Lecture 32 – Transposable elements I. What is a transposable
advertisement

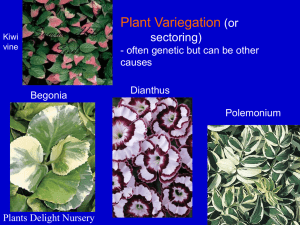
Lecture 32 – Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element? A. Any segment of DNA that can move from place to place in the genome 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome 1. in flies, ~12% of genome 2. in humans, 2 major classes a. LINEs (long interspersed elements) b. SINEs (short interspersed elements) c. collectively these and others account for ~45% of human genome II. How do transposable elements move? A. two general mechanisms 1. retrotransposons generate a new copy during transposition 2. DNA transposon excises and moves to new location 1 III. Consequences of transposition A. knocks out insertion into gene often gene expression B. can produce deletion or duplication by unequal cross over C. two nearby transposons can produce composite transposons whereby gene can move 2