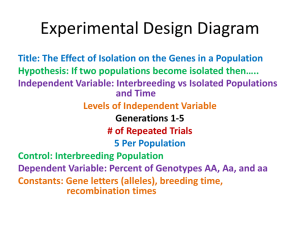
this slide kit - HCV
advertisement

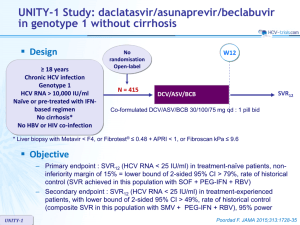
C-EDGE TN Study: grazoprevir/elbasvir in genotype 1, 4 or 6 Design Randomisation* 3:1 Double blind > 18 years HCV infection Genotype 1, 4, 6 Treatment-naïve HCV RNA > 10,000 IU/ml Compensated cirrhosis** allowed No HBV or HIV co-infection ** Metavir F4 or fibroscan > 12.5 kPa or FibroTest > 0.75 + APRI > 2 W12 W24 W28 N = 316 GZR/EBR 100/50 mg qd W16 N = 105 Placebo GZR/EBR * Randomisation was stratified on genotype (1 or 4 or 6) and cirrhosis (yes or no) • Objective • C-EDGE TN SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml) by intention to treat analysis : superiority to historical SVR12 of simeprevir + PEG-IFN + RBV (73%), at an overall 1-sided alpha value of 0.025, 99% power Zeuzem S. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163:1-13 C-EDGE TN Study: grazoprevir/elbasvir in genotype 1, 4 or 6 Baseline characteristics and patient disposition Age, years, mean Female Black / White / Asian GZR/EBR N = 316 Placebo N = 105 52.2 46% 53.8 47% 19% / 60% / 17% 17% / 70% / 12% 50% 42% 6% 3% 6.4 34% 22% 77 (62) 190 5 51% 38% 8% 3% 6.4 35% 21% 75 (64) 194 1 3/1/1 1/0/0 Genotype 1a 1b 4 6 HCV RNA log10 IU/ml IL28B CC Metavir F4 ALT, IU/L, mean (SD) Platelets < 109/L, mean Discontinuation, n For adverse event / lost to follow-up / death C-EDGE TN Zeuzem S. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163:1-13 C-EDGE TN Study: grazoprevir/elbasvir in genotype 1, 4 or 6 SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml), % (95% CI) % 100 99 (95-100) 100 (82-100) 157 131 18 10 Genotype 1a GT 1b GT 4 GT 6 94.6 (91.5-96.8) 92 (86-96) 316 All patients 80 (44-98) 75 50 25 0 Non-virologic failure 4 3 1 0 0 Breakthrough 1 1 0 0 0 Relapse 12 9 1 0 2 C-EDGE TN Zeuzem S. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163:1-13 C-EDGE TN Study: grazoprevir/elbasvir in genotype 1, 4 or 6 SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml) by subgroup, % (95% CI) 100 97 (92-99) 93 (87-97) 96 (92-98) 171 145 106 208 246 70 Male Female Non-CC No Yes 93 % (88-96) 97 94 (90-97) (90-100) 100 (96-100) 92 (88-96) 75 50 25 0 Sex C-EDGE TN CC IL28B genotype Cirrhosis 94 No 222 Yes HCV RNA > 800 000 IU/ml Zeuzem S. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163:1-13 C-EDGE TN Study: grazoprevir/elbasvir in genotype 1, 4 or 6 SVR12 in genotype 1 according to baseline NS3 and NS5A RAVs RAV at baseline % (n/N) SVR12 all patients % (N/n) SVR12 RAVs with ≤ 5-fold susceptibility SVR12 RAVs with > 5-fold susceptibility 57% (86/151) 43% (65/151) 97% (83/86) 89% (58/65) 97% (83/86) - 0% (0/0) - 19% (25/129) 81% (104/129) 96% (24/25) 100% (104/104) 96% (21/22) - 100% (3/3) - 12% (19/154) 88% (135/154) 58% (11/19) 99% (133/135) 90% (9/10) - 22% (2/9) - 14% (18/130) 86% (112/130) 94% (17/18) 100% (112/112) 100% (1/1) - 94% (16/17) - NS3 RAVs Genotype 1a Present Absent Genotype 1b Present Absent NS5A RAVs Genotype 1a Present Absent Genotype 1b Present Absent All 11 patients with virologic failure had baseline HCV RNA > 800,000 IU/ml (selection of NS5A RAV in 10/11) C-EDGE TN Zeuzem S. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163:1-13 C-EDGE TN Study: grazoprevir/elbasvir in genotype 1, 4 or 6 Baseline and emergent resistance variants in virologic failure cases NS3 RAVs Emerging Baseline at failure (in addition) GT Baseline HCV RNA (IU/ml) Day of virologic failure Breakthrough Relapse Relapse 1a 1a 1a 1,238,923 5,127,102 2,134,448 Rx D71 F/U D28 F/U D71 Q80K, S122G WT WT V36M None D168A Relapse 1a 948,279 F/U D70 Q80K D168A Relapse 1a 3,908,965 F/U D84 WT D168A Relapse Relapse Relapse Relapse Relapse 1a 1a 1a 1b 1a 5,282,871 1,846,427 1,939,436 4,475,338 3,913,374 FU D62 F/U D54 F/U D61 F/U D89 F/U D29 Relapse 6 15,689,194 F/U D25 Relapse Relapse 1a 6 1,574,151 15,056,901 F/U D56 F/U D25 WT WT WT T54S V55A V36I, L80Q, S122T, I132L, I170V WT L80K, I170V C-EDGE TN NS5A RAVs Emerging at Baseline failure (in addition) None None Y56H, D168A V170I D168A L31L/M L31M Q30H/Q M28V, Q30L, Y93H M28M/V, H58H/D L31M WT WT Y93H Q30R, L31L/M Q30R Q30R Y93H Q30R Q30R, L31M Y93N L31F None D168Y WT None None Y56Y/H, D168E M28V F28L M28G L31M L31V Q30R Zeuzem S. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163:1-13 C-EDGE TN Study: grazoprevir/elbasvir in genotype 1, 4 or 6 Adverse events, n (%) GZR/EBR N = 316 Placebo N = 105 Headache 52 (17%) 19 (18%) Fatigue 49 (16%) 18 (17%) Nausea 28 (9%) 8 (8%) Arthralgia 20 (6%) 6 (6%) Non-cirrhotic Cirrhotic Common AEs (> 5% in GZR/EBR) GZR/EBR N = 246 Placebo N = 83 GZR/EBR N = 70 Placebo N = 22 At least one adverse event 175 (71%) 57 (69%) 38 (54%) 15 (68%) Drug-related adverse event 96 (39%) 32 (39%) 18 (26%) 9 (41%) Serious adverse events 7 (3%) 3 (4%) 2 (3%) 0 (0%) Serious drug-related adverse event 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) Discontinuation due to adverse event 2 (1%) 0 (0%) 1 (1%) 1 (5%) Death 1 (<1%) 0 (0%) 1 (1%) 0 (0%) C-EDGE TN Zeuzem S. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163:1-13 C-EDGE TN Study : grazoprevir/elbasvir in genotype 1, 4 or 6 Laboratory abnormalities, n (%) GZR/EBR N = 316 Placebo N = 105 3 (1.0%) 4 (3.8%) 4 (1.3%) 0 (0%) 3 (0.9%) 0 (0%) 1 (0.3%) 0 (0%) 9 (2.9%) 4 (3.8%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 2 (0.6%) 1 (1.0%) Grade 2 Increased lipase 0 (0%) 0 (0%) Grade 1-2 101 (32.0%) 25 (23.8%) Grade 3-4 19 (6.0%) 5 (4.8%) Late elevation of ALT or AST > 2.0-5.0 x ULN > 5.0 x ULN Elevation of total bilirubin > 2.5-5.0 x ULN > 5.0 x ULN Decreased hemoglobin Grade 1-2 Grade 3-4 Increased creatinine Grade 1 C-EDGE TN Zeuzem S. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163:1-13 C-EDGE TN Study: grazoprevir/elbasvir in genotype 1, 4 or 6 Summary – A 12-week regimen of the oral fixed dose combination of once-daily, single-tablet of grazoprevir/elbasvir, achieved an overall SVR12 of 95% • • • • High efficacy in genotypes 1 and 4 SVR12 lower in genotype 6 High efficacy in cirrhotics (SVR12 = 97.1%) Lower efficacy observed among patients with high viral load (HCV RNA > 800,000 IU/ml) – Overall virologic failure rate was 4% • Baseline NS3 RAVS did not affect efficacy • Association between virologic failure and the presence of baseline NS5A RAVs, which was most apparent in genotype 1a with baseline RAVs demonstrating > 5-fold potency reduction to elbasvir • Emergence of (additional) NS3 and/or NS5A RAVs at failure was common – Grazoprevir/elbasvir was generally well-tolerated, with a similar safety profile in cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic patients – Limitations • No active-control group C-EDGE TN Zeuzem S. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163:1-13