Chapter 10 Cell Growth, Mitosis
advertisement

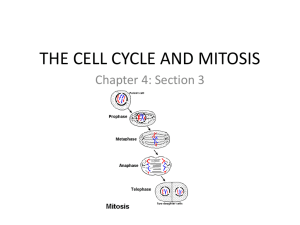
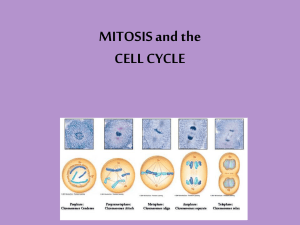
Chapter 10 Cell Growth & Division Cell Division There are 2 main reasons cell divides: 1. 2. The cell has more trouble trying to move nutrients and wastes across the cell membrane. The larger a cell becomes, the more demands it puts on its DNA. Bottom line – cells need to be replaced Cell Cycle • • • The sequence of growth and division of a cell An average cycle may be 22 hours Two general periods: 1. growth phase 2. division phase Interphase (Growth phase) Most of the cell’s life is spent in interphase Longest phase – (90% of cell’s growth) Centrioles – help to organize cell division Chromatin – DNA bound protein within the nucleus Interphase (Growth phase) New DNA is formed during 3 phases: G1 – 1st period of growth 1. Increase in size. 2. Makes new proteins and organelles. S1 – DNA is synthesized or replicated 1. Chromosomes are replicated. 2. New DNA molecules are made. G2 – final cell growth 1. Shortest phase 2. Prepares cell for mitosis Terms to know Chromosome – contains genetic information (DNA) passed from one generation to the next Spindle – microtubule that helps separate chromosomes A – centromere: center of chromosome B – chromatids: two identical “sister” parts of the chromosome Mitosis (Division phase) 4 phases: (PMAT) 1) 2) 3) 4) Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Mitosis Takes place within the nucleus of the cell 4 phases that blend from one to another Prophase 1st and longest phase of mitosis Chromatin become chromosomes Chromatids are joined by centromere Nucleus disappears Centrioles migrate to poles Spindles are formed Metaphase 2nd phase of mitosis Chromosomes meet in the middle of cell Pulled by spindles Each chromosome is attached to top of spindle Anaphase 3rd phase of mitosis Centromeres are split apart Chromatids are pulled apart and begin to drift to opposite poles Telophase Final phase of mitosis Begins when chromatids reach poles New nucleus starts to form Chromosomes start to unwind Spindles disappear Cytoplasm begins to divide Cytokinesis Cytoplasm pinches in half Each daughter cell has an identical set of chromosomes Plants apical meristem Rat – epithelial cells Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, or Telophase?