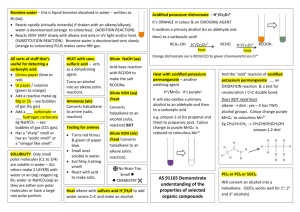
Heat with acidified potassium permanganate
advertisement

Bromine water – this is liquid bromine dissolved in Acidified potassium dichromate – H+/Cr2O72- water – written as Br2(aq). It’s ORANGE in colour & an OXIDISING AGENT Reacts rapidly (virtually instantly) if shaken with an alkene/alkyne); bromine water is decolourised (orange to colourless). (ADDITION REACTION) Reacts VERY VERY slowly with alkane and only in UV light and/or heat. (SUBSTITUTION REACTION). Bromine water is decolourised very slowly (orange to colourless) PLUS makes some HBr gas. It oxidises a primary alcohol to an aldehyde and then to a All sorts of stuff that’s useful for detecting a carboxylic acid. HEAT with conc. Dilute NaOH (aq) It oxidises a secondary alcohol to a ketone (same colour change). sulfuric acid – Acid-base reaction with RCOOH to make the salt RCOONa Tertiary alcohols aren’t oxidised by it. Conc. H2SO4 (as Litmus paper (blue to red) UI paper / solution (green to orange) Add a reactive metal eg Mg or Zn – see bubbles of gas (H2 gas) Add a ___ carbonate or ____ hydrogen carbonate eg NaHCO3 – see bubbles of gas (CO2 gas). Has a “sharp” smell or has an “acidic smell” or a “vinegary smell” dehydrating agent. Turns an alcohol into an alkene. catalyst) and heat with ROH + RCOOH makes an ester – esterification Heat with dilute sulfuric acid H+/H2O – is ACID hydrolysis of an ester – to produce ROH & RCOOH. HEAT with dilute NaOH (aq) Alkaline hydrolysis if ester – to produce ROH & RCOONa ; when this is with a fat/oil to make soap we call it saponification carboxylic acid! RCH2-OH H+/Cr2O72heat RCHO Heat alkene with dilute sulfuric acid H+/H2O to add water across C=C and make an alcohol. heat RCOOH. Orange dichromate ion is REDUCED to green chromium(III) ion Cr3+ Heat with acidified potassium permanganate – another oxidising agent H+/MnO4- It’s purple It will also oxidise a primary alcohol to an aldehyde and a carboxylic acid eg propan-1ol to propanal to propanoic And the “odd” reaction of acidified potassium permanganate ….. another OXIDATION reaction & a test for unsaturation / C=C double bond. Does NOT need heat. alkene diol : yes – it has TWO alcohol groups. Colour change purple MnO4- to colourless Mn2+ Eg CH3CH=CH2 CH3CH(OH)CH2OH acid. Colour change as purple Mn2+ Secondary alcohol is oxidised to a ketone. propan-1,2-diol H H H H H MnO4- is reduced to colourless H+/Cr2O72- H C C C H H H H C H C C O O H H H Tollens reagent, [Ag(NH3)2]+ ; warm with Tollens reagent – a silver mirror shows aldehyde; Ag+ + e- Ag . No silver mirror with a ketone. BIG HINT: “Has a characteristic smell” or “has a pleasant fruity smell” – chances are it is an ESTER. Esters also insoluble in water – get 2 layers. Fehlings solution or Benedicts solution – contain Cu2+ ion; warm with Fehlings / Benedicts solution – an orange precipitate shows an aldehyde; Cu2+ + e- Cu. No change with a ketone. SOLUBILITY: Only the small polar molecules (C 1 to 3 or 4) are soluble in water – ALL others make 2 LAYERS with water or an (aq) reagent eg Br2 water or NaHCO3(aq) as they are either non polar molecules or have a large non polar portion.