Ions and bonding
advertisement
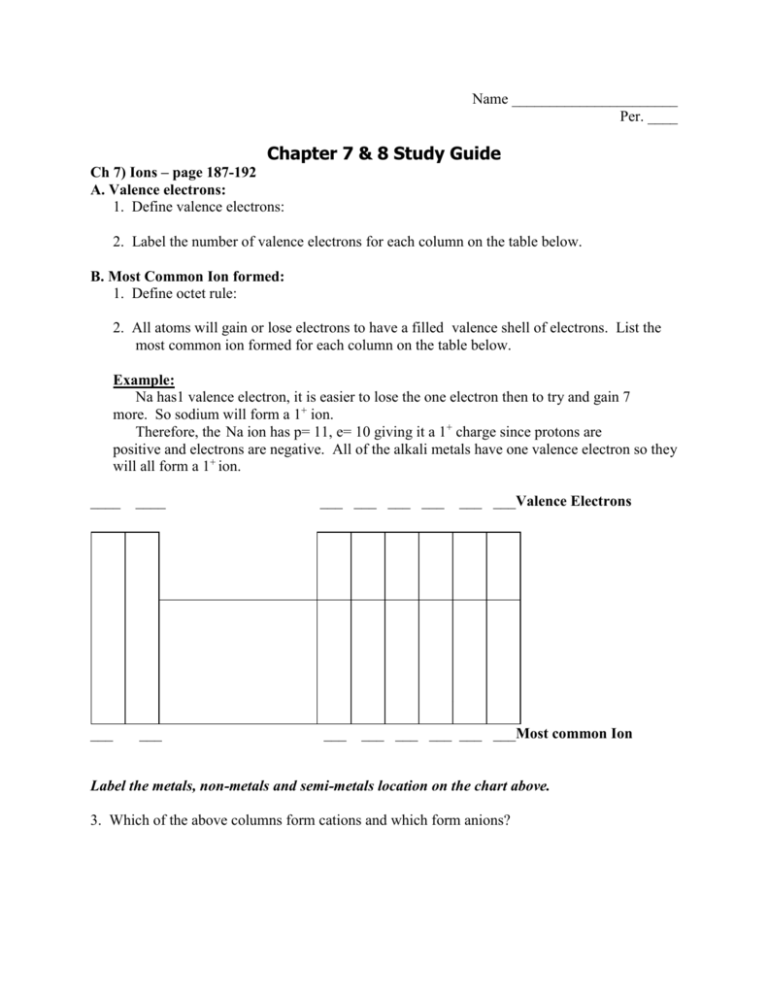
Name ______________________ Per. ____ Chapter 7 & 8 Study Guide Ch 7) Ions – page 187-192 A. Valence electrons: 1. Define valence electrons: 2. Label the number of valence electrons for each column on the table below. B. Most Common Ion formed: 1. Define octet rule: 2. All atoms will gain or lose electrons to have a filled valence shell of electrons. List the most common ion formed for each column on the table below. Example: Na has1 valence electron, it is easier to lose the one electron then to try and gain 7 more. So sodium will form a 1+ ion. Therefore, the Na ion has p= 11, e= 10 giving it a 1+ charge since protons are positive and electrons are negative. All of the alkali metals have one valence electron so they will all form a 1+ ion. ____ ____ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___Valence Electrons ___ ___ ___ ___ ___Most common Ion Label the metals, non-metals and semi-metals location on the chart above. 3. Which of the above columns form cations and which form anions? C) Ionic Compounds – pg. 194-198 1. Define ionic bond: 2. What types of elements form an ionic bond? Explain why and give an example of an ionic compound. 3. What are three properties of ionic compounds? Ch 8) Molecular Compounds – page 213 Part A) 1. Define covalent bond: 2. Define molecule: 3. Why is oxygen gas a diatomic molecule? 4. Why isn’t sodium chloride a molecule? 5. List three properties of molecular compounds. Part B) Bond Polarity – page 237 6. Define non-polar covalent bond: 7. Give an example of a non-polar covalent bond. 8. Define polar covalent bond and give an example. 9. Define electronegativeity: 10. Complete the chart below: Electronegativity difference Most probable type of bond 0-0.4 0.4-1.0 1.0-2.0 > 2.0 Example











