Organizational Behavior 10e
advertisement

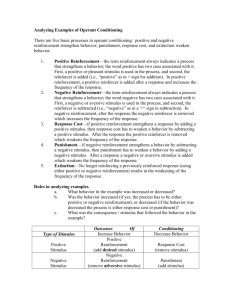
ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR WWW.PRENHALL.COM/ROBBINS T E N T H E D I T I O N Biographical Characteristics Age – Are older workers “better” or “worse” than younger workers? Gender – Any differences b/w male and female workers? Marital Status – So, should we hire only married employees?? Ability Physical Ability The Ability-Job Fit Employee’s Abilities Ability-Job Fit Job’s Ability Requirements Learning Learning • Involves change • Is relatively permanent • Is acquired through experience Theories of Learning Key Concepts • Unconditioned stimulus • Unconditioned response • Conditioned response Theories of Learning (cont’d) Key Concepts • Reflexive (unlearned) behavior • Conditioned (learned) behavior • Reinforcement Theories of Learning (cont’d) Key Concepts • Attention processes • Retention processes • Motor reproduction processes • Reinforcement processes Theories of Learning (cont’d) Key Concepts • Reinforcement is required to change behavior. • Some rewards are more effective than others. • The timing of reinforcement affects learning speed and permanence. Schedules of Reinforcement Schedules of Reinforcement Fixed-ratio Intermittent Schedules of Reinforcement Intermittent Schedules of Reinforcement (cont’d) OB MOD Organizational Applications Well Pay versus Sick Pay – Reduce absenteeism by rewarding attendance, not absence. Employee Discipline – The use of punishment can be counter-productive. Developing Training Programs – OB MOD methods improve training effectiveness. Self-management – Reduces the need for external management control.