Oral histology and Embryology Test
advertisement

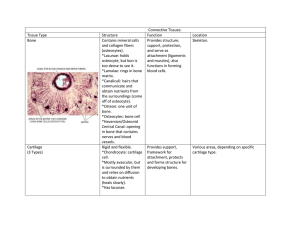
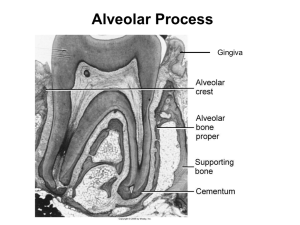
Board Review DH227, Lisa Mayo, RDH, BSDH Oral histology and Embryology Test 1. Junctional epithelium cells attach to enamel and implants by a. Desmosomes b. Hemidesmosomes c. Extra-cellular matrix d. Keratin 2. The PDL is attached to bone and cementum by a. Cementoblasts b. Hemidesmosomes c. Shapey’s fibers d. Stillman’s fibers 3. What type of primitive tissue gives rise to the enamel of a tooth? a. Ectoderm b. Mesoderm c. Endoderm d. None of the above 4. The dental pulp is derived from endoderm. The dentin and cementum are derived from mesoderm. a. Both statements are TRUE b. Both statements are FALSE c. The first statement is TRUE, the second statement is FALSE d. The first statement is FALSE, the second statement is TRUE 5. The buccopharyngeal membrane at what week in development? a. 2 weeks b. 3 weeks c. 4 weeks d. 6 weeks 6. Palatal closure occurs during which week in embryonic development? a. 2 b. 4 c. 8-12 d. 16 7. The first brachial arch gives rise to the mandible, and it innervated by the trigeminal nerve a. Both statement are TRUE b. Both statements are FALSE c. The first statement is TRUE, the second statement is FALSE d. The first statement is FALSE, the second statement is TRUE 8. Epithelial rests of Mallassez a. Are of mesodermal origin b. Are located in the PDL c. Are formed from cells of the dental papilla d. Can form into cysts e. B, D 9. Which component of a biofilm makes it resistant to penetration by medications applied to the surface? a. Gram negative bacteria b. Fluid channel c. Pellicle attachment d. Slime layer 10. The cellular organelle that contain digestive enzymes is the a. Mitochondria b. Ribosome c. Mitochondria d. Lysosome e. Centriole 11. The medium that carries nutrients and waste materials between the tissue and the capillaries is the a. Formed elements b. Ground substance c. Tissue fluid d. Endoplasmic reticulum e. Cytoplasm 12. An attached plaque between a cell and noncellular surface is called a a. Desmosome b. Hemidesmosome c. Tight junction d. Gap junction 13. The tissue component that is derived from the blood is the a. Cells b. Fibrous intercellular substance c. Amorphous intercellular substance d. Tissue fluid 14. The blood supply of the PDL and the alveolar bone proper anastomose and communicate because of the a. Compact structure of the alveolar bone proper b. Structure of the cribiform plate of the alveolar bone proper c. Lamina dura of the alveolar bone proper d. Bundle of the alveolar bone proper e. Arrangements of the Sharpey’s fibers in the alveolar bone proper 15. The embryonic origin of all connective tissue is a. Mesenchyme b. Endoderm c. Fascia d. Ectoderm e. Epithelium 16. Cells that devour debris within connective tissue of a patient with periodontitis are called a. Lysosomes b. Melanocytes c. Fibroblasts d. Macrophages e. Mast cells 17. With the exception of the ____, the oral and nasal cavities develop from the first brachial arch and the frontal process a. Lower lip b. Lower border of the cheeks c. Anterior portion of the hard palate d. Base of tongue e. Base of the nasal septum 18. Rathke’s pouch if the embryonic origin of the a. Thyroid gland b. Palate c. Globular process d. Pituitary gland e. Nasal septum 19. The lateral palatine initially grows downward toward the floor of the mouth. It does not grow medially at this time of initial development because of the presence of the a. Nasal septum b. Maxillary process c. Premaxilla d. Tongue e. Mandibular process 20. An infant born without a primary palate is resented for consultation. What teeth will never be present, even after a surgical repair of the existing condition? a. Both the primary and permanent incisors in the maxilla b. Both the first primary and permanent premolars in the maxilla c. Both 6-yr molars in the maxilla d. Both the primary and the permanent canines in the maxilla e. Only the primary incisors in the maxilla 21. The buccopharyngeal membrane if composed of a. Mesoderm, endoderm b. Ectoderm, mesoderm c. Ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm d. Ectoderm, endoderm 22. In the area of the formaen ceacum, epithelium invaginates deep into the tissues and will eventually become the a. Pituitary gland b. Lingual salivary gland c. Submandibular salivary gland d. Trachea e. Thyroid gland 23. What anatomic feature separates the root and the body of the tongue? a. The lingual frenum b. The fungifofrm papillae c. The median groove d. The third brachial arch e. The circumvallate papillae 24. The olfactory (nasal) pits appear on the lateral sides of these a. Maxillary process b. Olfactory process c. Mandibular process d. Frontal process e. Globular process 25. During palatal fusion, epithelial cells may become entrapped in the line of fusion. These cells may later contribute to the formation of a. Teeth b. Cleft lips c. Cleft palate d. Cysts e. Ectopic teeth 26. The earliest signs of development of the human face occurs during the third week in utero with the formation of the a. Stomodeum b. Maxillary process c. Olfactory pits d. Globular process 27. A cleft lip occurs when maxillary process fails to fuse with the a. Palatine process b. Globular process c. Lateral nasal process d. Mandibular process e. Opposing maxillary process 28. The 3 types of muscle tissue are: a. Skeletal, smooth, striated voluntary b. Cardiac, striated involuntary, smooth c. Nonstraiated involuntary, cardiac, skeletal d. Straited involuntary, smooth, cardiac 29. The site if muscle contraction is called a. Sarcomere b. Sarcolemma c. Actin d. Myosin e. Z Line 30. The part of the neuron that conducts impulses toward the cell body is called the a. Dendrite b. Axon c. Neurilemma d. Myelin sheath e. Neuroglia 31. Dentin, cementum, pulp are derived from a. Ectoderm b. Mesoderm c. Endoderm d. Epithelium e. Endothelium 32. In what structures of enamel is rodless enamel most often found? a. At the base of pits and fissures b. In the outermost enamel c. In the central region of enamel 33. The relationship of enamel and cementum at the CEJ that cannot occur is a. Enamel overlaps cementum b. Enamel and cementum just meet c. Enamel and cementum do not meet d. Cementum overlaps enamel 34. Which of the following microscopic structures show evidence of the curvature of the enamel rods? a. Bans of Hunter-Schreger b. Striped of Retzius c. Enamel lamellae d. Enamel tufts e. Enamel spindles 35. In a person born without teeth, what part of the bone of the maxilla and the mandible would be absent? a. The cribiform plate of the alveolar bone proper b. The alveolar bone c. The basal bone of the maxilla and the mandible d. The bundle bone of the alveolar bone proper e. The interradicular bone of the alveolar process 36. The reduced enamel epithelium will ultimately produce all of the following except: a. Junctional epithelium b. Hertwigs epithelial root sheath c. Primary enamel cuticle d. Secondary enamel cuticle 37. Which statement BEST describes the status of tooth enamel? a. Calcium is lost from enamel during pregnancy b. Calcium is withdrawn during periods of malnutrition c. Low blood calcium causes demineralization d. Calcium loss is similar to that of bone e. None of the above 38. The layer of dentin found adjacent to the pulp in young teeth is called a. Tome’s granular layer b. Predentin c. Interglobular dentin d. Dead tracts e. Sclerotic dentin 39. The stippled texture of the gingiva may be attributed to a. Keratinization b. Rete pegs c. Presence of submucosa d. Optimal blood supply e. Pigmentation 40. The dentinal fibers that occupy the dentinal tubules are part of the a. Korff’s fibers of the pulp b. Fibrillar dentin matrix c. Odontoblasts of the pulp d. Sclerotic dentin e. Interrod substance 41. Caries in the dentin of the tooth progresses through the a. Interglobular dentin b. Dentinal tuble c. Secondary dentin d. Predentin e. Sclerotic dentin 42. The outer, less calcified layer of cementum is called a. Cellular cementum b. Acellular cementum c. Cementoid d. Cementicles e. Sharpey’s fibers 43. The connective tissue that underlies the epithelium of the gingiva is a. Reticular b. Elastic c. Fibrous d. Submucosa e. Oxytalan 44. The periodontal fibers that are located in the root furcation area are the a. Sensory fibers b. Apical fibers c. Septum fibers d. Interradicaular fibers e. Transeptal fibers 45. The ends of the PDL fibers that are embedded in the cementum and bone are called a. Principal fibers b. Korff’s fibers c. Sharpey’s fibers d. Dentinal fibers e. Gingival fibers 46. Remnants of Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath sound in the PDL of a functional tooth are called: a. Enamel pearls b. Denticles c. Rests of Malassez d. Cementicles e. Intermediate plexus 47. Bone trabeculation increases as functional activity decreases; the PDL increases in width as functional activity decreases. a. The first statement is TRUE, the second statement is FALSE b. The first statement is FALSE, the second statement is TRUE c. Both statements are TRUE d. Both statements are FALSE 48. In the oral cavity, one way in which lining mucosa differs from masticatory mucosa is that a. Lining mucosa contains more muscle fibers b. Masticatory mucosa contains glands c. Lining mucosa has no submucosa d. Lining mucosa is not keratinized 49. The first permanent molas develops from a. Primary dental lamina b. Secondary dental lamina c. Enamel pearls 50. The first cell to reach an injured area is the a. Neutrophil b. Monocyte c. Macrophage d. Lymphocyte e. Plasma cell 51. The last visible layer in Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium is the a. Basal cell layer b. Prickle cell layer c. Granular layer d. Corneum layer 52. Dentin is the product of a. Dental lamina b. Dental organ c. Dental papilla d. Dental cuticle e. Dental sac 53. The cellular component that provides the internal support for the long odontoblastic processes is the a. Microtubule b. Microfilament c. Tonofibrils d. Cilia 54. The cellular organelle that provides the vast amount of energy required for the organic matrix deposition is the a. Endoplasmic reticulum b. Golgi complex c. Nucleus d. Mitochondria 55. The mandible and maxilla are formed through ____ bone formation. a. Endochondral b. Circumferential c. Intermembranous d. Lamellar e. Haversian 56. Bone and cementum are similar in all of the following aspects except for the presence of a. Canaliculi b. Approximately the same amt of inorganic components c. Lacuna d. Volkmann’s canals 57. Fibrous cartilage is found in all the following locations EXCEPT a. Intervertebral disk b. TMJ c. Pubic symphysis d. Epiglottis 58. What type of attachment is present between the epithelial cells and the basal lamina of the basement membrane? a. Desmosome b. Hemidesmosome c. Tight junction d. Gap junction 59. The color of the gingiva is influenced by: a. Rete pegs b. Pigment cells c. Vascularity d. B,C e. All the above ANSWERS 1.B 2.C 3.A 4.D 5.C 6.C 7.A 8.E 9.D 10.D 11.C 12.B 13.D 14.B 15.A 16.D 17.D 18.D 19.D 20.A 21.D 22.E 23.E 24.D 25.D 26.A 27.B 28.C 29.A 30.A 31.B 32.B 33.A 34.A 35.B 36.C 37.E 38.B 39.B 40.C 41.B 42.C 43.C 44.D 45.C 46.C 47.D 48.D 49.A 50.A 51.B 52.C 53.A 54.D 55.C 56.D 57.D 58.B 59.D