cells

SEMESTER 1 EXAM – STUDY GUIDE
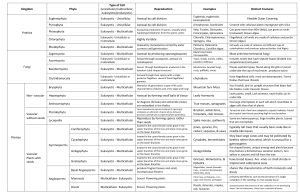
CLASSIFICATION
Binomial nomenclature – two-part scientific name (Genus species)
Characteristics of living things (MRS. GREN)
Levels of classification from kingdom to species (largest – smallest)
Characteristics of organism within each of the 5 kingdoms o Animal – multicellular, eukaryotic heterotrophs o Plant – multicellular, eukaryotic autotrophs o Fungi – multicellular, eukaryotic heterotrophs (decomposers) o Protist – unicellular, eukaryotic heterotrophs o Moneran – unicellular, prokaryotic heterotrophs/autotrophs
Dichotomous keys
Evidence used for classification o Behavior and physical appearance o Method of reproduction, locomotion, diet and habitat o Cells and DNA analysis
INSECTS
Characteristics of arthropods and insects
Special insect orders o Coleoptera – beetles (most diverse and populous insect order)
How do insects make sounds?
Insect mouthparts
Metamorphosis – growth and development o Molting – shedding skin o Incomplete – egg, nymph, adult o Complete – egg, larva, pupa, adult
MICROSCOPES
Founding Fathers of Microscopy o Hooke – observed cork cells; coined the term “cell” o Leeuwenhoek – observed bacteria and protists o Janssen – first compound microscope
Total magnification – eyepiece x objective lens
Parts and functions
CELLS
Levels of organization from cell – organism
Types of cells o somatic (body cells such as hair, skin, muscle, etc.) o gametes (sex cells such as egg and sperm)
Eukaryotic cells vs. Prokaryotic cells
Differences between plant and animal cells o Cell wall – gives a plant cell structure and support o Chloroplasts – organelle where photosynthesis occurs o Vacuole size – larger in plant cells used to store liquids
All organelles and functions of organelle
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport
Photosynthesis and Respiration
SCIENTIFIC METHOD
Steps of the scientific method – What takes place in each step? o Research/background information o State your purpose/problem question o State your hypothesis/make a logical prediction based on prior knowledge o Develop your procedure o Collect and record data (numerical and observable) o Analyze your results o Draw conclusions
Experimental factors o Independent variable – the factor you control o Dependent variable – what you are testing/measuring/observing o Experimental group – the testing group o Control group – the group used for comparison o Controls – what is kept constant throughout the experiment