year 12 Eggs tasks
advertisement
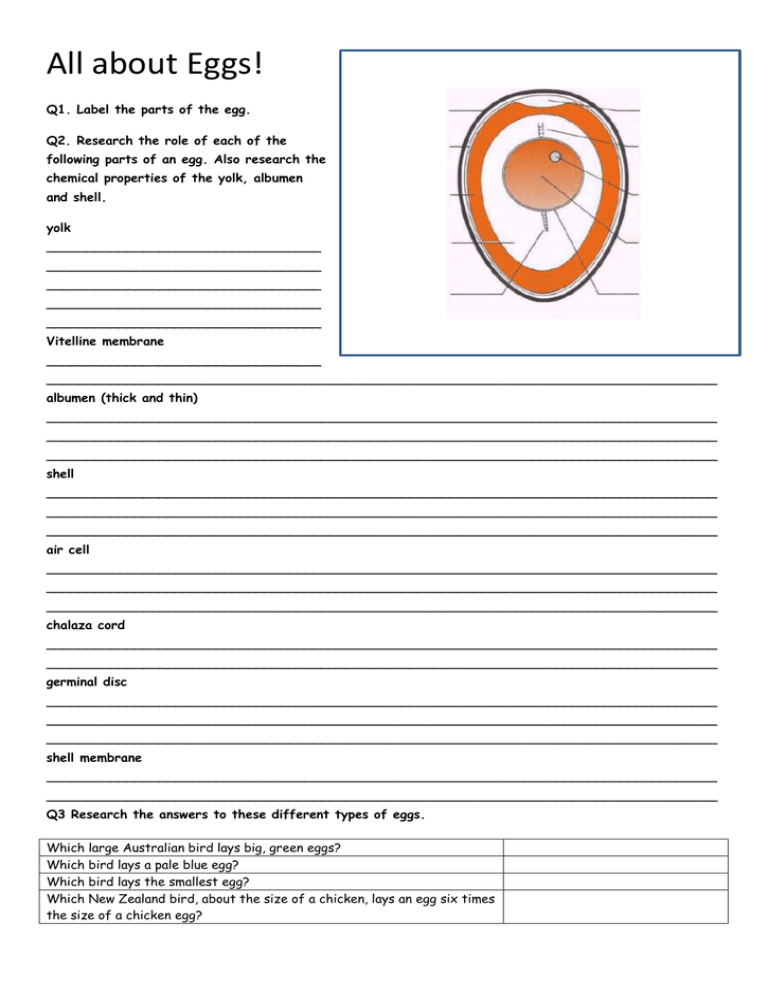
All about Eggs! Q1. Label the parts of the egg. Q2. Research the role of each of the following parts of an egg. Also research the chemical properties of the yolk, albumen and shell. yolk __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ Vitelline membrane __________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ albumen (thick and thin) ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ shell ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ air cell ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ chalaza cord ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ germinal disc ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ shell membrane ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Q3 Research the answers to these different types of eggs. Which large Australian bird lays big, green eggs? Which bird lays a pale blue egg? Which bird lays the smallest egg? Which New Zealand bird, about the size of a chicken, lays an egg six times the size of a chicken egg? Q4 Explain what happens to the air cell as the egg gets older? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Q5 How do the yolk and the egg white change as the egg gets older? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Q6 Complete the drawing to show a fresh egg in the bowl of water. As the egg gets older the air cell gets _________ causing the egg to ____________ in a bowl of water however, thin or cracked shells will also cause the egg to rise slightly. Q7 Other than placing an egg in a bowl of water, what are two other ways that the freshness of eggs can be tested?_____________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Q8 Describe how eggs should be stored to retain optimum freshness. ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Q9 Eggs contain proteins, which are made up of chains of amino acids. The characteristics and properties of proteins are determined by the sequence of the amino acids. Applying heat to proteins can cause the protein chains to uncoil and change shape. This change is a chemical process that cannot be reversed and its name is D_________________________. Q10. As in meats, when heat is applied for a longer time, the protein strands will entrap liquid and a gel will form. This process is called C___________________________. The temperature that egg yolks C________________ is ______degrees. The temperature that egg white C___________________ is _____degrees. This is how you can have soft boiled eggs or ‘sunny side up’. The temperature of C_____________________ also depends on the presence of other ingredients; adding _______________ and __________________will increase the temperature of C________________, whereas the addition of ______________ or ______________ decreases it. Lowering the temperature is useful in poaching eggs as the proteins become less stable in the lower __ and are quicker to denture giving a rounded rather than ragged appearance. Likewise, when beating egg whites to make a meringue, a small amount of __________ such as cream of tartar or vinegar can be added to ________________ the meringue. When egg whites are beaten, the protein is _______________, creating a foam that aerates the mixture as it stretches and traps in air bubbles. The addition of ________ may also help to create a more stiff foam. If using eggs to make a set custard such as ______________ or a custard base for an _____ __________, it relies on gentle cooking so that the eggs _______________ evenly within a temperature range of 65 and 70 degrees. Preparing the custard in a _______________ or cooking in a ____________________ helps to prevent the delicate mixtures from ___________ or separating. If the custard is overheated the _____________ from the egg and milk begin to over-coagulate to form small lumps and cause a loss of the smooth, rich texture. Read your textbook pages 61-62 and complete understanding the text questions 11-20. Read your textbook pages 83-86 and complete understanding the text questions 21-24 Properties of Eggs Eggs are an extremely important ingredient in many recipes and have a number of functional roles. Either complete this template or use the A3 paper to create a ‘functional egg poster’ for your study Q1. For each of the functions below; • explain the role of the egg. • name two food examples where the egg performs this function.





