaporative cooling moderates temperature in lakes and ponds and prevents terrestrial organisms from overheating. Evaporation of water from the leaves of plants or the skin of animals removes excess heat. 12 A liquid that is a completely homogeneous mixture of two or more substances is called a solution. This consists of the solute and solvent. A sugar cube (solute) in a glass of water (solvent) will eventually dissolve to form a uniform mixture of sugar and water (solution). The dissolving agent is the solvent and the substance that is dissolved is the solute. In our example, water is the solvent and sugar the solute. In an aqueous solution, water is the solvent. Water is not really a universal solvent, but it is very versatile because of the polarity of water 13 molecules. Water is an effective solvent as it can form hydrogen bonds. Water clings to polar molecules causing them to be soluble in water. Hydrophilic attracted to water Water tends to exclude nonpolar molecules. Hydrophobic repelled by water 14 Water transports molecules dissolved in it Blood, a water-based solution, transports molecules of nutrients and wastes organisms Nutrients dissolved in water get transported through plants Unicellular organisms that live in water absorb needed dissolved substances 15 Ice is less dense than water: the molecules are spread out to their maximum distance Density = mass/volume same mass but a larger volume 16 water expands as it solidifies water reaches maximum density at 4°C water freezes from the top down organisms can still live in the water underneath the ice during winter 17 The fact that water is clear allows light to pass through it Aquatic plants can receive sunlight Light can pass through the eyeball to receptor cells (in the back of the eye) 18