Ecology Practice Test
advertisement

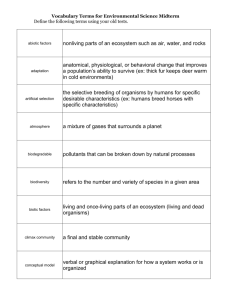
Ecology Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. Plants are a. producers. c. herbivores. b. consumers. d. omnivores. 2. What is the original source of almost all the energy in most ecosystems? a. carbohydrates c. water b. sunlight d. carbon 3. All the interconnected feeding relationships in an ecosystem make up a food a. interaction. c. network. b. chain. d. web. 4. The total amount of living tissue within a given trophic level is called the a. organic mass. c. energy mass. b. trophic mass. d. biomass. 5. What is an ecological model of the relationships that form a network of complex interactions among organisms in a community from producers to decomposers? a. food web c. food chain b. an ecosystem d. a population 6. What animals eat both producers and consumers? a. herbivores c. chemotrophs b. omnivores d. autotrophs 7. Only 10 percent of the energy stored in an organism can be passed on to the next trophic level. Of the remaining energy, some is used for the organism’s life processes, and the rest is a. used in reproduction. c. stored as fat. b. stored as body tissue. d. eliminated as heat. 8. Matter can recycle through the biosphere because a. matter is passed out of the body as waste. b. matter is assembled into chemical compounds. c. biological systems do not use up matter, they transform it. d. biological systems use only carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen. 9. The repeated movement of water between Earth’s surface and the atmosphere is called a. the water cycle. c. precipitation. b. the condensation cycle. d. evaporation. 10. Which of the following is NOT recycled in the biosphere? a. water c. carbon b. nitrogen d. energy 11. The greenhouse effect is a. the result of an excess of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. b. a natural phenomenon that maintains Earth’s temperature range. c. the result of the differences in the angle of the sun’s rays. d. an unnatural phenomenon that causes heat energy to be radiated back into the atmosphere. 12. Each of the following is an abiotic factor in the environment EXCEPT a. plant life. c. rainfall. b. soil type. d. temperature. ____ 13. Which is a biotic factor that affects the size of a population in a specific ecosystem? a. average temperature of the ecosystem b. type of soil in the ecosystem c. number and kinds of predators in the ecosystem d. concentration of oxygen in the ecosystem ____ 14. A wolf pack hunts, kills, and feeds on a moose. In this interaction, the wolves are a. hosts. c. mutualists. b. prey. d. predators. ____ 15. A symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit is a. commensalism. c. predation. b. mutualism. d. parasitism. ____ 16. Primary succession can begin after a. a forest fire. c. farm land is abandoned. b. a lava flow. d. a severe storm. ____ 17. What is one difference between primary and secondary succession? a. Primary succession is slow and secondary succession is rapid. b. Secondary succession begins on soil and primary succession begins on newly exposed surfaces. c. Primary succession modifies the environment and secondary succession does not. d. Secondary succession begins with lichens and primary succession begins with trees. ____ 18. Which of the following is NOT one of the factors that play a role in population growth rate? a. immigration c. emigration b. death rate d. demography ____ 19. One of the main characteristics of a population is its a. change over time. c. dynamics. b. geographic distribution. d. habitat. ____ 20. There are 150 Saguaro cactus plants per square kilometer in a certain area of Arizona desert. To which population characteristic does this information refer? a. growth rate c. age structure b. geographic distribution d. population density ____ 21. The movement of organisms into a given area from another area is called a. immigration. c. population shift. b. emigration. d. carrying capacity. ____ 22. What must occur in a population for it to grow? a. The birthrate becomes higher than the death rate. b. The birthrate stays the same and the death rate increases. c. The birthrate becomes lower than the death rate. d. The birthrate and the death rate remain the same. ____ 23. As resources in a population become less available, the population a. declines rapidly. c. reaches carrying capacity. b. increases slowly. d. enters a phase of exponential growth. ____ 24. A biotic or an abiotic resource in the environment that causes population size to decrease is a a. carrying capacity. c. limiting factor. b. limiting nutrient. d. growth factor. ____ 25. All of the following are limiting factors EXCEPT a. immigration. c. predation. b. competition. d. human disturbances. Completion Complete each statement. 26. When an animal kills and eats another animal this is an example of ___________________. 27. Organisms that require to eat other organisms to get their energy are known as ___________________. 28. ___________________ refers to the different living species that is found in an ecosystem. 29. When moving into a new area it is know as ___________________, versus ___________________, when an organism exits an area. 30. All the same species in an area make-up a ___________________. And all of the different species in area make-up a ___________________. The community includes all of these different species plus the ___________________, or non-living factors. 31. Only ___________________ of the energy is transferred between trophic levels and the other 90% is lost as ___________________. 32. For a population to increase in size ___________________ and ___________________ must be higher than the death rate and emigration. 33. An ecosystem has reached its ___________________ when the maximum amount of individuals is being supported. Short Answer Figure 3–1 34. Using Figure 3–1, explain the relationship between sharks and the sun. 35. Describe the role of algae illustrated in Figure 3–1. 36. Which organism in the food chain would be found at the bottom of a biomass pyramid? Why would this organism be found there? Other USING SCIENCE SKILLS Figure 3–4 37. Applying Concepts Write down 3 separate food chains that can be seen in this food web. 38. Inferring Figure 3–4 shows a food web arranged into trophic levels. How many energy-transferring steps away from the sun is the deer? How do you know? 39. Interpreting Graphics In Figure 3–4, how many first-level consumers are there for each producer? 40. Comparing and Contrasting In Figure 3–4, compare the amount of energy available to the wolf if it eats only first-level consumers with the amount of energy available to the wolf if it eats only second-level consumers.