7th Grade
advertisement

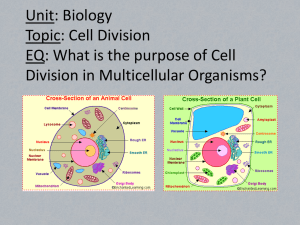
7th Grade TEST Review Commonality of Living Things: • Living things are made of one or more cells. • Living things need to acquire energy. • Living things grow and develop. • Living things contain DNA. • Living things must reproduce in order to continue the species. • Living things respond to stimuli. Scientific Classification: Living things are grouped according to many characteristics. The twopart scientific name given to living things includes the Genus and Species. The Genus is always capitalized, and the species is always lower case. (example: Tyrannosaurus rex) Scientific Classification: Within this classification system, there are 6 Kingdoms: 1) Animals –consumers; includes everything from insects to fish to coral to humans; use cellular respiration 2) Plants – producers; use photosynthesis 3) Fungi – mushrooms, lichen, yeast; grows on their food. 4) Protists – “oddball” kingdom; some have similarities of both plants and animals. 5) Eubacteria – single celled organisms; most plentiful organisms on Earth; found everywhere from cheese to our bodies; prokaryotes. 6) Archebacteria – single celled organisms that live in harsh environment s; prokaryotes. Prokaryotes: a singlecelled organism that does NOT have a nucleus. DNA floats freely within the cytoplasm. (“Pro” – “No”) Eukaryotes: Organisms that contain cells having a nucleus enclosed by a membrane. Eukaryotic cells have specialized organelles: Animal cells: Mitochondria is known as the ‘powerhouse’ of the cell. Nucleus is the control center and contains the DNA. Eukaryotic cells have specialized organelles: Plant cells have: Cell Walls - give support Chloroplasts - for photosynthesis (process a plant uses to make its own food) and green color Vacuole – storage compartment for fluid and wastes Cellular Respiration vs. Photosynthesis Photosynthesis: Carbon dioxide + water + light energy = glucose + oxygen Cellular Respiration: glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + energy *Notice that these two processes are opposite. Autotroph (Producer): Organism that makes its own food. (example: a plant uses photosynthesis) Heterotroph (Consumer): Organism that acquires energy by eating other organisms or their byproducts. (example: animals eat plants or other animals) Sexual Reproduction vs. Asexual Reproduction • 2 parents • Offspring is combination of both parents/unique • 1 parent • Offspring is an exact copy (clone) NOTE: Animals can reproduce sexually (humans) or asexually (Black worms). Plants can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Bacteria is the only kingdom that reproduces asexually exclusively. Biotic (Living) Animals Trees Plants Cells Bacteria Protists Fungi vs. Abiotic (Nonliving) Rocks Soil Air Water Climate Temperature Sun Mitosis • Body Cells (Non Reproductive) • Cell division that produces a new cell identical to the parent cell. (example: skin cells undergo mitosis in order to make new skin cells.) vs. Meiosis • Sex Cells (Reproductive Cells) • Cell division that produces a new cell with half the number of chromosomes. (Note: ONLY sex cells – egg and sperm – undergo meiosis.) Mitosis begins AND ends with diploid cells – cells that contain all their chromosomes. Meiosis begins with diploid cells but ends with haploid cells – cells that contain HALF the number of chromosomes. Meiosis results in 4 haploid cells. Reproductive cells (egg and sperm) always have half the number of chromosomes than body cells! These cells with half the number of chromosomes are called haploid cells. 20 10 10 10 10 *If an animal’s skin cells have 20 chromosomes, their egg or sperm cells will contain 10. Chromosomes are compressed strands of DNA that contain the genetic codes for traits. We inherit one chromosome from mom and one chromosome from dad to create a pair. Chromosomes are like SOCKS! They come in PAIRS! Humans have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) with one chromosome from each pair being inherited from each parent. Males are XY; Females are XX. Therefore, males determine the gender of the offspring. Punnett Squares Punnett Squares are used to illustrate the possible gene combinations of offspring from particular parents. Simply add rows and columns together to get the outcomes. Genetics Alleles = single traits represented by either capital or lowercase letters (T or t) Dominant = trait that dominates or covers up recessive traits if present; Identified by a capital letter. Recessive = trait that is covered up by the dominant trait unless there is no dominant trait present; Identified by a lower case letter. Genotypes = gene combination (Hh, hh, HH) Phenotypes = physical characteristics (green pea, brown hair, tall, freckles, etc.) Homozygous – gene combination containing the same traits Heterozygous – gene combination containing different traits BB or bb Bb Mendel’s 3 Laws 2 Law of Segregation: Allele pairs separate or segregate during gamete formation, and randomly unite at fertilization. 1 Law of Dominance: The dominant trait will be expressed whenever there is a dominant allele present. 3 Law of Independent Assortment: Traits are transmitted to offspring independently of one another. DNA • DNA is a DOUBLE HELIX. • DNA has 4 Nucleotide bases: Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine. • A always binds with T, and G always binds with C. (Remember to meet AT Gigi’s Cupcakes!) • The backbone of DNA is made of deoxyribose sugar. • Watson and Crick are responsible for proposing this model. RNA • RNA is a SINGLE HELIX. • RNA has 4 Nucleotide bases: Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, and Cytosine. (They are the same as DNA except that Uracil replaced Thymine.) • The backbone of RNA is made of ribose sugar. • A binds with U, and G binds with C. Human Body System Cells make up tissue. Tissue make up organs. Organs make up systems. All the systems work together to maintain life and a state of homeostasis. Circulatory System (Closed-circuit) The heart gets oxygenated blood from the lungs and sends it to all the body via arteries. (“Arteries - Away”) The blood returns to the heart via veins and picks up carbon dioxide as it goes. (“Veins – To”) Capillaries are the smallest vessels that connect arteries with veins. Life is in the BLOOD White blood cells – fight infection Red blood cells – deliver oxygen to the body and CO2 to the lungs Platelets – form clots to prevent bleeding Plasma – liquid part of blood; mostly water Respiratory System Gas exchange takes place in the alveoli of the lungs. This system breaks down food mechanically (teeth, tongue) and chemically (enzymes, acids) in order to get food small enough to be absorbed by the body for nutrition. Most digestion occurs in the small intestine. Waste is compacted and liquids reabsorbed from undigested foods in the large intestine. Nervous System: The Brain, Spinal Cord, & Nerves The Nervous System uses nerve cells to send and receive sensory signals. (sight, smell, hearing, touch, taste) Speciation is the evolutionary process by which new biological species arise. This may occur because of geographic isolation, climate differences, dietary needs, genetic mutations, etc. Many symbiotic relationships exist in nature: Mutualism – both organisms benefit Commensalism – one organism benefits while the other is unaffected Parasitism – one organism (parasite) benefits while the other (host) is harmed