Biological Classification Worksheet: Five-Kingdom System
advertisement

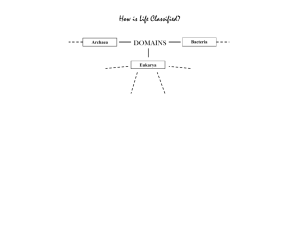
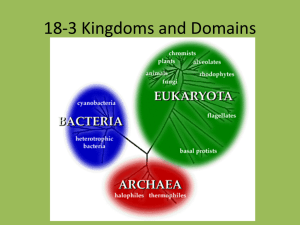
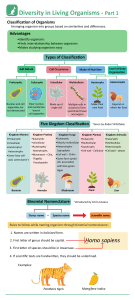
Name _______________________________________________ Biological Classification Worksheet Five-Kingdom System Animal Kingdom – eukaryotic, multicellular, heterotrophs, no cell walls, Ex. invertebrates (without backbones) and vertebrates (with backbones). Plant Kingdom – eukaryotic, multicellular, autotrophs, have cell walls, Ex. mosses, ferns, flowering and seed plants. Fungi Kingdom – eukaryotic, most multicellular and some unicellular, heterotrophs (break down other organic materials to obtain food), cells with cell walls but not green, Ex. mushrooms, molds, and yeasts. Protist Kingdom – eukaryotic, many are single-celled and others are multicellular, some heterotrophs and others autotrophs, Ex. come in a wide variety of forms: animal-like, such as amoeba, some are plant-like such as algae, and others are fungi-like. . Archaebacteia Kingdom – prokaryotic, unicellular, some autotrophs while others heterotrophs, Ex. bacteria and blue-green algae. Eubacteria Kingdom -- prokaryotic, unicellular, some autotrophs while others heterotrophs, live in extreme conditions, Ex. bacteria living near ocean thermal vents or in a cow’s stomach Seven Layers in each Kingdom The classification of humans – Homo sapiens The two part naming system is called Binomial nomenclature (consists of genus and species.). Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Primata Family: Hominadae Genus: Homo Species: sapiens (note: species is not capitalized.) Using the information above, answer the following questions. 1.What is the next smallest classification group after Order? ____________________ 2. What is the smallest/most specific classification group? _____________________ 3. Every living organism has these two classification groups as its scientific name? ___________________ and ____________________ 4. The first letter of every genus name is __________________________. 5. The first letter of every species name is ___________________________. 6. What is binomial nomenclature? _________________________________________________. 7. Which classification group has the most diversity (difference or variety)? __________________. 8. Which classification group has the largest number of organisms? ________________________ 9. In which classification group are the organisms most similar, being able to mate with each other? ____________________________. 7. Give one example of how you classification is used at school. 8. Why is the understanding of classification an important life skill?