08-09上B
河南农业大学 2008—2009 学年第二学期
《国际经济学》考试试卷( B 卷 )
题号 一 二 三
分数
得分 评卷人
四 总分
一、 选择题(每小题 2 分,共 40 分)
1.
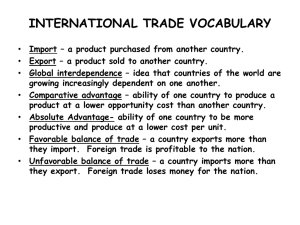
If Britain’s labor productivity in the production of umbrellas is greater than the rest of the world’s labor productivity in umbrellas, we would say that Britain has a(n) _______ in the production of umbrellas. a. comparative advantage b. absolute advantage c. opportunity cost d. superiority
2.
Which of the following theories predicts that a country will export those goods that use the country’s abundant factor(s) intensively in production and import those goods that use the country’s scarce factor(s) intensively in production? a. Absolute advantage b. Comparative advantage c. Heckscher-Ohlin theory d. the production differentiation model
3.
If Country A is labor-abundant and capital-scarce, Country B is labor-scarce and capital-abundant, Good X is produced in a labor-intensive process, and Good Y is produced in a capital-intensive process, we would expect that: a. Country A would export Good X. b. Country B would import Good Y. c. Country A would import Good X d. Country B would import both Good X and Good Y.
1
4.
The generalization that the real incomes of owners of the relatively abundant factor of production will rise and the real incomes of the owners of the relatively scarce factor of production will fall is called the : a. Factor-Price Equalization Theorem b. Stolper-Samuelson Theorem c. Leontief Paradox d. Heckscher-Ohlin Theory
5. With free trade, if Country X is relatively land abundant and relatively labor scarce and
Country Y is relatively land scarce and relatively labor abundant, the factor-price equalization theorem predicts that: a. wages will rise in Country X and fall in Country Y until they equalize. b. wages will rise in Country Y and fall in Country X until they equalize. c. wages will rise in Country X and land rents will fall in Country X until they equalize. d. wages will fall in Country X and land rents will rise in Country X until they equalize.
6. Which of the following was tested by Leontief? a. comparative advantage b. Stolper-Samuelson Theorem c. absolute advantage d. Heckscher-Ohlin Theory
7. Which of the following is not an example of intra-industry trade? a. Europe exports Airbus airplanes and imports Boeing airplanes. b. Americans export Jeeps and import Jaguars. c. Japan exports cars and imports oil. d. America exports films to the rest of the world and imports foreign films
8. Which of the following could lead to balanced growth?
(1) Proportionate increases in the endowments of all of a country’s productive inputs
(2) Technological improvements in the one sector of production a. (1) b. (1) + (2) c. (2) d. neither (1) nor (2)
9. Which of the following statements is true?
(1) Development of a newly found natural resource such as oil and gas can diminish growth of production in other industries.
(2) Significant increases in worker skills and capital can result in a significant increase in the production of manufactures and can retard production of natural resources.
(3) Immiserizing growth exists when an increase in production in a country’s export industry will result in an increase in economic welfare in that country. a. (1) + (3) b. (2) + (3) c. (1) + (2) d. (3)
2
10. A tariff will allow domestic producers to:
(1) expand production and sales.
(2) contract production and sales.
(3) raise prices.
(4) lower prices a. (1) + (2) b. (2) + (3) c. (1) + (3) d. (2) + (4)
11. Which of the following involves the allocation of import licenses by selling the licenses on a competitive basis to the highest bidders? a. resource-using application procedures b. import-license auction c. fixed favoritism d. domestic content requirement
12. Which of the following has overseen the global rules of government policy toward international trade since 1995? a. World Trade Organization b. General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade c. International Monetary Fund d. World Bank
13. Which of the following is occurring when a firm lowers its price to limit the decline in the quantity sold during a period of recession? a. persistent dumping b. cyclical dumping c. seasonal dumping d. predatory dumping
14. A
……… can in some cases ……… its welfare by ……… a. small country – improve – imposing a tariff b. small country – improve – increasing a tariff c. large country – reduce – engaging in free trade d. large country – improve – imposing a tariff
15.
Adam Smith asserted that international trade between two countries would be ……… whenever one country had an ……… in production of one good and the other country had an
……… in production of the other good. a. mutually beneficial – absolute advantage - absolute disadvantage b. mutually beneficial – absolute disadvantage - absolute advantage c. mutually beneficial – comparative advantage – comparative advantage d. mutually beneficial – absolute advantage – absolute advantage
16. Which of the following arguments for protection postures ( 做出某种姿态、态度 ) that temporary protection is needed for an industry with initially high costs and lower costs in the long run? ( ) a.
developing government argument b.
infant industry argument c.
dying industry argument d.
national defense argument
3
17. Which of the following is a limit on the total quantity of imports of a product allowed into a country in a given period of time? a. import tariff b. import quota c. fixed favoritism d. voluntary export restraint
18. Which of the following removes trade barriers between member countries, but allows the member countries to maintain their own trade barriers against trade with nonmember countries? a. economic union b. customs union c. common market d. free-trade area
19. _______ determine(s) which products have been produced within a free-trade area and which products have been produced outside the area and therefore are subject to barriers to entry. a. Trade diversion b. NAFTA c. Results of origin d. The most favored nation (MFN) principle
20. Which of the following statements about export subsidies is accurate?
(1) Overall, export subsidies often hurt the domestic market and help the foreign market.
(2) Export subsidies reduce the amount produced domestically and increase the amount imported.
(3) An export subsidy increases the price paid by foreign buyers and reduces the price that consumers pay in the domestic market. a. (1) b. (2) c. (2) + (3) d. (1) + (2) + (3)
得分 评卷人
二、简答题(每题 6 分,共 30 分)。
1. 经济增长有可能使一国的贸易条件改善,也有可能使之恶化,那么为什么大部分经济学
家认为福利恶化型增长在现实中是不太可能的呢?
2. 贸易集团的类型有哪些?并分别对他们加以具体说明。
3. “根据 Rybczynski 定理,一国劳动力数量的增长将导致该国劳动力密集产品产量的增长,
4. “我们的国家应当停止与其他国家进行贸易,因为商品进口使我们的就业机会减少,并
4
5. 什么是自愿出口限制(VER)?为什么很多国家的政府迫使外国出口者加入这一安排而不
仅仅是用进口配额或关税来限制同样数量的进口?这是否是由于 VER 可以给进口国带来比配
额或关税更大的国民福利收益?
得分 评卷人
三、计算题(一题,共 10 分)
假设美国目前每年以每双 20 美元的价格从中国进口 100 万双鞋。征收 50%的关税后,美
国的国内价格为 30 美元。在墨西哥,鞋的价格是每双 25 美元。又假设由于北美自由贸易区
的成立,美国改为每年从墨西哥进口 120 万双鞋,而不再从中国进口鞋。请分别指出美国消
费者、美国生产者、美国政府以及全世界整体会得到的收益或承受的损失。
得分 评卷人
四、论述题(一题,共 20 分)
在土地便宜的美国,用来养牛的人均土地要高于用于种植小麦所用的人均土地。但是在
那些比较拥挤的国家里,土地昂贵而劳动力便宜,用于养牛的人均土地通常比美国用于种植
小麦的人均土地要少。我们是否仍然可以说,与种植小麦相比,养牛业是土地密集的?为什
么是或为什么不是?
5