Document 15347644
advertisement

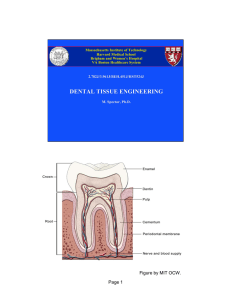
Identify hard tooth structures Mention functions of enamel, dentin and cementum Define smear layer and its role Define iatrogenic trauma to tooth and mention its type in oral cavity Describe how iatrogenic trauma can be avoided Define thermogenesis Mention causes of thermogenesis during an operative dentistry procedure Explain how thermogenesis be controlled Describe effect of speed and pressure of rotary instrument on pulp health Define desiccation Mention causes desiccation and its effects Describe eccentricity ,its causes and effects Hard tissues Enamel Dentin Cementum Soft tissue Pulp Protection for dentin & pulp Maintain the esthetic of the tooth through translucency A good insulator of heat Forms reparative dentin in response to any irritation Forms smear layer for protecting the pulp (Biological importance) Whenever dentin is cut or abraded, a thin altered layer is created on the surface Few micrometer thick Formative or developmental Nutritive Sensory or protective Defensive or reparative Iatrogenic Trauma Thermogenesis Speed Pressure Desiccation Vibration Pin drilling & insertion Trauma to the tissues of oral cavity caused by the operating dentist Mechanical Thermal Chemical Use Sharp cutting instruments completely dissipate energy applied during the actual cutting Avoid undue over-cutting of enamel & dentin it exposes more dentinal tubules Avoid unnecessary application of pressure in scooping out carious dentin to avoid pressure pain Avoid using rotary instruments without proper cooling Generation of heat The friction between the cutting tool & tooth structure Increased amount of pressure during cutting by rotary instruments Hardness of the tissues to be cut (more heat generates when cutting enamel than cutting dentin) Increased area of tool to tooth contact Type of bur (material): Steel generates more heat than the corresponding size carbide because steel has lower hardness & cutting efficiency Diamond points generate more heat than the corresponding size carbide due to ‚their abrasive action and wider area of tooth contact Use small sized burs Apply minimal amount of pressure Avoid use of eccentric tools Restrict use of diamond points to enamel Use coolant during cavity preparation (Air-water spray) Never cut under dry condition at any rotational speed High speed produces higher amount of heat Cutting under dry condition at any rotational speed causes variable pulp changes Cutting with low speed instruments requires more pressure than cutting with high speed instruments It induces deleterious pulp response Injurious Harmful Destructive Absolute dryness of dentin Overheating of dentin during cutting procedures Using chemicals as alcohol to sterile the cavity Using air as a coolant or in performing final toilet of cavity Sensitivity Pulp pathology Increased Permeability of vital dentin to any irritant Aspiration of odontoblasts from the pulp toward the cut dentin at the area of prepared cavity Occurs due to eccentricity or run-out of rotary instruments Having the axis away from the center 1- Annoyance & discomfort to the patient 2- Heat generation 3- Rebound response: due to increased speed of rotation, limited area of necrosis occurs at an area remote from the cut dentin 4- Calciotraumatic effect: alteration areas of hyper & hypocalcification near the pulpal surface of the cut dentin 5- Uncontrolled cutting 6- May cause cracks in enamel 7- May show different degree of pulp changes 8- Reduction in growth rate of dentin, absence of pre-dentin layer & formation of irregular dentin Sodium hypochlorite used as canal irrigant is toxic ballooning, bleeding , periodontal pain, facial emphysema and angioneurotic edema may occur Protective shield For dentist Protective glasses for patients Dentinal pins are used for extra retention of a restoration confine pin drilling within the elastic limit of dentin Oversized pins, dull pins & clogged flutes develop minute fracture lines or crazed enamel Pin insertion induces internal stresses Injurious pin drilling may lead to pulp exposure Luting cements used with cemented pins à may irritate the pulp Thermal & galvanic irritations can be transmitted through pin to underlying pulp The greater the pin diameter the higher is the thermal conductivity