ANAT & PHYS 2015-16 Anatomy & Physiology 2015
advertisement

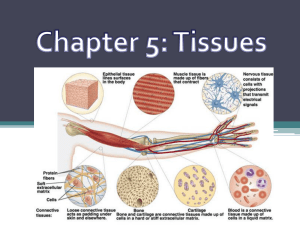
Anatomy & Physiology MIDTERM STUDY GUIDE 2015-16 Your midterm will be comprised of 100 scantron questions. Completion of this study guide is OPTIONAL. However, completion will help you know what to study. You will not be allowed to use it on the midterm. Remember, this is a study guide. To make it useful, complete a few days before the test. Then spend the last 2 nights before the test to review it. Chapter 1 HUMAN BODY 1. How is an anatomical study different from a physiological study? 2. What are the 6 levels of organization? 3. Be prepared to match the following body systems to their functions. a. b. c. d. Digestive Endocrine Integumentary Lymphatic e. f. g. h. Muscular Respiratory Skeletal Urinary d. e. f. Nervous Respiratory Urinary 4. Be prepared to match the following systems to their organs: a. b. c. Cardiovascular Digestive Endocrine 5. What is anatomical position? 6. Know the following landmark regions and how they relate to each other with all directional terms. Example: The patellar region is anterior to the popliteal region. BODY REGIONS DIRECTIONAL TERMS abdominal antecubital axillary brachial buccal carpal deltoid femoral frontal mental patellar pelvic thoracic tarsal Anterior Deep Distal Inferior Intermediate Lateral Medial Posterior Proximal Superficial Superior ANAT & PHYS 2015-16 7. What are the 2 dorsal body cavities? What are the 3 ventral cavities? 8. What are the 3 body planes? How does each separate the body? Example: Which type of section can be used to separate the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity? Chapter 3 TISSUES 1. Name the four main types of tissues. In one word, state the function of each type of tissue. 1) ________________________ = ____________________________ 2) ________________________ = ____________________________ 3) ________________________ = ____________________________ 4) ________________________ = ____________________________ 2. Which tissue type is most abundant and widely distributed throughout the body? __________________ 3. Which of the four main types is associated with each characteristic and/or functions? Connects, binds and supports structures Covers the body Covers the organs inside body cavities Facial expressions Generates & transmits nerve impulses Include tendons & ligaments Insulates (fat) Lines the cavities, tubes, ducts and blood vessels inside the body Locomotion Maintains posture Makes up the brain & spinal cord Most abundant & widely distributed tissue Movement Peristalsis Has an apical surface and a basement membrane Produces heat Protection against microbial invasion Protects & cushions organs and tissues Pumps blood Regulates & controls body functions Secretes serous fluids to lubricate structures Transports substances (blood) 4. What are the 4 functions of epithelial tissue? 5. What is the difference between SIMPLE and STRATIFIED epithelial cells? What are the 3 shapes of epithelial cells? (Draw and name below) 6. What are the 2 basic components of connective tissue? 7. What two types of cells make up nervous tissue? Which of these is conducting? Nonconducting? 8. Identify which of the following is characteristic of SMOOTH (SM), SKELETAL (SK)AND CARDIAC (C)muscle. (Some may have more than one answer.) ____ Found in walls of hollow organs, i.e. stomach _____ Involuntary movement _____ Only found in the heart _____ Responsible for facial expressions and body movements _____ Striated _____ Tapered cells (similar to an eye) _____ Voluntary movement ANAT & PHYS 2015-16 9. What kind of tissue (epithelial, connective, nervous, smooth muscle, skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle) is found in the Blood vessels? brain & spinal cord? stomach? ligament? heart? lining of esophagus? bone? sweat gland? blood? fat? skin? Chapter 4 SKIN & BODY MEMBRANES 1. Name the four types of body membranes. Which are connective? Epithelial? 2. Which of the 4 BODY MEMBRANES adapted for absorption and secretion? dry? forms two layers: visceral & parietal? secretes a lubricating fluid? 3. What are the two main layers of skin? 4. What function does the hypodermis serve? 5. What are the 5 layers of the epidermis from superficial to deep? Which are living? dead? Deteriorating? Which layer Contains melanocytes? Is a transitional layer of living, dead and dying cells? Is continuously shed? Is made of 8-10 layers of living cells? Is mitotic? Only found on hands and feet? 6. The dermis is made of two layers: the papillary layer and the reticular layer. Know the difference between the two in terms of location, components and function. For instance, which layer… composes fingerprints? contain pain receptors? contain sweat and oil glands? contains blood vessels 8. What are the two types of sudoriferous glands? Which one secretes water, salts, and metabolic wastes? Which secretes fatty acids and proteins? What is the function of each types secretion? contains deep pressure receptors? contains touch receptors? is attached to the epidermis? ANAT & PHYS 2015-16 9. What do sebaceous glands secrete? What is the function of their secretion? (3 answers) 10. What is hair composed of? What are the 3 types of hair shafts and what kind of hair does each form? What parts of the body do not contain hair? 11. What are nails composed of? 12. What are the three categories of burns? What skin layers are damaged in each? What does each look like? 13. What is the Rule of Nines? 14. How is a benign tumor different from one that is malignant? 15. What are the three types of skin cancer? 16. Which type of cancer is evaluated by the ABCD rule? is least malignant? is most common? is most deadly? metastasized rapidly?