Tissues
advertisement
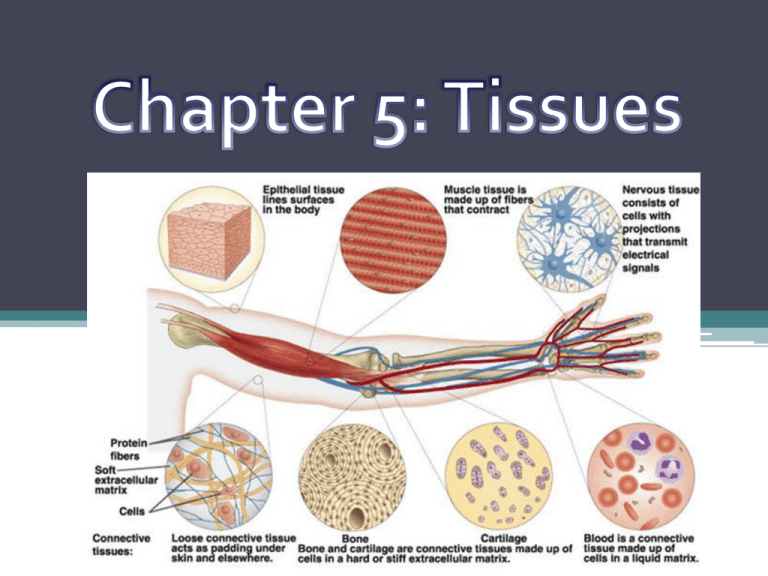
Introduction • Tissue: ▫ Def – cells organized into groups and layers all with the same function ▫ Rely upon extracellular matrix (contains nutrients needed for cells to thrive, transmits signals) • Four types (Table 5.1): ▫ ▫ ▫ ▫ 1) Epithelial 2) Connective 3) Muscle 4) Nervous Epithelial Tissue • Location ▫ Lines exposed surfaces of body ▫ Forms inner lining of body cavities ▫ Covers organs • Function ▫ Protection, absorption, secretion • Characteristics ▫ One side is exposed, one side is anchored to basement membrane (connective tissue) ▫ Tightly packed cells with little to no blood vessels ▫ Readily divide Connective Tissue • Location ▫ Throughout body (bone, blood, cartilage) • Function ▫ Support and protection, binds structures, fills spaces, stores fat, produce blood cells, protect against infection, repair tissue damage • Characteristics ▫ Cells have spaces between them filled with extracellular matrix ▫ Can usually divide and have good blood supply ▫ Can be flexible or rigid in nature Muscle Tissue • Location ▫ Throughout body (skeletal muscles, heart muscle, muscles in tracts and tubes) • Function ▫ Provide movement • Characteristics ▫ Cells can shorten ▫ Contract/relax in response to stimuli Nervous Tissue • Location ▫ Brain, spinal cord, and nerves throughout body • Function ▫ Transmit signals across body ▫ Coordinate, regulate, integrate body functions • Characteristics ▫ Respond to changes in their surroundings ▫ Basic cell :neuron Epithelial Tissue Classification • Classified by shape and # of layers • Shape ▫ Squamous ▫ Cubiodal ▫ Columnar • # of Layers ▫ Simple- one layer ▫ Stratified- multiple layers Simple Squamous • Form ▫ Single layer, flattened, tilelike cells ▫ Tightly packed ▫ Easily damaged • Function ▫ Diffusion (substances pass through easily) and filtration • Locations ▫ Alveoli in lungs ▫ Capillaries Simple Cuboidal • Form ▫ Single layer cube-shaped cells ▫ Central nucleus • Function ▫ Secretion and absorption • Location ▫ Lining of kidney tubules ▫ Lining of some gland ducts (thyroid, salivary, pancreas, liver) ▫ Covers ovaries Simple Columnar • Form ▫ Single layer elongated, column-like cells ▫ Can be ciliated ▫ Goblet cell scattered • Function ▫ Protection, secretion, and absorption • Location ▫ Lining of digestive tract ▫ Female reproductive tubes (cilia aid in egg movement) Pseudostratified Columnar • Form ▫ Single layer elongated cells with nuclei at different heights, often ciliated ▫ Appear layered ▫ Goblet cells scattered • Function ▫ Movement of particles ▫ Trap dust/microorganisms • Location ▫ Lining of respiratory passages Stratified Squamous • Form ▫ Several layers of tile-like cells ▫ Thick ▫ Divide and push old cells up • Function ▫ Protection (microorganisms) ▫ Keritinize (harden and die) providing layer to prevent water loss • Location ▫ Outer layer of skin ▫ Linings of cavities opening to the outside Stratified Cuboidal • Form ▫ Several layers of cubeshaped cells • Function ▫ Protection • Location ▫ Linings of larger ducts of glands ▫ Ovary follicle Stratified Columnar • Form ▫ Several layers ▫ Outer layer elongated cells • Function ▫ Protection and secretion • Location ▫ Parts of pharynx ▫ Parts of male reproductive system Transitional • Form ▫ Several layers of rounded cell that can stretch to form layers of flattened cells • Function ▫ Stretch ▫ Forms barrier to prevent diffusion of materials back • Location ▫ Bladder ▫ Ureter ▫ Parts of urethra Glandular Epithelium • Function: secrete and produce • Endocrine vs Exocrine ▫ Endocrine- released into interstitial fluid or bloodstream ▫ Exocrine- released into duct or onto surface • Serous vs Mucous ▫ Serous- found in cavities closed to the inside ▫ Mucous- found in cavities with exposure to outside Connective Tissue Cells • Fibroblasts- fixed cells that secrete protein fibers ▫ Characteristics: Collagenous- thick threads with a high tensile strength but only a little elasticity Elastic- thin, networked thread; not as strong but elastic Recticular- thin delicate threads; forms framework in some organs • Macrophages (histiocytes)- roaming cells that eat cellular debris and foreign particles by phagocytosis • Mast cells- fixed cells that release heparin and histamine Loose Connective • Form ▫ Scattered cells and fibers in matrix ▫ Mainly fibroblasts ▫ Very low tensile strength ▫ Thin, delicate • Function ▫ Binds organs together (especially skin to underlying organs) • Location ▫ Beneath many epithelial layers including skin ▫ Between muscles Adipose (fat) • From ▫ Specialized form of loose connective where fat cells store enough fat to crowd other things out of the tissue • Function ▫ Storage of energy (in fat), insulation, protection, cushion • Location ▫ All throughout body ▫ Beneath skin, spaces in between muscles, around kidneys, behind eyes, surface of heart, around joints Dense Connective • Form ▫ Few cells, highly packed with thick collagenous fibers ▫ Very strong ▫ Few elastic fibers • Function ▫ Binds organs together (muscle to bone, bone to bone) ▫ Protective layer of eye • Location ▫ Tendons and ligaments ▫ Deep layers of skin ▫ Eye Cartilage • Form ▫ Cartilage cell (chondrocytes) surrounded with a gel-like matrix ▫ Rigid • Function ▫ Supports ▫ Protects underlying tissue (cushions bones) ▫ Forms framework with some flexibility ▫ Provides attachment • Location ▫ Ends of bones ▫ Ears ▫ Nose Bone • Form ▫ Bone cells (osteocytes) surrounded by rigid matrix of calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate salts ▫ Most rigid connective tissue • Function ▫ Supports, protects, provides framework ▫ Muscle attachment ▫ Form blood cells ▫ Store/release inorganic chemicals • Location ▫ Bones Blood • Form ▫ Cells suspended in plasma matrix ▫ Three types: RBCs, WBCs, plasma • Function ▫ Transports materials (exchange of materials) ▫ Help maintain internal environment • Location ▫ Blood Muscle Tissue • Location ▫ Throughout body (skeletal muscles, heart muscle, muscles in tracts and tubes) • Function ▫ Provide movement • Characteristics ▫ Cells shorten Muscle Tissue Types • Skeletal ▫ Voluntary, striated, multiple nuclei/cell ▫ Ex: Skeletal muscles (quadriceps, triceps) • Cardiac ▫ Involuntary, striated, one nucleus/cell ▫ Ex: Heart muscle • Smooth ▫ Involuntary, unstriated, one nucleus/cell ▫ Ex: Esophagus, stomach wall Skeletal Muscle Tissue • Form ▫ Long thread-like cells with banding, striations, along the length ▫ Cell w/ many nuclei • Function ▫ Voluntary movements ▫ Talk, smile, swallow, breathe, sing, etc. • Location ▫ Attached to bones Cardiac Muscle Tissue • Form ▫ Complex network of branching, striated cells connected by intercalated disks • Function ▫ Movement of heart ▫ Involuntary movement • Location ▫ Heart (only!) Smooth Muscle Tissue • Form ▫ Spindle-shaped cells lacking striations and poorly organized • Function ▫ Movement of internal organs ▫ Involuntary movement • Location ▫ Walls of internal organs (stomach, intestines, bladder, uterus, blood vessels Nervous Tissue • Location ▫ Brain, spinal cord, and nerves throughout body • Function ▫ Transmit signals (nerve impulses) across body ▫ Coordinate, regulate, integrate bodily functions • Characteristics ▫ Respond to changes in their surroundings ▫ Basic cell: neuron Nervous Tissue Types • Neurons ▫ Basic cellular unit of nervous system ▫ Transmit the messages ▫ Senses environmental changes • Neuroglial cells ▫ Support neurons ▫ Bind nervous tissue ▫ Supply nutrients to neurons Types of Membranes • Epithelial: 3 Types 1. Serous- release serous fluid and line cavities not exposed to the outside, lubricate membrane surface 2. Mucous- release mucous and line cavities that open to outside (oral/nasal cavity, digestive/respiratory/ urinary/reproductive tubes) 3. Cutaneous- skin • Connective 1. Synovial- lines joints