Classification
advertisement

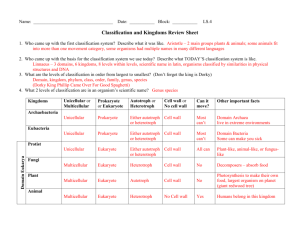
Classification Unit #10 1 What is it’s name? 2 Scientific Names 1. Felis cattus (animal) - Dog - Bird - Fish - Cat 4. Panthera pardus (animal) - Leopard - Jaguar - Cheetah - Cougar 2. Ursus arctos (animal) - Grizzly bear - mountain lion - King cobra - Asian elephant 5. Apis mellifera (insect) - Black fly - Leaf hopper - Mealworm - Honey bee 3. Dionaea muscipula (plant) - Bigleaf maple - Dandelion - Venus flytrap - Buttercup 6. Equus caballus (animal) - Sheep - Horse - Goat - Mule 3 Finding Order in Diversity • To identify organisms (living things) scientists developed a classification system. • Taxonomy- the classification of organisms • Carolus Linnaeus-BINOMIAL NOMENCLATURE • Two-part scientific name • First name: genus (Capitalized) • Second name: specie (lower case) • Ursus maritimus- polar bear 4 8 levels of classification Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Specie Darn! Ken poured coffee on Fred’s good shirt 5 Classification 6 Kingdoms of Life Characteristics CSCOPE Unit 10 lesson 02 What does this represent? Mary Jane Marlatt Kenneth Gastgeb Irene Jelinek Dennis Ryan Tim Ryan Ruth Gastgeb Jessica Ryan Kyla Guerrero Gabriel Guerrero Alayna Guerrero Abigail Guerrero Isaiah Guerrero What do scientists use to show evolutionary relationships between organisms on earth? CLADOGRAMS How do scientists determine relationships between organisms and how closely they are related? What type of living things inhabit the earth? ARCHAEA Major Characteristics • • • • • • Formerly called “Archaebacteria” Prokaryote Unicellular (one celled) Have a cell wall Autotroph or heterotroph Asexual reproduction BACTERIA Major Characteristics • • • • • • Prokaryote Unicellular (one celled) Have cell wall (peptidoglycan) Autotroph or heterotroph Asexual reproduction Helpful and harmful PROTISTA Major Characteristics • • • • Eukaryote Most unicellular Some colonial, some multicellular May have a cell wall ( usually cellulose, silica, or pectin) • Autotroph or heterotroph • Asexual or sexual reproduction FUNGI Major Characteristics • Eukaryote • Most multicellular, some unicellular • Cell wall (chitin) • Heterotroph • Asexual or sexual reproduction PLANTAE Major Characteristics • • • • • Eukaryote Multicellular Cell wall (cellulose) Autotroph Asexual or sexual reproduction ANIMALIA Major Characteristics • • • • • Eukaryote Multicellular No cell wall Heterotroph Sexual reproduction