Vocabulary List #1 Term Definition Paraphrase Example Affirmative
advertisement
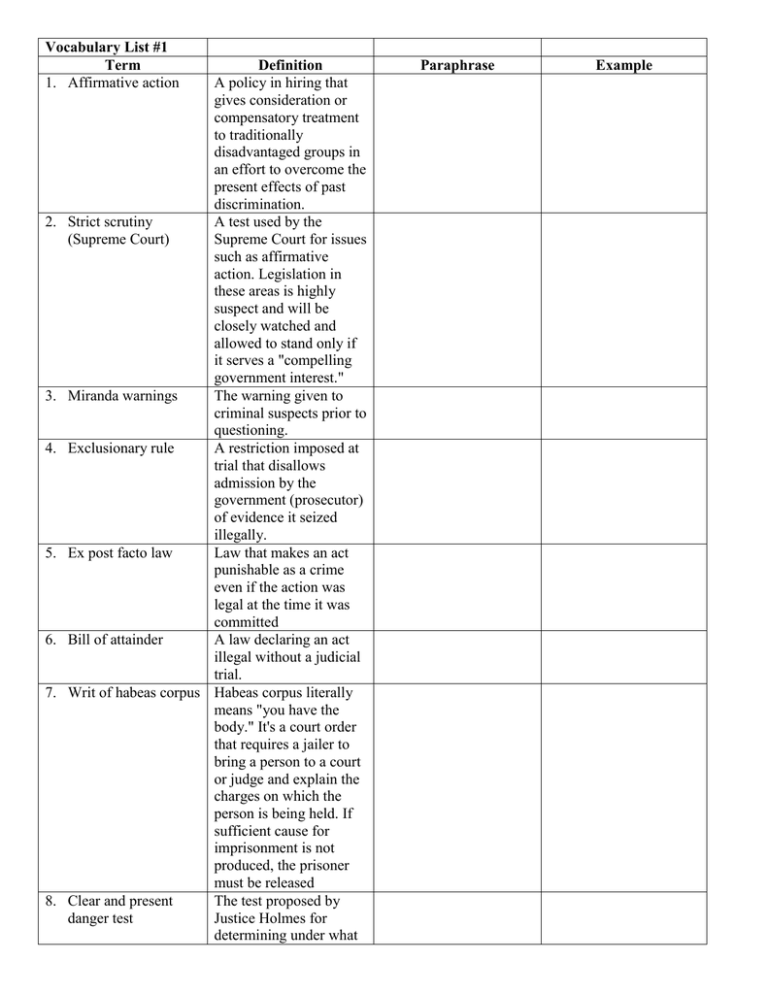
Vocabulary List #1 Term 1. Affirmative action 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Definition A policy in hiring that gives consideration or compensatory treatment to traditionally disadvantaged groups in an effort to overcome the present effects of past discrimination. Strict scrutiny A test used by the (Supreme Court) Supreme Court for issues such as affirmative action. Legislation in these areas is highly suspect and will be closely watched and allowed to stand only if it serves a "compelling government interest." Miranda warnings The warning given to criminal suspects prior to questioning. Exclusionary rule A restriction imposed at trial that disallows admission by the government (prosecutor) of evidence it seized illegally. Ex post facto law Law that makes an act punishable as a crime even if the action was legal at the time it was committed Bill of attainder A law declaring an act illegal without a judicial trial. Writ of habeas corpus Habeas corpus literally means "you have the body." It's a court order that requires a jailer to bring a person to a court or judge and explain the charges on which the person is being held. If sufficient cause for imprisonment is not produced, the prisoner must be released Clear and present The test proposed by danger test Justice Holmes for determining under what Paraphrase Example 9. Free exercise clause 10. Establishment clause 11. Selective incorporation 12. Civil rights 13. Civil liberties circumstances government may restrict free speech. Under this test, restrictions are permissible when speech provokes a "clear and present danger" to the public order The 1st Amendment provision guaranteeing freedom of worship and religious practice. Government cannot take official action to support any religion; used to restrict government efforts to aid religious organizations and schools, require prayers in public schools, or require teaching fundamentalist theories of creation in public school. The process in which Supreme Court selectively applies provisions of the Bill of Rights to the states through the 14th Amendment. Those powers or privileges guaranteed to individuals or protected groups by government, which are protected from arbitrary removal by government or by private individuals. In the U.S., they include the right to vote, equal treatment before the law, and equal access to and benefits from public facilities. Those personal freedoms possessed by all individuals and protected from arbitrary interference by government. They include the protection of 14. Office of management and budget 15. Entitlement program 16. Judicial activism 17. Judicial restraint 18. Stare decisis 19. Amicus curiae brief 20. Solicitor general persons, opinions, and property. A division of the Executive Office of the President charged with running the government efficiently and economically, helping to prepare the annual budget. A benefit provided by the government to which recipients have a legally enforceable right. A doctrine holding that judges should take an active role in making decisions that lead to socially desirable ends, primarily by exercising the power of judicial review. A doctrine holding that judges should not take an active role in making decisions that lead to socially desirable ends. Instead, judges should restrain their own opinions and desires and defer policy decisions to legislators and the executive branch— elected officials who are accountable to voters. Court policy to follow precedents established in past cases; to stand on decided cases. A "friend of the court." brief is a document filed with a court containing a legal argument supporting a desired outcome in a particular case. It is filed by a party not directly involved in the litigation but with an interest in the outcome of the case. Responsible for handling appeals on behalf of the US government to the Supreme Court











