Embryology of Dental Structures
advertisement

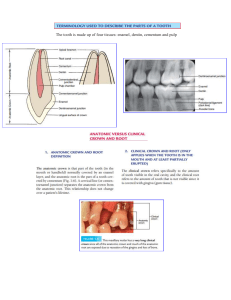
Embryology of Dental Structures Embryonic Stages Ovum: 1st week/fertilization Embryo: 2-8 weeks o Stomodeum (Primitive Mouth): develops in 3rd week o Buccopharyngeal membrane ruptures: 4th week o Primary Dentition Initiated: 6-8 weeks Fetus: 9-36 weeks o Permanent Dentition Initiated: 20th week in utero till 10th month after birth Fertilization » morula » blastocyst » trophoblast » embroyblast Embryo Ectoderm: nasal cavity, enamel, nervous system, appendage of skin, hait and nails and glands Mesoderm: skeletal system, muscles, tongue, blood and lymph cells, kidney, dentin, cementum, pulp Endoderm: pharynx, stomach, intestines, bladder, vagina Brachial Arches 1st (Mandibular): mandible, lower lip, muscles mastication, anterior portion of the tongue, maxillary process 2nd (Hyoid) Facial muscles, posterior portion of the tongue, sides and front of the neck, portion of the hyoid bone, portion of the muddle ear 3rd.: posterior portion of the tongue, portion of the hyoid bone Odontogenesis Tooth Development (occurs over 2 yrs): bud, cap, bell, detinogensis, amelogenesis, apposition of dentin and enamel, eruption, function Ectoderm oral epithelium » enamel organ » enamel dental lamina Mesenchyme Cells dental papilla » dentin and pulp dental sac » cementum and periodontal ligaments Tooth Germ enamel organ, dental papilla dental sac Epithelial Components (4 distinct cell layers) OEE IEE STI STR Layers of Dentin Primary- mantle and circumpupal dentin Secondary- starts after tooth the formation of the apical foramen, which occurs once tooth is in occlusion Tertiary- reparative dentin Structural Components of Dentin Dentin tubule Peritublular (intratubular) dentin Intertubular dentin -Tome’s Granular Layer: layer of dentin that underlies cementum, covers the root Principle Cells of the Pulp Odontoblasts Fibroblasts Undifferentiated mesenchymal cells Macrophages Lymphocytes Functions of the Pulp Inductive Formative Protective Nutritive Reparative Five Funtional Stage of Ameloblasts Morophogenesis Organization and differentiation Secretion Maturation Protection -Hypoplastic Enamel: strong but pitted, yellow to grey in color, thin enamel -Hypocalcified Enamel: weak, white/yellowing spotting, insufficient number of crystals deposited in enamel -Chemical Composition of Enamel: 96% inorganic, 4% organic -Chemical Composition of Cementum: 65% inorganic, 23& organic, 12% water