Classical Conditioning
advertisement

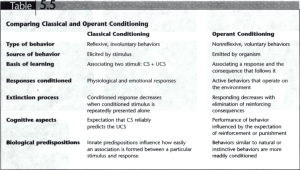
Name ________________________________________________________________ Number __________ Conditioning & Social Learning Classical Conditioning, Operant Conditioning and Social Learning Classical Conditioning Ivan Pavlov Classical conditioning: a learning procedure in which associations are made between a _____________ _____________ and a ______________ ________________ - - Classical conditioning is a type of ______________________. o When something makes you react in a certain way, it is called a stimulus. o People and animals learn to respond to a new stimulus the same way that they respond to one they already know. o A person’s or animal’s old response becomes attached to a new stimulus. Neutral stimulus: _____________________________________________________________________ Unconditioned stimulus (UCS): an event that elicits a certain predictable response without previous training <____________> Unconditioned response (UCR): an organism’s automatic (or natural) reaction to a stimulus <_____________________________> Conditioned stimulus (CS): a once-neutral event that elicits a given response after a period of training in which it has been paired with an unconditioned stimulus <____________> Conditioned response (CR): the learned reaction to a conditioned stimulus <____________________> Generalization, Discrimination and Extinction Generalization occurs when an animal responds to a second stimulus similar to the original CS, without prior training with the second stimulus. When Pavlov conditioned a dog to salivate at the sight of a circle, he found that the dog would salivate when it saw an oval as well. Generalization:____________________________________________________________________ Pavlov also taught the dog discrimination–to respond only to the circle, not the oval. Generalization and discrimination are complementary processes and are part of your everyday life. Discrimination: the ability to respond differently to _________________________________stimuli Extinction: the gradual ______________________________________________ response when the conditioned stimulus is repeatedly presented without the unconditioned stimulus Example: The response the Jaws theme song elicits from people. Even though a classically conditioned response may be extinguished, this does not mean that the CR has been completely unlearned. Spontaneous recovery does not bring it back in full strength, however. Taste Aversion A taste aversion is an example of _________________________________________. Example: Suppose you eat snails for the first time. Later in the evening, you feel sick. You will probably think the snails made you sick and you will note like the smell or thought of them next time someone serves them. Operant Conditioning Operant conditioning: learning in which a certain action is _______________________________, resulting in corresponding increases or decreases in occurrence Reinforcement: stimulus or event that _________________________ and increases the likelihood that the response will be repeated - Positive (good) and negative (bad) In the Big Bang Theory YouTube video, what was the item that Sheldon used as positive reinforcement for Penny? What did Sheldon use as negative reinforcement on his roommate? B.F. Skinner has been the psychologist most closely associated with operant conditioning. – – – Skinner trained rats to respond to lights and sounds in a special enclosure called a _____________________. A rat, placed in the Skinner box, must learn how to solve the problem of how to get food to appear in a cup. The food that appears in the cup is a _________________ _________________________ in this experiment. Shaping and Chaining Shaping: technique in which the desired behavior is “modeled” by first rewarding any act similar to that behavior and then requiring ever-closer approximations to the desired behavior before giving the reward - One type of operant conditioning that is good for teaching skills is called shaping. Shaping teaches a new behavior ____________________. At first you are given a reward for behavior similar to the skill you are learning. To keep getting rewards, you must get better at the skill. ___________________________________________. Response chain: learned reactions that follow one another in _____________________, each reaction producing the signal for the rest. - If you want to learn a complex skill, you need to learn several different behaviors. You also have to learn how to put the behaviors together in the right order. O For example, if you want to learn how to swim, you have to learn several behaviors like kicking your feet, stroking your arms and breathing. O Then you have to __________________________________________. Social Learning Albert Bandura’s Bobo Doll Experiment illustrates social learning. Social learning – a form of learning in which the organism ______________ and _______________ the behavior of others There are two types of social learning: Cognitive and modeling “Psychology cannot tell people how they ought to live their lives. It can however, provide them with the means for effecting personal and social change. “ - Albert Bandura Cognitive Learning Cognitive learning - a form of learning that involves __________________________ and may result from observation or imitation. Types of Cognitive Learning Latent learning – alternation of a behavioral tendency that is not demonstrated by an ____________ observable change in behavior. Example: You need to get to a store that you have been to only once before. You are not sure how to get there. As you drive, you see signs and landmarks that you remember from the first trip. You did not try to learn the signs and landmarks on your first trip, but you were still able to remember what they looked like when you needed them. Latent learning is possible because we create cognitive maps. Cognitive map – a mental picture of _________________________ or relationships between events We create them naturally as we explore our surroundings. They help us remember how things relate to one another. Example: A rat in maze looking for an alternate route to food Learned helplessness – a condition in which repeated attempts to control or influence a situation __________, resulting in the belief that the situation is ______________________ and that any effort to cope will fail. They no longer even try. They become convinced they are helpless. o _______________________- – You believe you can never change a situation. o _______________________ – You believe that because you cannot change one situation, you cannot change anything. o __________________- You blame yourself for your own failures, not your circumstances. Learned helplessness can lead to depression, guilt and self-blame. Modeling The second type of social learning is called modeling. Modeling – learning by __________________ others, copying behavior Types of Modeling ____________________ – copying the exact behavior or others. If other people look up, you do too. Simple modeling does not involve learning. You already know the skill. You simply copy the behavior of people around you. _________________________________- You use observational learning when you copy another person to learn a new skill. You may watch someone perform a dance step. By watching, you are able to learn the step then do it yourself. _______________________________ – This type of modeling helps people do things that they are afraid of doing. When you watch someone do something you fear, and not get hurt, you are more willing to try it for yourself. Used to treat phobias. Behavior Modification It is possible to use classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and social learning to deliberately change someone’s behavior. Behavior modification – a ____________________________________ of learning principles to change people’s actions and feelings It begins by clearly defining a problem. A plan is then developed using different learning techniques. Applying What You Have Learned With a partner, come up with a school-related example for each of the types of learning below: 1. Classical conditioning 2. Operant Conditioning 3. Cognitive mapping 4. Latent learning 5. Learned helplessness 6. Modeling 7. Behavior modification