Skin and body membranes - Doral Academy Preparatory
advertisement

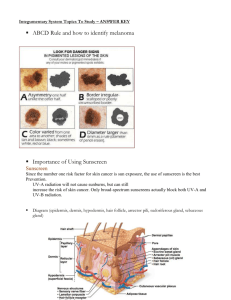
SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES THE SKIN Fun Facts: Avg. makes up about 9-11 lbs. or 7% of your weight Regenerates every 25-45 days Every minute you lose 30,000-40,000 dead skin cells SKIN STRUCTURE (EDH) Epidermis (epithelial) Dermis (fibrous) Hypodermis (subcutaneous – fat) SKIN STRUCTURE (EDH) SKIN STRUCTURE Epidermis—outer layer Stratified squamous epithelium SKIN STRUCTURE Dermis Dense connective tissue Not part of the skin Anchors skin to underlying organs Mostly adipose tissue (subcutaneous tissue) 5 LAYERS OF THE EPIDERMIS (CLGSB) Stratum corneum Statum lucidum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Statum basale 5 LAYERS OF THE EPIDERMIS (CLGSB) Stratum basale 5 LAYERS OF THE EPIDERMIS (CLGSB) Stratum spinosum 5 LAYERS OF THE EPIDERMIS (CLGSB) Stratum granulosum 5 LAYERS OF THE EPIDERMIS (CLGSB) Stratum lucidum 5 LAYERS OF THE EPIDERMIS (CLGSB) Stratum corneum NOTE: Thick skin- covers palms, fingertips, soles of feet Thin skin – covers rest of body missing stratum lucidum and sometimes stratum granulosum MELANIN Pigment produced by melanocytes Amount of melanin produced depends upon genetics and exposure to sunlight MELANIN – SKIN COLOR GENETICS is the key factor Quantity of melanin (yellow to reddish- brown to black) protects skin from UV radiation Melanocytes use enzyme tyrosinase to convert tyrosine into dark brown melanin pigment, albinos lack DNA code to make tyrosinase ALBINISM IN HUMANS MELANIN – SKIN COLOR Sunlight increases melanin production by the release of hormones freckles or moles are accumulations of melanin other pigments such as carotene or hemoglobin contribute to skin color MELANIN – SKIN COLOR Prolonged exposure causes substantial melanin buildup which helps protect the DNA of viable skin cells from UV radiation by absorbing the light and dissipating the energy as heat DERMIS Two layers Papillary layer (upper dermal region) Reticular layer (deepest skin layer) DERMIS Papillary layer (upper dermal region) DERMIS Reticular layer (deepest skin layer) DERMIS OVERVIEW Collagen fibers give skin its toughness Elastic fibers give skin elasticity Blood vessels play a role in body temperature regulation SKIN APPENDAGES Glands Hair Hair follicles Nails SEBACEOUS GLANDS Produce oil Glands are activated at puberty SEBACEOUS GLANDS SWEAT GLANDS Produce sweat Widely distributed in skin Two types Eccrine Apocrine SWEAT GLANDS HAIR Produced by hair follicle Consists of hard keratinized epithelial cells Melanocytes provide pigment for hair color HAIR Hair follicle- shaft, follicle (root) Growth- 4 in./year or 2 mm/week HAIR Associated hair structures Hair follicle Arrector pili muscle Sebaceous gland Sweat gland NAILS Scale-like modifications of the epidermis NAILS Consists of: free edge Body Root Cuticle Lunula Growth- 0.5 mm/week NAILS NAILS Did you know that your fingernails grow much faster than your toe nails? 3-4 times faster! SKIN INFECTIONS AND ALLERGIES Contact dermatitis Cold sores Caused by virus Impetigo Exposures cause allergic reaction Caused by bacterial infection Psoriasis Cause is unknown Triggered by trauma, infection, stress SKIN INFECTIONS AND ALLERGIES BURNS Burns Tissue damage and cell death caused by heat, electricity, UV radiation, or chemicals BURNS Associated dangers RULE OF NINES Way to determine the extent of burns Body is divided into 11 areas for quick estimation Each area represents about 9% of total body surface area RULE OF NINES SEVERITY OF BURNS First-degree burns Second-degree burns Third-degree burns SEVERITY OF BURNS CRITICAL BURNS Burns are considered critical if Over 25% of body has second-degree burns Over 10% of the body has third-degree burns There are third-degree burns of the face, hands, or feet