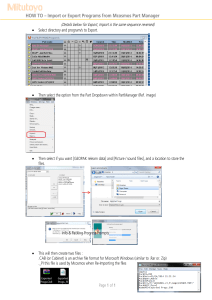
INTERNATIONAL TRADE
advertisement

INTERNATIONAL TRADE VOCABULARY • Import – a product purchased from another country. • Export – a product sold to another country. • Global interdependence – idea that countries of the world are growing increasingly dependent on one another. • Comparative advantage – ability of one country to produce a product at a lower opportunity cost than another country. • Absolute Advantage- ability of one country to be more productive and produce at a lower cost per unit. • Favorable balance of trade – a country exports more than they import. Foreign trade is profitable to the nation. • Unfavorable balance of trade – a country imports more than they export. Foreign trade loses money for the nation. FREE TRADE Arguments For Free Trade 1. Increased competition = improved products. 2. Trade restrictions damage export industries. 3. Specialization and comparative advantage lowers prices. 4. Greater political cooperation. TRADE BARRIERS • Protectionism – idea that country should impose barriers to international trade in order to protect domestic industries. Arguments Against Free Trade 1. Job security is threatened. 2. Protection of nation’s economic security is needed. 3. Protection of infant industries is needed. Trade Barriers • • • • Tariff (protective, revenue) Quota – a limit on the value or number of products to be brought in from another country Embargo – a refusal to trade with another country. Trade Cartel – a group of nations band together to control the supply & price of a product. (OPEC) OPEC COUNTRIES TRADE AGREEMENTS • NAFTA – North American Free Trade Agreement (US, Canada, Mexico) • CAFTA – Central American Free Trade Agreement (US, Central American Countries • WTO – World trade Organization – app. 150 nations seeking to increase trade and limit trade barriers. • EU – European Union – 27 European countries have created a single economic entity.