Changing States of Matter
advertisement

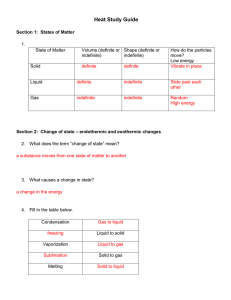
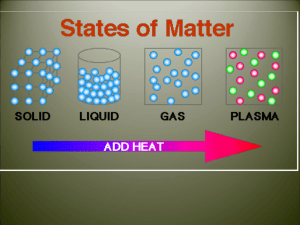
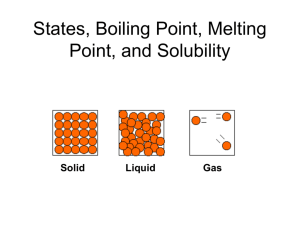
Changing States of Matter Notes 10/9/12 Next Entry in your science journal 6.P.2.2 Explain the effect of heat on the motion of atoms through a description of what happens to particles during a change in phase. Remember this … • Thermal Energy Heat energy • Vibrate A rapid, back and forth motion • ….OK we need to add a little more “energy” to Thermal Energy Add this title to the top of your notes… Changing States of Matter A Physical Property Add this your notes…Cornell Notes Thermal Energy: The total energy of a substance’s particles due to movement or vibration. Something hot will have more thermal energy than when it is cool. *Adding or removing thermal energy makes matter change states. Phase Change is a change from one state (solid or liquid or gas) to another without a change in chemical composition. – ice liquid = phase change for water. – water boils steam = phase change for water. States of matter Copy this to your notes… Three common states of matter on earth: 1) Solid 2) Liquid 3) Gas Fourth state of matter common in the universe: 4) Plasma States of Matter Review • A solid is matter that has a definite shape and a definite volume. Particles are closely packed. (show video 0 to 2:24) • A liquid is matter that has a definite volume but does not have a definite shape. Particles are more free to move. • A gas is matter that does not have a definite shape or a definite volume. Particles are free to move and move fast enough to bounce off each other. (2:24 to 4:04) (4:04 to 7:57) States of Matter copy to notes • Plasma, consider plasma a gas that has been energized and can give off energy. – Plasma is not common on earth but the most common state in the universe. – Examples: fluorescent lights, the Sun (7:57-847) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Wispy_%27 Plasma_Dancer%27_on_the_limb_of_the_ Sun.ogv • Melting: The change in state of a solid to a liquid. – Requires increasing thermal energy so the molecules vibrate faster. • Example - The melting point of ice is 0 deg Celsius. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Melting_ice cubes.gif • Melting Point The temperature when melting starts to occur. (video 8:50-11:09) • Vaporization: The change in state of a liquid to a gas. – – – Requires increasing thermal energy. Two types of vaporization are boiling and evaporation. Example - The boiling point of water is 100oC. • Vaporization Point The temperature when boiling or evaporation starts to occur. (11:09 – 12:34) 2 kinds of vaporization READ ONLY: 1. Evaporation: Vaporization that happens ONLY at the surface of a liquid. Due to increasing thermal energy along with air pressure and surface tension 1. Example: Water evaporates from a lake or ocean. 2. Boiling: Vaporization that happens at the surface and below the surface of a liquid. Due to adding heat to the substance. 1. Example: The boiling point of water is deg Celsius. 100 • Condensation: The change in state of a gas to a liquid. – Requires decreasing thermal energy. (video 12:35 – 13:06) • Freezing: The change in state of a liquid to a solid – this requires decreasing thermal energy so the molecules vibrate slower. – Example - The freezing point of water is 0 deg Celsius. • Freezing Point The temperature when freezing occurs. (video 13:07 to 13:35) • Sublimation: Change in state from a solid directly to a gas. – Requires increasing thermal energy –Examples: dry ice, moth balls, snow on very cold day. (video 13:35 – 14:25) Video questions and discussion (video14:25 to end) Graphic Organizer Solid Liquid Gas Increase t _ _ _ _ _ _ e _ _ _ _ _ Solid Liquid Gas Decrease t_ _ _ _ _ e _ _ _ _ _ Using the word bank draw and label this diagram on changing the states of matter. Melting, Solid, Condensation, Freezing, Sublimation, Gas, Vaporization. Liquid Changing States of Matter…check your answers Sublimation Melting Solid Vaporization Gas Liquid Freezing Condensation