28. Joints
advertisement

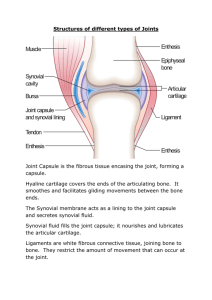
Joints Definition: The physical connection between two or more bones in the body. More about Joints: The study of joints is ‘arthrology’. The joints are very important as they make the movement of various body parts possible. For example, the elbow and the knee joint. The movement of our hands for picking up something, for bending , for walking , for chewing, for doing any kind of physical exercise are possible due to the presence of joints. Thus joints help us in the physical movement of the body. At the either side of the joints the bones are attached to the muscle by ‘tendons’. These help to pull the bones towards or against each other. There are basically three types of joints as follows: 1) Fibrous joint: The bones are connected by ‘ligaments’ formed of fibrous connective tissue, collagen. These joints are also known as fixed joints or immovable joints, as it is rigid and does not allow any movement of the bones connected. Examples of fibrous joints are bones of the skull, teeth in the jaw bone, joint between the tibia- fibula, radio-ulna and bones of pelvic girdle. 2) Cartilaginous joint: The bones are connected by the cartilage. These joints allow slight movement between the bones. These are partially movable and the example includes the joint between centra of 2nd vertebrae in the spine, ribs and sternum. 3) Synovial joint: The bones are highly movable joints. The cavities between the bones that participate in the joint have a synovial fluid between them. This fluid helps to lubricate and protects the bones from friction. The following are the types of the joints based on their shape, mechanism of working and degree of movement a) Ball and Socket joint: It is the most mobile joint. It comprise of a bone with an articulate head that fits into the hollow round cavity of another bone. For example,the shoulder joint, hip joint b) Hinge joint: This type of joint allows the bone movement in only one direction. For example, elbow joint, knee joint and interphalangeal joints ( fingers) c) Pivot joint: This type of joint allows rotation around an axis. For example, Atlanto-axial joint in the neck region that helps to move the head around. d) Saddle joint: This type of joints allows the bone tomove in more than one direction. The articular surface of one bobe is saddle shaped. For example, the thumb bones make it move back-forth and sideways too. e) Gliding joint: This type of joint allows the gliding of one bone over the other bone. For example, joints present in the ankle and wrist. Related Words: Arthrology, Fibrous joints, cartilaginous joints, synovial joints, ball and socket joints, hinge joints, gliding joints, saddle joints, pivot joint, interphalangeal joint Video Links: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FknWsN9EVJA http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QWRV4WZrzDs http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zWo9-3GJpr8 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LT7id_j19Oo http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qr_10yaKhbo