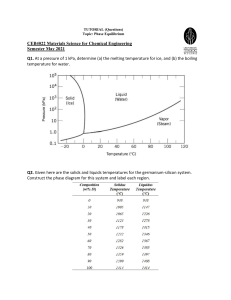
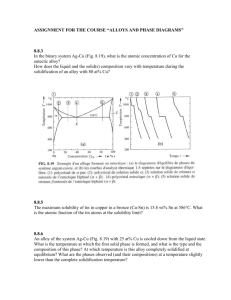
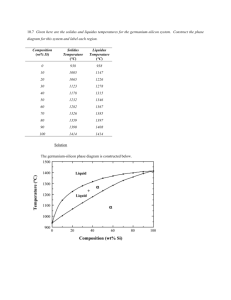
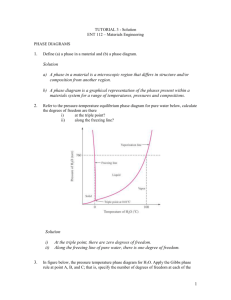
Review - mvhs
advertisement

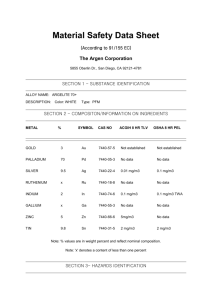
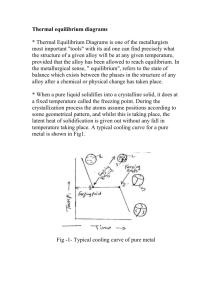
Material Science Quiz Review Vocabulary • Alloy: Substance that has metalllic properties and is made from two or more metal components • Aluminum: Lighweight, strong element that replaced fabric and wood in airplanes • Annealing: Process of heating and slowly cooling to increase ductility • Ceramic: Good thermal insulator, poor electrical conductor, formed by heat to cause vitrification • Cold Working:Strengthening a metal by plastic deformation at a temperature too low for atoms to rearrange, creating dislocations • Component: An element or alloy with the same chemical and physical characteristics • Composite: Material composed of two or more distinct materials • Dislocation: Defect in a crystal where the lattice is distorted (atoms misaligned) • Elastic Deformation: Stretching or compression of a material where the material returns to its original shape after removal of load • Eutectic: Alloy composition with the lowest melting point • Grog & Grogette: First material scientists • Liquidus Line: The liquid phase is located at temperatures above this line • Material Science: The study of stuff • Melting Point: The temperature at which an element transitions from solid to liquid phase • Metal: Opaque, lustrous, dense, malleable, good conductors of heat and electricity • Nitinol: Memory shape alloy used in stents • Phase: A volume of material where the properties are uniform • Phase Diagram: Diagram that shows phases of an alloy • Plastic Deformation: Stretching or compression of a material where the material will not return to its original shape after removal of load • Polymer: Organic compounds composed of monomers of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen • Quenching: Rapid cooling of a heated material by emersion in a liquid/salt, strengthening the material • Slush Zone: A loose term that identifies a phase composed of both liquid and solid • Solder: Tin and lead alloy • Solidus Line: The solid phase is located at temperatures below this line • Solubility Limit: Maximum percentage of solute that will dissolve completely into a solvent. • Vacancy:A missing atom in a crystal lattice Metals History • First Era: Using things as found or with slight adaptation. Gold, silver copper. Hammered to shape. Jewelery • Second Era: Changing things with heat or chemicals. Bronze, iron. Plows, swords. • Third Era: Understanding, making new materials. Alchemists’ effort to convert base metals to gold leads to an understanding of metallurgy. % Composition Calculations • 60-40 lead-tin means 60% lead and 40% tin by weight. • 2 kg of lead makes 2 kg/.60, or 3.3 kg of leadtin alloy • 440 g of alloy contains 440 g x .40, or 176 g of tin Draw and label a phase diagram below from the following descriptions • • • • • a) The α element is copper b) The α element melting point is 1085°C c) The β element is nickel d) The β element melting point is 1455°C e) Label the solidus line running linearly (straight line) between the two melting points • f) Label the liquidus line running through the following points: (25% Ni, 1225°C), (50% Ni, 1300°C), (75% Ni, 1375°C) • g) Label the phases of solid, slush, and liquid 1500°C 1400°C T e m 1300°C p e (°C) r a t 1200°C u r e 1100°C 1000°C 0 10 20 30 50 40 % Weight 60 70 80 90 100