BIOLOGY I EOC Study Guide
advertisement

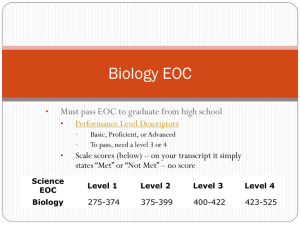
Name:________________________________________ Period:__________ BIOLOGY 1 EOC Study Guide If found: Please Return to Ms. Atkinson in room #27 Samuel W. Wolfson High School 7000 Powers Ave. Jacksonville, FL 32217 BIOLOGY I EOC Study Guide Nature of Science BENCHMARK SC.912.N.1.1 (Also assesses SC.912.N.1.4, SC.912.N.1.6, SC.912.L.14.4, LA.910.2.2.3, LA.910.4.2.2, MA.912.S.1.2, and MA.912.S.3.2.) Define a problem based on a specific body of knowledge, for example: biology, chemistry, physics, and earth/space science, and do the following: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. pose questions about the natural world; conduct systematic observations; examine books and other sources of information to see what is already known; review what is known in light of empirical evidence; plan investigations; use tools to gather, analyze, and interpret data (this includes the use of measurement in metric and other systems, and also the generation and interpretation of graphical representations of data, including data tables and graphs); pose answers, explanations, or descriptions of events; generate explanations that explicate or describe natural phenomena (inferences); use appropriate evidence and reasoning to justify these explanations to others; communicate results of scientific investigations; and evaluate the merits of the explanations produced by others. These are questions and activities you should already know how to do and are for review. a. Evaluate a scientific investigation using evidence of scientific thinking and/or problem solving. b. Interpret and analyze data to make predictions and/or defend conclusions. c. Compare and/or contrast the structure and function of the compound microscope, dissecting microscope, scanning electron microscope, and/or the transmission electron microscope. d. Evaluate the merits of scientific explanations produced by others. e. Assess the reliability of sources of information according to scientific standards. f. Describe how scientific inferences are made from observations and identify examples from biology. Properties of Water BENCHMARK SC.912.L.18.12 Discuss the special properties of water that contribute to Earth’s suitability as an environment for life: cohesive behavior, ability to moderate temperature, expansion upon freezing, and versatility as a solvent. Page #’s 1. Explain the following properties of water using definitions and examples: a. hydrogen bonding b. polarity c. cohesive behavior d. ability to moderate temperature e. expansion upon freezing f. versatility as a solvent 2. Explain how the special properties of water make it essential for life on Earth. 3. Know the difference between adhesion and cohesion (Adhesion will not be tested) 2 BIOLOGY I EOC Study Guide Macromolecules BENCHMARK SC.912.L.18.1 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of biological macromolecules. SC.912.L.18.11 Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions. Identify f actors, such as pH and temperature, and their effect on enzyme activity. Page #’s 4. Diagram the basic molecular structures and define the primary functions of the following four major categories of biological molecules. a. carbohydrates, c. proteins b. lipids, d. nucleic acids. 5. Explain how enzymes speed up the rate of a biochemical reaction by lowering the reaction’s activation energy. a. Diagram 6. Describe the effect of environmental factors, such as concentration, pH, and temperature on enzyme activity. Cell Theory BENCHMARK SC.912.L.14.1 Describe the scientific theory of cells (cell theory) and relate the history of its discovery to the process of science. (Also assesses SC.912.N.1.3, SC.912.N.2.1, SC.912.N.3.1, and SC.912.N.3.4.) Page #’s 7. Describe and/or explain the cell theory. 8. Describe how continuous investigations and/or new scientific information influenced the development of the cell theory. 9. Identify the ways in which a the cell theory developed over time (e.g., through scientific argumentation, critical and logical thinking, and consideration of alternative explanations). 10. Using the development of the cell theory explain how a theory is formed. 11. Explain the differences between a Scientific Theory and a Scientific Law. 3 BIOLOGY I EOC Study Guide Plant/Animal Cells BENCHMARK SC.912.L.14.3 Compare and contrast the general structures of plant and animal cells. Compare and contrast the general structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. (Also assesses SC.912.L.14.2.) Page #’s 12. Diagram and describe the function of the following prokaryotic structures: a. cell wall k. microtubules l. microfilaments b. cell membrane (plasma membrane) c. cytoplasm, m. vacuoles d. nucleus n. mitochondria e. nuclear envelope o. Golgi apparatus f. nucleolus p. Chloroplasts g. chromatin q. Lysosomes h. ribosomes i. endoplasmic reticulum j. plasmid r. Cilia s. flagella 13. Compare and contrast the general structures of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 14. Explain the role of the cell membrane as a highly selective barrier (make sure you include the difference between active and passive transport). 15. Identify the structures and their function of cell organelles located only in plants 4 BIOLOGY I EOC Study Guide Plants Organs BENCHMARK SC.912.L.14.7 Benchmark SC.912.L.14.7 Relate the structure of each of the major plant organs and tissues to physiological processes. Page #’s 16. Explain how the structures of plant tissues and organs are directly related to their roles in physiological processes. 17. Assess the function of plant tissues and organs in the context of physiological processes. 18. Know Structure and function of these plant organs Roots Stems Leaves Flowers Fruits cones. 19. Describe and explain: photosynthesis, cellular respiration transpiration cellular reproduction 20. Define and give structure these plant tissues meristematic, ground, dermal tissue vascular tissues. 5 BIOLOGY I EOC Study Guide 21. Define and give function these plant structures cambium, guard cells, phloem, seed, stomata, and xylem. Photosynthesis/Cellular Respiration BENCHMARK SC.912.L.18.9 Explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. (Also assesses SC.912.L.18.7, SC.912.L.18.8, and SC.912.L.18.10.) Page #’s 22. Explain how the products of photosynthesis are used as reactants for cellular respiration and vice versa. 23. Explain how photosynthesis stores energy and cellular respiration releases energy. 24. Identify the reactants, products and/or the basic function of photosynthesis. 25. Identify the reactants, products and/or the basic functions of aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration. 26. Decribe the role of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to energy transfers within the cell. Mitosis/Meiosis BENCHMARK SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. (Also assesses SC.912.L.16.8, SC.912.L.16.14, and SC.912.L.16.16.) Page #’s 27. Differentiate the processes of mitosis and meiosis. 28. Describe the role of mitosis in asexual reproduction, and/or the role of meiosis in sexual reproduction, including how these processes may contribute to or limit genetic variation. 6 BIOLOGY I EOC Study Guide 29. Describe specific events in the stages of the cell cycle and phases of mitosis. Mitosis includes phases, structures, and major events of each phase. 30. Explain how mitosis forms new cells and its role in maintaining chromosome number during asexual reproduction. 31. Explain how cancer (uncontrolled cell growth) may result from mutations that affect the proteins that regulate the cell cycle and the relationship between mutations and uncontrolled cell growth. 32. Describe the process of meiosis, including independent assortment and crossing over. 33. Explain how meiosis results in the formation of haploid gametes or spores. Mendel’s Laws BENCHMARK SC.912.L.16.1 Use Mendel’s laws of segregation and independent assortment to analyze patterns of inheritance. (Also assesses SC.912.L.16.2.) Page #’s 34. Give an example of each of Mendel’s laws of segregation and independent assortment and how are they used to analyze patterns of inheritance. 35. Identify inheritance patterns caused by various modes of inheritance. 36. What is the difference between a dominant and recessive trait? Use P and F 1 generations in your answer. 37. Distinguish between the P and F1 generations when assessing dihybrid crosses or patterns that include codominance, incomplete dominance, multiple alleles, sex-linkage, or polygenic inheritance. 38. Understand the different ways, percent, ratios, or fractions, that inheritance outcomes may be expressed. 39. Define codominance. 40. Define incomplete dominance. 41. Know how to read a Punnett squares to predict outcomes of a cross. DNA Replication BENCHMARK SC.912.L.16.3 Describe the basic process of DNA replication and how it relates to the transmission and conservation of the genetic information. (Also assesses SC.912.L.16.4, SC.912.L.16.5, and SC.912.L.16.9.) Page #’s 7 BIOLOGY I EOC Study Guide 42. Describe the process of DNA replication and/or its role in the transmission and conservation of genetic information. 43. Describe gene and chromosomal mutations in the DNA sequence. 44. Explain how gene and chromosomal mutations may or may not result in a phenotypic change. 45. Explain the basic processes of transcription and/or translation, and their roles in the expression of genes. 46. Explain that the basic components of DNA are universal in organisms. 47. Explain how similarities in the genetic codes of organisms are due to common ancestry and the process of inheritance. 48. Analyze gene mutations in a single gene by the changes in the base pairs. 49. How mutations influenced by the process of meiosis? 50. Describe the process of transcription and translation as related to protein synthesis. Cardiovascular System Benchmark SC.912.L.14.36 Describe the factors affecting blood flow through the cardiovascular system. Page #’s 51. Students will identify factors that affect blood flow and/or describe how these factors affect blood flow through the cardiovascular system. 52. Describe these factors blood pressure, blood volume, resistance, disease, and effects of exercise on the cardiovascular system. Immune System Benchmark SC.912.L.14.52 Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines, and antibiotics. Page #’s 53. Identify and/or explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune responses. 54. Describe how the human immune system responds to vaccines and/or antibiotics. 55. Explain the significance of genetic factors, environmental factors, and pathogenic agents to health from the perspective of both individual and public health. 8 BIOLOGY I EOC Study Guide 56. Define genetic factors, environmental factors, and pathogenic agents to health and how they affect us. BENCHMARK SC.912.L.16.10 Biotechnology Evaluate the impact of biotechnology on the individual, society and the environment, including medical and ethical issues. 57. Explain and give examples of the possible impact of biotechnology on the individual, society, and/or the environment. Human Reproduction BENCHMARK SC.912.L.16.13 Describe the basic anatomy and physiology of the human reproductive system. Describe the process of human development from fertilization to birth and major changes that occur in each trimester of pregnancy. Page #’s 58. Identify and/or describe the basic anatomy and physiology of the human reproductive system. Male human reproductive system: Female human reproductive system: seminal vesicle Ovaries prostate gland oviduct (fallopian tube) vas deferens uterus urethra cervix epididymis vagina scrotum penis testes 59. Describe the process of human development from the zygotic stage to the end of the third trimester and birth. 60. How do these structures function in relation to the developing fetus? placenta umbilical cord amniotic sac amniotic fluid 61. Items assessing the production of hormones in the context of the physiology of the human reproductive system are limited to a conceptual understanding of the production of hormones. 9 BIOLOGY I EOC Study Guide 62. Recognize that these terms (implantation, morula, blastocyst, gastrulation, neurulation) are related to the early stages of development. Evolution BENCHMARK SC.912.L.15.1 Explain how the scientific theory of evolution is supported by the fossil record, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, biogeography, molecular biology, and observed evolutionary change. (Also assesses SC.912.L.15.10, SC.912.N.1.3, SC.912.N.1.4, SC.912.N.1.6, SC.912.N.2.1, SC.912.N.3.1, and SC.912.N.3.4.) Page #’s 63. Identify evidence and/or explain how the scientific theory of evolution is supported by the fossil record, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, biogeography, molecular biology, and observable evolutionary change. 64. Examples of and basic trends in hominid evolution from early ancestors to modern humans. 65. Items assessing evolution will focus on a conceptual understanding of the supporting scientific evidence. 66. Why are fossil records so important in the development of the theory of evolution? 67. Tell how each of the following items contributed to the theory of evolution: adaptive radiation convergent evolution co-evolution punctuated equilibrium. 68. What are the trends in hominid evolution? 69. What are the key features that separate man from other hominids? 70. How does the development of language or the manufacturing of tools will relate to changes in the skull or brain size. 71. How are homologous structures and vestigial organs used when referring to comparative anatomy and comparative embryology? 10 BIOLOGY I EOC Study Guide 72. What is the overall contribution made by each of the following scientists: Darwin Lamarck Lyell Malthus Mendel Wallace Mechanisms of Change BENCHMARK SC.912.L.15.6 Discuss distinguishing characteristics of the domains and kingdoms of living organisms. (Also assesses SC.912.L.15.4, SC.912.L.15.5, SC.912.N.1.3, and SC.912.N.1.6.) Page #’s 73. Identify the distinguishing characteristics of these domains and/or kingdoms of living organisms. The Domains of: Archea Bacteria Eukarya The Kingdoms of: Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia 74. Identify and/or describe how and/or why organisms are hierarchically classified based on evolutionary relationships. 75. Explain the reasons for changes in how organisms are classified. 76. Distinguish between prokaryotic, eukaryotic, unicellular and/or multicellular organisms, autotrophs, and/or heterotrophs. 11 BIOLOGY I EOC Study Guide 77. Describe the use of evolutionary classification, phylogeny, and the use of cladograms, but they may not assess the definition of those terms. Evolution: Origins of Life BENCHMARK SC.912.L.15.8 Describe the scientific explanations of the origin of life on Earth. (Also assesses SC.912.N.1.3, SC.912.N.1.4, and SC.912.N.2.1.) Page #’s 78. Describe scientific explanations of the origin of life on Earth. 79. Identify situations or conditions contributing to the origin of life on Earth. 80. Items may address the conditions required for the origin of life on Earth but may not require specific knowledge of the age of Ear th or its eras, periods, or epochs. 81. How did contributions of scientists such as Pasteur, Oparin, Miller and Urey, Margulis, or Fox aid in the development of the scientific explanation of the origin of life Natural Selection BENCHMARK SC.912.L.15.13 Describe the conditions required for natural selection, including: overproduction of offspring, inherited variation, and the struggle to survive, which result in differential reproductive success. (Also assesses SC.912.L.15.14, SC.912.L.15.15, and SC.912.N.1.3.) Page #’s 82. Explain the 4 conditions required for natural selection that result in differential reproductive success. 83. Describe the scientific mechanisms, such as genetic drift, gene flow, and nonrandom mating, which results in evolutionary change. 84. Explain how mutation and genetic recombination increase genetic variation. 85. Assess how mutation and genetic recombination increases genetic variation and results in evolution. 86. How does meiosis contribute to genetic variation? 12 BIOLOGY I EOC Study Guide Theory of Evolution BENCHMARK SC.912.L.17.5 Analyze how population size is determined by births, deaths, immigration, emigration, and limiting factors (biotic and abiotic) that determine carrying capacity. (Also assesses SC.912.L.17.2, SC.912.L.17.4, SC.912.L.17.8, and SC.912.N.1.4.) Also Assesses SC.912.L.17.2 Page #’s 87. Define and explain how population dynamics, abiotic factors and/or biotic factors, and carrying capacity effect population size in an ecosystem. 88. Explain that different types of organisms exist within aquatic systems due to chemistry, geography, light, depth, salinity, and/or temperature. 89. Describe the potential changes to an ecosystem resulting from seasonal variations, climate changes and/or succession. 90. Identify positive and/or negative consequences that result from a reduction in biodiversity. 91. Know the effects of these chemical factors in aquatic systems: pH, oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, phosphorous, and salinity. 92. Know the consequences to reduction in biodiversity of catastrophic events, climate changes, human activities, and the introduction of invasive and nonnative species. Food Web BENCHMARK SC.912.L.17.9 Use a food web to identify and distinguish producers, consumers, and decomposers. Explain the pathway of energy transfer through trophic levels and the reduction of available energy at successive trophic levels. (Also assesses SC.912.E.7.1.) Page #’s 93. Describe the energy pathways through the different trophic levels of a food web or energy pyramid. 94. Know how matter moves through these different biogeochemical cycles: Carbon Water 95. Know how changes in matter or energy in trophic levels impacts organisms in food webs. 96. Know the how photosynthesis and cellular respiration describe energy movement through food webs. 97. Be familiar with energy measured in joules (J)? 13 BIOLOGY I EOC Study Guide Human Impact BENCHMARK SC.912.L.17.20 Predict the impact of individuals on environmental systems and examine how human lifestyles affect sustainability. (Also assesses SC.912.L.17.11, SC.912.L.17.13, SC.912.N.1.3, and HE.912.C.1.3.) Page #’s 98. Predict how the actions of humans may impact environmental systems and/or affect sustainability. 99. Evaluate possible environmental impacts resulting from the use of renewable and/or nonrenewable resources. 100. Know how renewable and nonrenewable resources affect environmental costs and benefits of those using resources. 14