Circulatory Unit PPT
advertisement

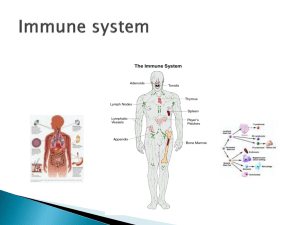
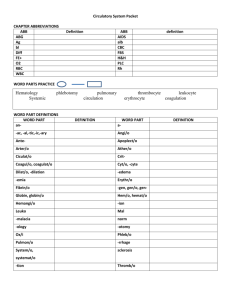
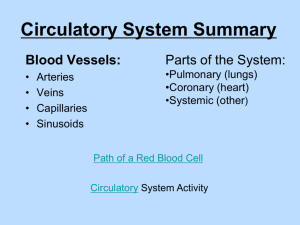
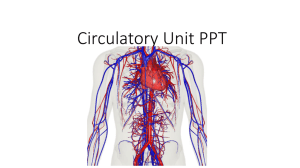
Circulatory Unit PPT Chapter Abbreviations • Using packet B. • Please put back when you are finished Word parts practice: Word part definitions: •TRY first without the packet • Use packet A • Put back when finished Lab station work: • Working with your lab group try to come up with as many words by just using your WORD PARTS chart. • Write them out with shiny desk materials Lab station work examples • Arteriomalacia • Atherosclerosis • Coagulation • Hemoglobin • Normal • Circulation • pulmonary Chapter reading: • Please read pages 185-88 Circulatory Vocab • Using your Word part charts fill in your vocabulary chart W.A.: Instructions • From website: • Click circulatory • Click on website assignment worksheet. (recommended to print this one) • http://app.discoveryeducation.com/player/view/assetGuid/E2964DE9-60674C4B-9B37-EA2A4C499994 Circulatory coloring • You will be in your lab stations • Change colors when you meet an “X” • Answer the questions when you are finished What do you know? • What are 3 Types of blood vessels? • What color are they? • Why are they different colors? • What is blood made up of? Components of blood • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R-sKZWqsUpw Components of Blood: take notes on your WA worksheet • Solid components: • Erythrocytes • • • • Contain hemoglobin Live about 120 days Made by red marrow in bones Liver and spleen remove dead RBC’s • Leukocytes • Thrombocytes Components of Blood: take notes on your WA worksheet • Solid components: • Erythrocytes • Leukocytes • Function: to fight disease and infection • Fewer WBC than RBC • Larger than RBC • Live about 9 days • Move out of the blood vessels into lymph tissue to help with immunity • Pus = WBC and bacteria • Thrombocytes WBC break down • Make a chart on your W.A. worksheet. WBC function Basophil Eosinophils Neutrophils Lymphocytes Monocytes • Using pages 187-88 fill in the function of each WBC Components of Blood: take notes on your WA worksheet • Solid components: • Erythrocytes • Leukocytes • Thrombocytes • • • • Help with clotting Produced in red bone marrow Live about 10 days Clotting process: platelets stick to damaged tissue and to each other. Group together to control blood loss from blood vessel. Components of Blood: take notes on your WA worksheet • Liquid component: • Plasma • Whole blood = 55% plasma • Made up of: • • • • • • Water Protein Salts Nutrients Vitamins hormones Components of blood review: Desk Review Components of blood B E N L M Blood Types • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ttjn1jVACk8 Blood Typing Key Terms • Antigens: foreign object, pathogen • Antibodies: proteins secreted by lymphocytes • Antibodies bond with antigens = lock and key phenomenon Antigen = lock antibody = key Blood Type Inherited • Each person inherits 2 genes. • Dominant genes • Are A and B • Shown as “I” • EX: • Recessive genes •O • Shown as “i” • Ex: Punnett Square 4 Blood Types • Blood type is determined by antigens on the surface of RBC •A • Only A antigens •B • Only B antigens • AB • Both A and B antigens •O • Neither A or B antigens • Your immune system has a tolerance against it own antigens. (you like your own antigens) EX: Antigen A type A blood. It will NOT form anti-A antibodies. Blood Type Antigens on RBC’s Antibodies in Plasma A A Anti - B B Complete the table showing which blood can be safely transfused from the donor to recipient. Recipient D O N O R Blood Type A B AB O A + B AB O Transfusions • Need to mix serum of the patient with the blood cells of the donor. • If Type A gets matched with Type B then antibodies will clump together • If this test is not done hemolysis (rupture of blood cells) can occur Blood • Type O Blood • Universal donor • Because it lacks A and B antigens • Type AB Blood • Universal recipients because they lack anti-A and anti-B antibodies. • (they won’t attack new blood coming in) Rh Factor Antigen • Found in RBC • Rh- : people who do not have antigens on RBC • Rh+ : people who do have the antigen on RBC • About 85% of Americans are Rh+ • If RH + blood is given to Rh- then the body thinks it is an invading pathogen and starts to form antibodies for the lock and key Rh Factor Health Concerns • When an Rh- mother delivers an Rh+ baby, some of the baby’s blood may contact the blood of the mother • The mother’s blood then forms antibodies against Rh+ RBC • If the mother has another Rh+ pregnancy the antibodies will attack the baby’s blood causing erythroblastosis fetalis. Bell ringer Review Answer the following questions with your lab group A. The heart is ____________________ (Directional Term) to the lungs. B. The heart is divided into ________ and ______ sides C. The word pulmonary is another term for _______________ D. Name the 3 different blood vessels in the circulatory system E. Name 3 components of blood Health Matters of the Circulatory System Anemia – most common blood disorder • Etiology: • Inadequate amount of hemoglobin, RBC or both • S/S: shortness of breath, pallor (pale), rapid heart rate. • TX: dietary supplements, blood replacement. Hemophilia • Etiology: rare sex linked genetic blood disease in which the blood is missing a clotting factor. • S/S: prolonged or uncontrolled bleeding • TX: giving plasma that contains the missing clotting factor, no cure Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) • Etiology: dysfunction of the immune system caused by a virus. Virus will cause DNA to become infected damaging WBC. • HIV is transmitted through exchange of body fluids. • S/S: may not show for 6-10 years: fatigue, weakness, painful joints, diarrhea. • TX: no cure, experimental medicines. Leukemia (blood cancer) • Etiology: abnormal malignant increase in the number and longevity of WBC. WBC are immature and less effective in fighting disease • S/S: bleeding gums, anemia • TX: radiation, chemotherapy, bone marrow transplantation Elephantiasis • massive accumulation of lymphatic fluid in body tissues, causing abnormally large growth of tissue. • Etiology: caused by obstruction of the lymph vessels by tiny worms (filariae) that are common in tropic and subtropic areas. • S/S: fever, chills and ulcer formation • TX: no cure, oral medications and mosquito control measures. Sickle cell anemia • Etiology: genetic condition that results in malformed RBC • The “sickled” cells are more fragile and cause pain as vessels are blocked and less oxygen is delivered. • S/S: sometimes no symptoms, may cause death • TX: no cure Allergy • Etiology: hypersensitive response by the immune system to an outside substance which becomes an allergen. • Allergens cause antibodies to be produced. EX: pollen, dog/cat fur, feathers. • S/S: inflammation of the respiratory, GI and integumentary systems, may become life threatening. • TX: drugs Autoimmune Diseases • Etiology: conditions in which the immune system of the body turns against itself. • EX: • Systemic lupus erythematosus: affects connective tissue, kidneys, lungs and heart • Hashimoto’s disease: destruction of the thyroid • Myasthenia gravis: affects the nerves and causes paralysis TX: immunosuppressive drugs and steroids to relieve inflammation. Erythroblastisis fetalis • Etiology: Antibodies from an Rh negative mother may enter the blood stream of her unborn Rh positive infant, damaging the red blood cells (RBCs). The infant responds by increasing RBC production and sending out immature RBCs that still have nuclei. • S/S: baby may have brain damage • TX: intrauterine blood transfusion Hodgkin’s disease • Etiology: cancer of the lymph system that usually appears in people between the ages of 15-30. • S/S: painless enlargements of the lymph nodes, itching, weight loss, fever, difficulty swallowing. • TX: chemotherapy or radiation of the lymph nodes. Splenomegaly • Etiology: enlargement of the spleen caused by an acute infection such as scarlet fever • S/S: symptoms are similar to leukemia and anemia. • TX: may require removal of spleen Thrombosis • Etiology: condition in which a blood clot (thrombosis) forms in the vessels. Clot slows the flow of blood to tissues • Embolus: when the clot breaks away, it could lodge in a blood vessels and cause tissue death • S/S: pain in the area of the clot because of lack of oxygen • TX: elevation, anticoagulants, may have surgery to remove clot. Lymphatic System • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X4Wn0j3eJrA Lymphatic system • Using your book starting on pg 234 fill in the Lymphatic system section of guided notes • What structures do the lymphatic & immune systems share? • Lymph nodes, spleen, and thymus gland • What is the function of both systems? • Produce disease fighting immune cells. Lymphatic Systems KEY • What systems are the lymphatic & immune systems similar to & why? • Circulatory & cardiovascular systems because it contains a network of vessels to transport lymph fluid. • What is the function of lymph? • Transport various substances around the body. • What does lymph contain? Does it contain RBC or Platelets? • Lymph contains WBC; carries less protein than blood, same amount of water, salts, sugar & waste material; no RBC or platelets. • What are the smallest parts of the lymphatic system? • Lymphatic capillaries • What is the fluid in the spaces between tissues called? • Interstitial fluid • What are lymph nodes & what is their function? • Specialized organs that produce lymph cells and filter harmful substances from tissues. These special cells devour foreign substances. Known as “macrophages” • What are lymphocytes? • WBC that produces antibodies • What is the function of the lymph vessels? • Gather substances and fluid that have leaked from blood capillaries into the tissues and transport them back into the bloodstream. Bring lipids (fat) from small intestine to bloodstream. Lymph travels in only one direction. Practice Quizzes Directions: Fill in the chart. Blood Type Receive blood from: A (example A, O) Donate blood to: Directions: Fill in the chart. KEY Blood Type Receive blood from: Donate blood to: A (example A, O) A, AB B B, O B, AB AB A, B, AB, O AB O O A, B, AB, O List 2 Components of blood, and what makes up each component 1. 2. List 2 Components of blood, and what makes up each component KEY 1. Formed elements – RBC, WBC, Thrombocytes. 2. Plasma – water, salts, hormones, vitamins, protein, nutrients Directions: Match up the WBC with its function(s). a. neutrophils b. Basophils c. eosinophils d. lymphocytes e. monocytes 1. destroy large unwanted particles in the bloodstream 2. control inflammation and allergic reactions 3. protect the body against formation of cancer cells 4. remove small unwanted particles from the blood 5. release heparin to stop clotting 6. produce histamine to cause blood vessel dilation 7. kill parasites 8. essential to immune system Directions: Match up the WBC with its function(s). KEY a. neutrophils b. Basophils c. eosinophils d. lymphocytes e. monocytes 1. (E) destroy large unwanted particles in the bloodstream 2. (C) control inflammation and allergic reactions 3. (D) protect the body against formation of cancer cells 4. (A) remove small unwanted particles from the blood 5. (B) release heparin to stop clotting 6. (B) produce histamine to cause blood vessel dilation 7. (B, C) kill parasites 8. (D) essential to immune system