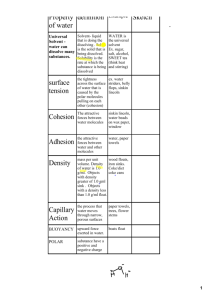
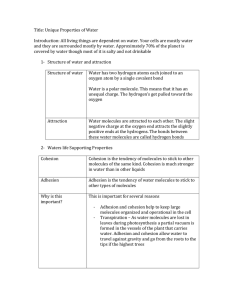
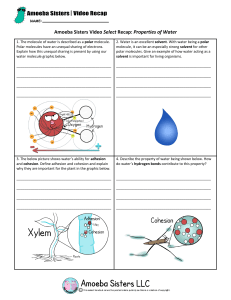
AP Biology Practice Worksheet, Water and Life Name: Answer Key Learning Objective 4.9: The student is able to predict the effects of a change in a component(s) of a biological system on the functionality of an organism(s). Instructions: Complete all empty boxes. 1. pH Practice [H+] 10-3 [10-8] 10-7 10-1 [OH-] pH [10-11] 10-6 [10-7] 10-13 3 8 7 1 Acidic, Basic, or Neutral Acid Base Neutral Acid 2. Properties of water Property Cohesion Adhesion Explanation Hydrogen bonds hold water molecules together and adhere them to hydrophilic surface High specific heat Heat is absorbed or released when H bonds break Benefit to life Water column is pulled up through plant vessels (xylem) Photosynthesis Transpiration Blood plasma Temperature changes in environment and organisms are moderated Homeostasis High heat of vaporization Hydrogen bonds must be broken for water to evaporate Solar heat is dissipated from tropical seas Evaporative cooling Water molecules with high kinetic energy evaporate; remaining molecules are cooler Cools surfaces of plants and animals Less dense as a solid H bonds in ice are farther apart than in a liquid Floating ice insulates bodies of water for life below Universal solvent Polar water molecules surround and dissolve polar solutes Most chemical reactions in life involve solutes dissolved in water Buffers in cells Acid/Base reactions Homeostasis 1 3. Biology of Water Phenomenon Hydrangeas can be pink, blue, or white depending on the pH of the soil. Water move up xylem in a tall tree Property Universal solvent A runner sweats during a run Acid precipitation formed Water strider walk on water Buffers help maintain homeostasis in blood During the winter, air temperatures in the northern United States can remain below 0 for months; however, the fish and other animals living in the lakes survive Transport of nutrients and waste products in organisms Participate in dehydration and hydrolysis of macromolecules Drainage of tears from the eye Evaporative Cooling Universal solvent Cohesion, specifically Capillary Action Universal solvent Less dense as a solid Cohesion, Adhesion High Specific Heat Universal solvent Polarity (general) Cohesion, specifically Capillary Action 4. Molar solutions Compound in solution Molecular Formula Glucose C6H12O6 Lactic acid C3H6O3 Salt NaCl Urea CO(NH2)2 Sodium hydroxide NaOH Elements and mass of 1M (grams) C-12 (6) = 72 H- 1 (12)= 12 O-16 (6)=96 C-12 (3) = 36 H- 1 (6)= 6 O-16 (3)=48 Na=23 Cl=35 C-12 (1) = 12 H-1 (4)= 4 O-16 (1)=16 N-14 (2)=28 Na=23 O-16 (1)=16 H-1(1)=1 Molecules 1L, 1M solution Mass of .5M 6.02 x 1023 180/2=90g/L 180 g/L 6.02 x 1023 90/2=45g/L 90 g/L 6.02 x 1023 58/2=29g/L 58 g/L 6.02 x 1023 60/2=30g/L 60 g/L 6.02 x 1023 40/2=20g/L 40 g/L 2