Case Study Approach in Teaching Entrepreneurship
advertisement

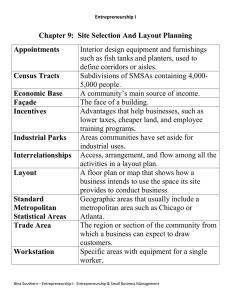
Case Study Approach in Teaching Entrepreneurship: Contextual Relevance & Effectiveness Theresa Lau K.F. Chan Hong Kong Polytechnic University Dept. of Management & Marketing Thomas W.Y. Man Hong Kong Institute of Education Department of Information Technology Why Using Case Studies in Teaching Entrepreneurship? Bringing undergraduate classes to life, sparking discussion about realistic business venture Providing a forum for discussion of controversial issues in “entrepreneurship” Developing students’ diagnostic skills Integrating functional disciplines Cultivating deep (vs.surface) learning, e.g. Developing intellectual & imaginative powers Understanding & judgments Problem-solving skills Ability to communicate Defining Case Method & Process It involves giving students a real historic business situation consisting of a detailed factual description of an issue faced by an organization together with the surrounding facts, circumstances, events, and management opinions Students analyze and discuss the case with the objective of determining an appropriate action Instructors (skilled discussion leader) ask challenging pertinent questions and stimulate the class into reaching the correct conclusions Case Method Objectives Greater learning with active student involvement Increased coursework relevancy and applicability Exposing students to a chunk of reality The Challenges of Teaching Entrepreneurship Integrative: synthesis of accounting, marketing, management, strategy, etc. Both techniques application and concepts orientation required Teaching process: Lecture provides conceptual inputs while case study method provides students with realistic application and practice Combination Approach: Lecture case study lecture case study Lecture Effectiveness of Case Method in Teaching Entrepreneurship (1) A comprehensive case on business new venture in mainland China is constructed based on archive, field work and in-depth interview To make the case contextual relevant, it is designed to facilitate students’ understanding & familiarity of the local environment. the motorcycle industry the mainland business environment Effectiveness of Case Method in Teaching Entrepreneurship (2) A Pre- & Post- test of students’ perception on the following attributes before and after using the case study method Self Esteem Achievement Innovativeness Personal control Effectiveness of Case Method in Teaching Entrepreneurship (3) The subject: A class of undergraduate final students taking entrepreneurship as an elective in a business program Number of students is 20 Female and male is half to half Majority is local Hong Kong students Other background (e.g. age, education) is similar Effectiveness of Case Method in Teaching Entrepreneurship (4) Effectiveness of Case Method in Teaching Entrepreneurship (5) Using pair comparison analysis, it is found that: “Self-esteem” is increased after case study (statistically significant at 95%) “Achievement orientation” is increased after case study (statistically significant at 95%) “Innovativeness” is increased after case study (statistically significant at 95%) No statistical significance on “personal control” after case study Interpretation (1) Students’ self esteem is increased because the incidents in the real case show that the founder/ entrepreneur is just an ordinary person, not a superman! Self-image Self-confidence Determination to start-up Students’ achievement-orientation is increased because the case analysis reveals that besides profit incentive, business growth & success, personal achievement are also the great drive for entrepreneurs Interpretation (2) Students’ attribute on innovativeness is increased because the case study provides them with an opportunity to learn how entrepreneurs act and behave with innovation in business development process, including Creative business ideas Novel ways of operation Unique marketing techniques Students’ perception on “personal control” is unchanged due to fact that case study could not provide strong evidence on self control on business environment, particularly in the mainland context. Feeling of helplessness High level of external locus of control Vulnerable to environmental uncertainty Conclusion Teaching Entrepreneurship by case study method can help enhance students’ perceived attributes on “self-esteem”, “achievement-orientation” & “innovativeness” but not “personal control” Case context should be local in order to increase its effectiveness. Combination of lecture and case approach is more desirable