Ch. 8 and 9.1
advertisement

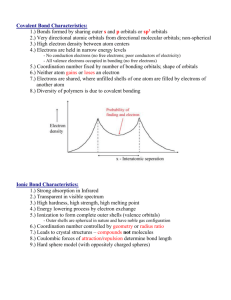
Do Now: What are the three types of bonds? Compare them. Which compounds contain which bonds? Why? •Properties of metals? High electrical and thermal conductivity, luster (shiny), malleable, ductile Metallic Bond Valence electrons are delocalized. The bond results from the electrostatic attraction between the delocalized electrons and the metallic ions. Positive ions (cations) in a "sea" of delocalized electrons. Ionic Bond •Transfer of electrons •Metals lose elelctron(s) to form positive ions (cations) •Nonmetals gain electron(s) to form negative ions (anions) Li Lower IE : : Li. :Cl: . + - :Cl: .. More negative EA Ionic Compounds •Properties??? Brittle, crystalline substances with high melting points, most soluble in water, conduct electricity when melted and in solution, Lattice Energy Molecular Compounds - Covalent Bonding • Gas, Liquid,Solid with generally low melting points, brittle, do not conduct electricity • Looking at hydrogen molecule, H2 • High electron density between nuclei. The atoms are held together because the two positive nuclei are attracted to the concentration of negative charge between them. The shared pair in a covalent bond acts as “glue” Lewis Structures • Use Lewis Dot Diagrams • Lone pairs (nonbonding pairs – unshared) • Bonding Pairs –shared between two nuclei Draw Lewis structures for N2, O2, and F2 •Compare bond length and bond enthalpy, enthalpy change DH to break bond •Estimate DH for synthesis of ammonia Energy Calculations •Estimate DHfo for potassium chloride provided with: •Lattice energy of KCl: -690 kJ/mol •First IE for K: 419 kJ/mol •Electron affinity of Cl: -349 kJ/mol •Bond Energy of Cl2: 239 kJ/mol •Enthalpy of sublimation for K: 64 kJ/mol Ionic and Covalent Bond are on the extremes, what about HCl •Polar covalent bond •Dipole moment – measure of is the measure of net molecular polarity, tell us about the charge separation in a molecule. Electronegativity – ability of atom to attract electrons. Explain trend What type of bond exists between… •H and O •S and S •Li and Cl - Lewis Structures •Type of structural formula that uses dots or dashes to indicate bonds Bromine molecule, Br2 Water, H2O Ethyne, C2H2 Methane, CH4 DO NOW •Draw the Lewis Structure for NCl3 and HCN •Indicate the shared and unshared pairs of electrons •What is another term for shared electrons? alence V hell S lectron E air P epulsion R This theory states that pairs of valence electrons are arranged as far apart from each other as possible Draw Lewis Structures for • H2, C2H2, BH3, NH3, H2O, PCl5, SF6 • In the last two examples, will you satisfy the octet rule? Explain Example Shape Angle H2 and C2H2 Linear 180º BH3 Trigonal Planar 120º Methane Tetrahedral ~109.5º ? Ammonia Trigonal Pyramidal ~107º Water Bent (V-shaped) ~104.5º Phosphorus Pentachloride Trigonal Bipyramidal 90º, 120º Sulfur hexafluoride Octaheral 90º A molecule’s attractive forces impacts its melting and boiling points as well as many other properties. •Will a molecule that is highly attracted to another molecule of its kind have a high boiling point or a low boiling point? In which state will the substance typically be found at room tempterature? First let’s review: Distinguish between polar and nonpolar bonds. What do those terms mean and how do you make this determination? Polarity of Molecule •Polar Molecule (Dipoles) – have a positive end and a negative end •Nonpolar Molecule - has an equal distribution of electrons and therefore no positive or negative ends Polar or Nonpolar Molecules… •H2 •CO2 •H2O Shape of molecule and polarity of bonds determines polarity of molecule. Valence Bond Theory • Covalent bonds form when a pair of electrons is shared by overlapping atomic orbitals on adjacent atoms. Consider HF, draw the valence electron configuration for H and F X __ X __ 2p __ X H 1s__ F 2s__ Methane, CH4 •Draw the valence electron configuration for C and H Carbon’s four sp3 hybrid orbitals Add four hydrogen s orbitals Boron Trihydride, BH3 •Draw the valence electron configuration for B Boron’s three sp2 hybrid orbitals, has 1 empty p orbital Add three hydrogen s orbitals Ethyne, C2H2 •Draw the valence electron configuration for C Each carbon has two sp orbitals and two p orbitals Add two hydrogen s orbitals • Sigma (s) bond – results from end to end overlap of atomic orbitals • Pi (p)bond – side be side overlap of atomic orbitals Try C2H4 Which bonds are s? p? Summary of Valence Bond Theory Hybridization VSEPR theory shape Example sp Linear (2) C 2H 2 sp2 Trigonal planar ( 3) BH3 sp3 Tetrahedral, bent (2 shared, 2 unshared), pyramidal (4) CH4 sp3d sp3d2 Trigonal bipyramidal (5) PCl5 Octahedral (6) SF6