Ch. 13 America in the Cold War and Civil Rights Years: Review Key
advertisement
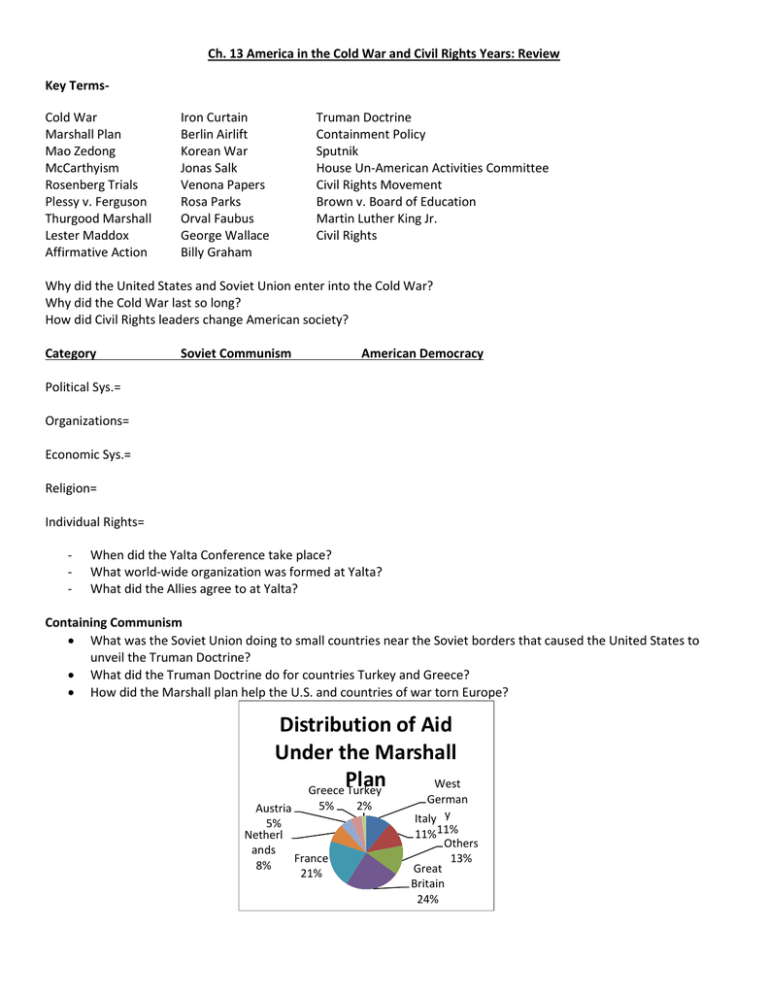
Ch. 13 America in the Cold War and Civil Rights Years: Review Key TermsCold War Marshall Plan Mao Zedong McCarthyism Rosenberg Trials Plessy v. Ferguson Thurgood Marshall Lester Maddox Affirmative Action Iron Curtain Berlin Airlift Korean War Jonas Salk Venona Papers Rosa Parks Orval Faubus George Wallace Billy Graham Truman Doctrine Containment Policy Sputnik House Un-American Activities Committee Civil Rights Movement Brown v. Board of Education Martin Luther King Jr. Civil Rights Why did the United States and Soviet Union enter into the Cold War? Why did the Cold War last so long? How did Civil Rights leaders change American society? Category Soviet Communism American Democracy Political Sys.= Organizations= Economic Sys.= Religion= Individual Rights= - When did the Yalta Conference take place? What world-wide organization was formed at Yalta? What did the Allies agree to at Yalta? Containing Communism What was the Soviet Union doing to small countries near the Soviet borders that caused the United States to unveil the Truman Doctrine? What did the Truman Doctrine do for countries Turkey and Greece? How did the Marshall plan help the U.S. and countries of war torn Europe? Distribution of Aid Under the Marshall Plan West Greece Turkey 5% Austria 5% Netherl ands France 8% 21% 2% German Italy y 11%11% Others 13% Great Britain 24% Why did Stalin feel he needed to create a buffer zone between the Soviet Union and the West? What were Satellite countries? Name 3 satellite countries the Soviet Union turned Communist? When trade and contact between eastern and western Europe fell apart, what term was used to describe form of isolation? Berlin was the capitol of Germany, what part of Germany was this capitol located? How many zones was Berlin divided into? What was the event called that provided aid to allied zones in Berlin? The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was formed from countries that chose the Democratic government. This group shared the responsibility of Collective Security which meant they would help each other out if invaded by another country. What organization did Stalin and the Soviets form? Containment in Asia - What large Asian country fell to communism? - Who led that country in 1949? - What former Japanese colony was divided into two countries after WWII? - Which country invaded the other and tried to unify it as a Communist State? - What line of latitude separates North and South Korea? Race to Space In 1957 the Soviet Union launched the first man-made satellite into space, what was it called? Why did both the U.S. and Soviets feel it was important to be the first to establish a space program? The Cold War at home - President Truman established Loyalty Review Boards to investigate individuals suspected of “un-American” activities, what was this committee called? - Why were Julius and Ethel Rosenberg on trial in 1950 during the Rosenberg Trials? - Who was the Senator whom led hearings during the “Red Scare” and which the term “McCarthyism” is known for? Domestic Policy What was the act of legislation known as, that gave returning service men and women the opportunity to receive and education and low mortgage rates for home ownership? What term was used to describe the increase in U.S. population after WWII? What disease did the vaccine created by Jonas Salk treat? Civil Rights During the Civil Rights Movement, what were most minority, disabled, women, and young and old groups fighting for? In 1896, the Supreme Court ruling in Plessy v. Ferguson allowed for what of the races in public schools and public places? What did Brown v. Board of Education do for the Civil Rights Movement? Who refused to give up her seat in a Montgomery, Alabama bus to a white rider and was arrested for it? How did Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. choose to fight struggle for equality during the Civil Rights movement? Arkansas Governor Orval Faubus refused to allow African-American students into an all-white Little Rock High School. He ordered the National Guard to block the entrance. What were these students known as? What Alabama Governor stood at the door of the University of Alabama to prevent them from enrolling? What did MLK do to protest the arrest of Rosa Parks in Montgomery, Alabama? What was MLK’s largest protest called during the Civil Rights era? What was the name of the speech delivered by MLK in Washington? What was the program called which increased minority representation in colleges, the professions, and many businesses? What does the author want you to know about the U.S. and France? Why are they shooting arrows and not bullets?










