atoms lose or gain electrons to achieve noble gas electron
advertisement

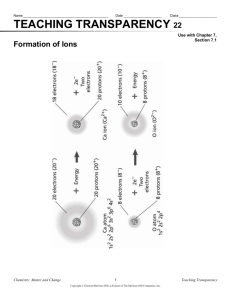
More on Ions Record into your notes Achieving Noble Gas Electron Configuration An ion forms when an atom • loses electrons (OIL, oxidation) or gains electrons (RIG, reduction) to achieve noble gas electron configuration Recognize the appearance of Bohr’s Model after an atom loses or gains electrons to form ions and/or how two atom share their electrons covalently to achieve noble gas electron configuration. Supplemental packet page 50 Atomic Number: Name: sodium-23 ion 23 Symbol: 11 mass # 1+ Na 23 #p ______ 11 #n ______ 12 #e 11 ••• •• • •• ••• More protons than electrons Electronic 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s0 Configuration: 12 magnesium-24 ion Name: 24 Symbol: 12 mass # 24 #p 12 ______ #n 12 ______ #e 10 ______ Electronic Configuration: Physical Properties: metal cation positive ion 1+ charge Chemical Properties: combines w/ anions Lewis Dot: ______ 10 Atomic Number: Ionic Structure 2+ Mg ••• •• • •• ••• More protons than electrons [Na]1+ Physical Properties: metal cation positive ion 2+ charge Properties: combines w/ anions [Mg]2+ 17 Physical Properties: Name: Symbol: • Chemical mass # 35 #p ______ #n ______ #e ______ Properties: Lewis Dot: Electronic Configuration: Atomic Number: 8 Physical Properties: Name: Symbol: • Chemical Lewis Dot: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s0 Atomic Number: Chemical mass # 16 #p ______ #n ______ #e ______ Electronic Configuration: Properties: Lewis Dot: Supplemental packet page 50 Atomic Number: Name: sodium-23 ion 23 1+ 11Na Symbol: mass # 23 #p ______ 11 #n ______ 12 #e 11 ••• •• • •• ••• More protons than electrons Electronic 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s0 Configuration: 12 magnesium-24 ion Name: 24 2+ 12Mg Symbol: mass # 24 #p 12 ______ #n 12 ______ #e 10 ______ Electronic Configuration: Physical Properties: metal cation positive ion 1+ charge Chemical Properties: combines w/ anions Lewis Dot: ______ 10 Atomic Number: Ionic Structure ••• •• • •• ••• More protons than electrons [Na]1+ Physical Properties: metal cation positive ion 2+ charge #n ______ 18 #e ______ 18 Properties: combines w/ anions [Mg]2+ 17 1s2 2s2 2p6 Configuration: Atomic Number: Name: 8 oxygen-16 ion 16 Symbol: 8 mass # 16 #p 8 ______ #n 8 ______ #e 10 ______ Electronic Configuration: Physical Properties: nonmetal anion negative ion 1- charge Chemical Properties: combines w/ cations Lewis Dot: More electrons than protons Electronic Chemical Lewis Dot: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 •• chloride-35 ion Name: ••• 35 1Symbol: 17Cl •• •• • •• •• •• • mass # 35 •• #p ______ 17 Atomic Number: O 2- •• •Cl• •• •• [ 3s 3p 2 6 ••• •• • •• ••• More electrons than protons 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s0 ]1- Physical Properties: nonmetal anion negative ion 2- charge Chemical Properties: combines w/ cations Lewis Dot: •• •O• •• •• [ ]2- Please note the movement of the red colored valence (outermost) electron on sodium. It is transferred over to the fluorine atom. Bohr Models Lewis dot structures Please note the movement of the red colored valence (outermost) electron on the 1) _______ atom. It is transferred over to the 2) ________ atom. Fill in the blanks ANS. 1)Mg, 2)Cl Record into your notes Ions isoelectronic (“same electronic configuration”) with noble gases [Ne] [Na]1+ •• •Cl• •• •• [ 1s2 2s2 2p6 [Ne] [Mg]2+ 1s2 2s2 2p6 ]1- [Ar] 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 •• •O• •• •• [ ]2- [Ne] 1s2 2s2 2p6 Please note the addition of the red colored valence (outermost) electrons to each atom listed. Recognize boron, B, is a semimetal, not a nonmetal. Draw the following into your notes opposite page 64 nonmetals gain just enough electrons to achieve noble gas e- configuration of the noble gas in their period (row) •• • • • • • • • • • •• •• •• •• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •• •• 10Ne 5B 6C 8O 9F N 3– O 2– F– nitride ion oxide ion fluoride ion nonmetals ions Please Note: the nonmetals like to gain electrons & the stability of these ions is associated with 8 valence electrons (an octet) semimetal C 4– carbide ion 7N Chapter 5 - Introduction to Chemical Bonding Ions isoelectronic (“same electronic configuration”) with noble gases [Ne] [Na]1+ •• •Cl• •• •• [ ]1- [Ar] ]2- [Ne] Electrostatic repulsions Like charges repel [Ne] [Mg]2+ Electrostatic attractions Opposites attract •• •O• •• •• [ Ionic Bonding (transferring electrons to achieve noble gas electron configuration) [Na]1+ •• •Cl• •• •• [ 1.Opposites attract (cation attracts an anion) 2.Brought together by electrostatics 3.Ions coming together to balance charge ]1- sodium chloride •• •Cl• •• •• [ ] 1- [Mg]2+ •• •Cl• •• •• [ ]1- magnesium chloride [Mg]2+ •• •O• •• •• [ ]2- magnesium oxide Looking ahead to Chapter 6 Covalent Bonding (sharing electrons to achieve noble gas electron configuration) 1. Bonding for FONCl BrISCH nonmetals 2. Brought together by sharing of electrons 3. Achieving an OCTET of valence electrons versus Chapter 5 - Ionic Bonding Ionic Bonding (transferring electrons to achieve noble gas electron configuration) 1. Opposites attract (cation attracts an anion) 2. Brought together by electrostatics 3. Ions coming together to balance charge Please note the addition of the red colored valence (outermost) electron by the in coming hydrogen atom which will be shared by both atoms. Covalent Bonding (sharing electrons to achieve noble gas electron configuration) nonmetals bond to hydrogen to achieve noble gas e- configuration of the noble gas in their period (row) •• • • H • • • • • Achieving an OCTET valence Addition of hydrogen • • H • •• •• •• •• • • H H• • H• • H• • • • • • • • • • • •H • •H • •H • • • • • • • • • •• •• H• H 1H 5B 10Ne 7N 6C CH4 methane gas NH3 ammonia gas 8O H2O water molecules of nonmetals hydrides Looking ahead to Chapter 6 9F HF hydrogen fluoride [Na]1+ Ionic substances Supplemental packet page 64 Io nic co mpou nds a re he ld together b y stron g el ectrica l fo rces betwe en o ppos itel y cha rged ions (e.g ., Na , Cl ). Th ese forces a re referred •• to as ionic bonds . Typ ica lly, i onic compo unds ( ionic salts ) h ave rel ative high mel ting poi nts (mp NaCl = 80 1 °C).and exist • Cl • 1- ph ys ica lly as sol ids at ro om tempe rature . It ta kes a l ot o f en ergy to brea k a n io nic bon d. Ca n you give a dditiona l exam ples of ioni c • • compo unds ? •• [ + ] – Mole cul ar compo unds . Two or mo re atoms may combi ne with on e an othe r to form an u nch arged mol ecu le. The ato ms i nvolved are un usua lly th ose of n onme tall ic elem ents . Withi n th e mo lecule, ato ms a re he ld to on e an othe r by strong forces call ed covalent bonds di atom ic m olecule s - there are roo m te mpera ture are vari able . se ven dia tomic molecules that beha ve as discrete uni ts. The physi cal sta tes for these mol ecu les at H H gas NN O O gas gas F gas F Cl Cl gas Br Br liquid I mo lecules with multiple bon ding patterns H molecules of nonmetals hydrides H C H H N H Si H H •• P H H •••• H H H S H H H •••• O H H H H •• I solid H •• • •• • F •• • •• • Cl Sum mary What is the favorite charge of these elements as ions? Indicate charge. Is there a relationship between the type of element that likes to have positive charge? a negative charge? Li Be B C N O F ion charge: 1+ 2+ 3+ 4- 3- 2- 1- How many atoms will each element bond to in order to be stable? of bonds that each element will make. Li number of bonds: Be B C N O Indicate the number F 1 2 3 4 3 2 1 Is there a relationship between ion charge and the number of bonds an element will make? If so, describe the relationship. . Supplemental packet page 64 H •• N N gas •• To these molecules, Add missing nonbonding pair of electrons • O• •O• •gas • •• gas •••F• •• •••Cl• •• •••Br• •• •••I• •• H gas •F• • gas • •• •Cl• • gas • •• •Br• • liquid • •• •I• • solid • •• Favorite bonding modes for nonmetals C, N,O, halogen, H C N O F H •Know the preferred total number of bonds to these elements 4 3 211 •N O , nitrogen and oxygen may have variable number of bonds (2) (1) (4) (3) Supplemental packet page 68 valence shell electron pair repulsion VSEPR = ________ ________ ________ ________ ________ Dete rmine the ang les betwee n bo nds, nam e th e ge ometry abou t th e centra l atom a nd g ive th e its hybri dizati on. IdealIdeal bonding for carbon = Four bonds to carbon - Four bonding modes Geometries 109.5 109.5 H C H bo nd a ngle s ge ometric name H H 120C C 120 120 H 120 H 109.5 H109.5 H tetrahedral 180 H trigonal planar C C H linear O 180 C O linear Ideal bonding angles for carbon Non-Ideal Geometries : : : bon d an gles H N H H107.5 107.5 geo metri c n ame pyramidal or trigonal pyramid N H q<120 bent H : O H 104.5 H geo metri c n ame bent O : : N N H : bon d an gles : N C H Bond angles are less than ideal angle Electron pair occupies a lot of space & is held close to nucleus of central atom