What is Plate Tectonics?
advertisement
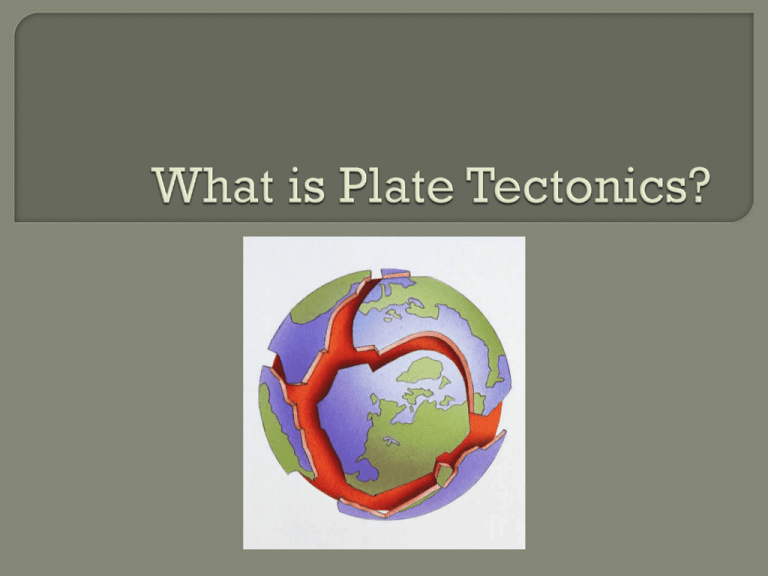
What do you notice about these two pictures? The Earth’s surface is broken into rigid plates that move in relationship to one another. Plate tectonics is a theory that describes the formation of movements and interactions between the tectonic plates. What is a theory? In 1912, a German scientist named Alfred Wegener proposed a hypothesis called continental drift. What is a hypothesis? He proposed that the continents had moved or drifted apart over time. He studied this hypothesis his entire life, but was never successful. He could not explain how the continents had shifted over time. He did however, pave the way for plate tectonics. Theory that the continents have moved or drifted over time from one location to another. Ice Age: Continental Drift In the 1950’s and 1960’s scientists made major discoveries about earthquakes and volcanoes. These discoveries led to the theory of plate tectonics. The theory states that the continents are embedded on plates. As these plates move, they carry the continents with them. Oceans are also a part of the plates. This theory is supported by knowledge of important geologic processes (earthquakes and volcanoes). Data indicates that earthquakes and volcanoes do not occur randomly. Instead they are primarily located on plate boundaries. The theory of plate tectonics helps to explain this pattern. These plate boundaries are areas of high heat flow, where molten rock moves upward to Earth’s surface, causing volcanic activity. A mid-ocean ridge is a long chain of volcanic mountains on the ocean floor with a deep central valley.