Plate Tectonics Revision
advertisement

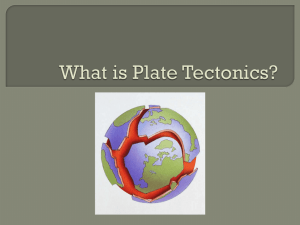
Plate Tectonics Revision 6th year Geography Learning Outcome • Revise Core Book – Chapters 1 – 3 – Plate Tectonics – Earthquakes – Volcanoes – Examine the exam questions on these topics Theory of Plate Tectonics • Earths plates move • Landforms result Tectonic Cycle • Continuous destruction and formation of the earth’s crust at plate boundaries. Theory of Plate Tectonics • Wegener 1912 – Continental Drift • Hess – Sea Floor Spreading Destructive Plate Boundaries • • • • • • • • Collision of plates Subduction Volcanoes Eg; Mount Saint Helens Fold Mountains Eg; Alps Earthquakes Eg; Kobe Constructive Plate Boundaries • • • • • Plates separate Rift Valley Eg; African Rift Valley Mid Ocean Ridges Eg; Mid Atlantic Ridge Conservative Plate Boundaries • • • • • Plates slide past each other Earthquakes Eg; Haiti 2010 Transform fault Eg; San Andreas Fault Exam Questions – Plate Tectonics • Explain how the theory of plate tectonics has aided our understanding of the occurrence of volcanic activity. • ‘Plate boundaries are zones where crust is both created and destroyed.’ Examine the above statement with reference to examples you have studied. Earthquakes • Focus • Tremor • Epicentre Measuring Earthquakes • Seismographs (record earthquake waves) • Richter Scale (energy / magnitude) • Modified Mercalli Scale (damage seen) Effects Short Term • Death • Destruction • Tsunamis • Fire • Homelessness Long Term • Migration • Disease • Economic slowdown Case Study • • • • • • • South East Asian Earthquake and Tsunami December 2004 9.0 Richter Scale Indian Plate slid beneath Burma Plate Affected 11 countries 320,000 deaths 1.5 million people displaced Exam Questions - Earthquakes • Examine how earthquakes are measured and may be predicted. • Describe and explain an earthquake that you have studied under the following headings; – Plates involved – What caused the earthquake – Long & Short Term Effects – Recovery Volcanoes Volcanoes occur at... • Mid-Ocean Ridges (Constructive Plate Boundaries) • Subduction Zones (Destructive Plate Boundaries) • Hotspots Products of Volcanic Eruptions • • • • • Lava Pyroclasts Poisonous gases Ash, pumice, dust Water vapour Volcanic Landforms External • Lava Plateau • Volcanic cones • Craters • Calderas • Volcanic plugs Internal • Batholiths • Sills • Dykes • Laccoliths • Lopoliths Effects of Volcanoes Positive • New land (Iceland) • Geothermal energy • Fertile soil • Tourism Negative • Lava flows destroy and kill • Lahars destroy and kill • Poisonous gases harm health and kill • Ash can disrupt air travel Case Study • • • • Soufriere Hills, Montserrat, Carribbean. Dormant for 300 years Active since 1995 June 1997- 9 people killed, 100 homes destroyed. • Pyroclastic flow 160 kmph • 24 hour monitoring- Montserrat Volcano Observatory Exam Questions • Explain with the aid of an example you have studied why volcanic activity happens at plate margins. • Explain how the study of plate tectonics has helped us to understand the global distribution of volcanoes. • Volcanoes can have both positive and negative effects. Examine the effects of a volcano that you have studied.