Acidic Erosion - Strobel Dentistry
advertisement

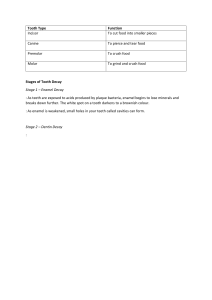
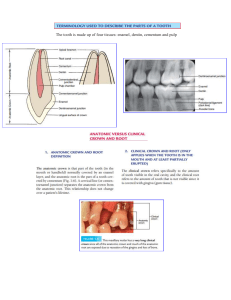
Acidic Erosion Definition: Loss of tooth structure caused by acid exposure eroding the enamel. Causes Intrinsic - acid reflux, bulimia, GERD and frequent vomiting Extrinsic – frequent consumption of foods and beverages with high acidic content. Check out the acidity levels of common items here! Symptoms: Thin enamel Rough ridges or ledges on surfaces of enamel Shiny surfaces Cupping or divots on occlusal surfaces Incisal edges of the teeth become grooved and chipped, exposing underlying dentin Incisal chipping on the teeth, which may appear darker/more yellow as dentin is exposed Treatment: The key here is prevention and management. Keep the acidity level of your mouth as close to neutral as possible by minimizing length and frequency of exposure with any acidic drinks and foods. Identify your risk factors. Avoid or reduce frequent intake of acidic beverages Use a straw when drinking to minimize acid contact with tooth surfaces. Select beverages containing calcium, phosphate or fluoride, and rinse with water or drink milk after acid exposure in order to lessen erosive attacks. Use dentifrices with a high fluoride concentration to strengthen enamel surfaces and low abrasiveness levels: MI paste, Prevident toothpaste, Sensodyne Pronamel toothpastes. Avoid tooth brushing immediately after acid exposure; wait at least 30 minutes to allow the tooth surface recovery from acid attacks. Chew sugarless gum If you think you may suffer from acid reflux, bulimia or GERD, see your primary care physician for diagnosis and treatment options. Strobel Dentistry, Ltd. 25 E. Washington St., Ste. 1917, Chicago, IL, 60602 (312) 726-3135 : www.strobeldentistry.com : strobeldentistry@live.com