Chapter 21 - Genomics I: Analysis of DNA and Transposable Elements
advertisement

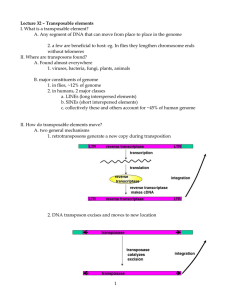
Chapter 21 Genomics I: Analysis of DNA and Transposable Elements Study Outline 1. Overview of chromosome mapping 2. Cytogenetic mapping via microscopy a. A goal of cytogenetic mapping is to determine the location of a gene along an intact chromosome b. In situ hybridization can localize genes along particular chromosomes 3. Linkage mapping via crosses a. The relative locations of molecular markers can be determined by linkage mapping b. Linkage mapping commonly uses molecular markers called microsatellites 4. Physical mapping via cloning a. A physical map of a chromosome is constructed by creating a contiguous series of clones that span a chromosome b. YAC, BAC, and PAC vectors are used to clone large segments of DNA c. Researchers can make genetic maps of large eukaryotic chromosomes d. Positional cloning can be achieved via chromosome walking 5. Genome-sequencing projects a. Shotgun sequencing has followed different strategies b. The human genome project was the largest genome-sequencing project in history c. Innovations in DNA sequencing have made it faster and less expensive d. Many genome sequences have been determined 6. Transposition a. Transposable elements move via one of three transposition pathways b. Each type of transposable element has a characteristic pattern of DNA sequences c. Transposase catalyzes the excision and insertion of transposons d. Retrotransposons use reverse transcriptase for retrotransposition e. Transposable elements may have important influences on mutation and evolution