Heat Study Guide
advertisement

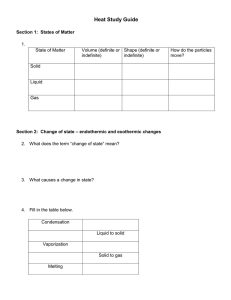
Heat Study Guide Section 1: States of Matter 1. State of Matter Solid Volume (definite or Shape (definite or indefinite) indefinite) definite definite How do the particles move? Low energy Vibrate in place Liquid definite indefinite Slide past each other Gas indefinite indefinite Random High energy Section 2: Change of state – endothermic and exothermic changes 2. What does the term “change of state” mean? a substance moves from one state of matter to another 3. What causes a change in state? a change in the energy 4. Fill in the table below. Condensation Gas to liquid freezing Liquid to solid Vaporization Liquid to gas Sublimation Solid to gas Melting Solid to liquid 5. Place the three states of matter (liquids, solids and gases) in the diagram below, according to their level of energy (least to greatest). Write in the name of each of the three endothermic changes of state in the correct place on the diagram.(melting, vaporization, sublimation) vaporization (boiling) __ melting gas____ ___liquid_ _solid___ Sublimation 6. When energy is taken in by a substance and changes state, it is called a(n) _endothermic change. 7. When energy is lost by a substance and it changes state, it is called a(n) _exothermic_ change Section 3 – Temperature and Thermal Energy 8. What is temperature? the average kinetic energy of a substance 9. What is kinetic energy? energy of motion 10. How do we find an average? add all data and divide by the number of data inputs 11. How does the temperature of an object increase? By an increase in energy 12. What are the three scales (languages) we can use when we talk about temperature? degree Celsius ,degree Fahrenheit, and Kelvin 13. The Celsius scale was developed based on the freezing point and boiling point of water. Fill in the table. Freezing pt. of water Boiling pt. of water Average human body temp. 0 0 Celsius 0 100 370 Fahrenheit 320 2120 990 14. The Kelvin scale was developed with the idea that “zero” should mean no kinetic motion. What do we call this special number that means that none of the particles in a substance are moving at all? absolute zero 15. What is thermal energy? The total amount of kinetic energy in a substance 16. Which picture above has the highest temperature? pot of boiling water Which picture has the most thermal energy? Why? the ocean because there is enormous amount of total kinetic energy Section 4 - Heat and Heat transfer 17. What is heat? The transfer of thermal energy 18. What is the difference between heat and temperature? heat is the transfer of thermal energy and temperature is the average kinetic energy of a substance 19. What is conduction? Give an example. conduction is thermal l energy traveling through direct contract touching a hot spoon 20. What is convection? Give an example. The movement of thermal energy through a fluid (gas or liquid) hot air rising from a candle or heat source 21. What is radiation? Give an example. thermal energy traveling by electromagnetic waves the thermal energy from the sun 22. Thermal energy moves from ___warm_____objects/areas to __cool______ objects/areas. 23. What is thermal expansion? the increase in volume of a substance due to an increase in temperature Section 5 – Phase Change Diagrams 24. What does the term melting point mean? What does the term freezing point mean? The temperature at which a substance melts is melting point. Freezing point is the temperature at which a substance freezes 25. How are melting point and freezing point the same? This is when there is a phase change and there is both a liquid and a solid. In an endothermic change it is melting and exothermic it is freezing. 26. Is the melting point the same for all substances? Explain your answer. No, all substances have a unique boiling point. 27. What does the term boiling point mean? the temperature at which a liquid boils Use this graph to answer questions 28 to 35. 28. A point A, what state of matter in the matter in? solid 29. At point B, what is happening to the matter? going through a phase change solid to liquid 30. At point C, what begins to happen to the substance? What state or states of matter is the substance in, between points C and D? At C the liquid begins to heat, between C and D a liquid 31. Point D starts another change of state. What is it called? vaporization or boiling 32. What state or states of matter is the substance in between points D and E? gas and liquid 33. Right after point E on the graph, what state or states of matter is the substance in? gas 34. What is the melting point of this substance? What is the boiling point? How did you know? melting point is 750, boiling point 1400 these are plateaus where there is no change in temperature 35. Is there a change in temperature during a phase change (freezing, melting, etc)? No