RNA and Protein Synthesis
advertisement

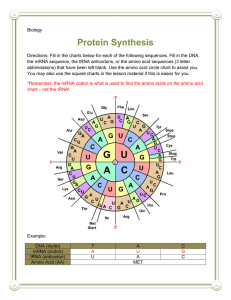
RNA and Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein • Focus Questions: – How does the message coded in the base sequence of DNA eventually create a protein? – How does the code get out of the nucleus? – What happens at the ribosome that causes amino acids to eventually join to form a protein? One Gene One Protein • Genes: each gene is responsible for the production of a single protein (or part of a protein) – Human DNA contains over a 100,000 different genes • Proteins: determine the structure and function of an organism – Polypeptides of long chains of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds • Ex: Enzymes, Structural proteins RNA RNA: – Sugar is ribose instead of deoxyribose – Has nitrogenous base URACIL instead of thymine (U instead of T) • Uracil also would pair with adenine (U-A) – Only single stranded 3 Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA: (mRNA): – Copies genetic code from the DNA inside the nucleus (Transcription) – Leaves nucleus and goes to ribosome where is the message is read (Translation) 2. Ribosomal RNA: (rRNA) – Form the different parts of the ribosome 3. Transfer RNA: (tRNA) – Transfers different amino acids to the ribosomes where they are eventually assembled into protein chains – Each amino acid is coded for by a different triplet codon on mRNA – tRNA has an anticodon that will pair up with codon on mRNA Translation of Genetic Code at Ribosome 3 types of RNA work together How do Genes Code for Proteins? Transcription: (Information goes from DNA to mRNA) • Happens in nucleus • Enzymes unzip the portion of the DNA to be copied in the middle of the strand • A single stranded mRNA strand is created from the DNA template – Enzyme RNA polymerase helps this happen • mRNA leaves nucleus through pores and goes to ribosome • http://www-class.unl.edu/biochem/gp2/m_biology/animation/gene/gene_a2.html • If the DNA template strand to be copied is • ATTGCATG • What would be the sequence of bases in the mRNA strand? – Remember it has U instead of T • Triplet Codon: set of 3 nitrogenous bases on a mRNA strand – Each set of 3 can code for a different amino acid – There are 20 different amino acids There are 64 ways you can combine the four Nitrogenous bases in sets of 3 – AAA, GCC, ATA, ATC, GTA etc. – Sometimes more than one codon can code for the same amino acid • Ex: AAA and AAG both code for phenylalanine – 3 codons signal protein synthesis to stop – 1 codon signals protein synthesis to start (AUG) Translation: (from mRNA to protein) • Occurs at ribosomes • Process of converting information coded in mRNA into sequence of amino acids • Involves transfer RNA – Bring specific amino acids to ribosomes so they can be assembled into proteins – Has “anticodon” that matches up with each triplet codon on mRNA – Bottom of tRNA has anticodon triplet Translation Process: – 1st triplet codon of mRNa attaches to ribosome – tRNA carrying amino acid pairs with mRNA codon – Usually mRNA at start is AUG (“start codon”) – mRNA slides along ribosome to next codon – New tRNA with amino acid pairs to mRNA codon – Amino acids get joined by enzyme by a peptide bond – Process continues and chain of amino acids form until a stop codon on mRNA is reached – Protein detached from ribosome Transcription Video: (really good watch this!!) • http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/media/DNAi_transcription_vo1lg.mov Translation Video: (really good watch this!!) • http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/media/DNAi_translation_vo1lg.mov Transcription and Translation Activity: • Game where you make a Protein • http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/dna/transcribe/