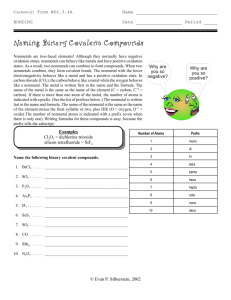
Naming Compounds as Ionic or Covalent
advertisement

WRITE THIS ON THE BACK OF YOUR WORKSHEET Directions: Name these compounds. List if they are either ionic or covalent. 1. PBr3 2. Na2SO4 3. CF4 Directions: Write the formula for the following compounds. 1. carbon monoxide 2. sulfur dichloride 3. diboron dihydride Naming Compounds as Ionic or Covalent Ionic and Covalent Bonding If a compound is made from a metal and a nonmetal, its bonding will be ionic. If a compound is made from two nonmetals, its bonding will be covalent. Naming of the bonds.... For ionic compounds, write positive ion first, followed then write the negative ion. CATION – metal, always positive, goes first ANION – nonmetal, always negative, goes second Suffixes Rule 1 – If a single element, compound ends in "IDE." Rule 2 – If a polyatomic, compound ends in "ATE" or "ITE." Numerical Prefixes Remember: you only use prefixes for covalent compounds! 1- mono 6- hexa 2- di 7- hepta 3- tri 8- octa 4- tetra 9- nona 5- penta 10- deca Examples: P2S3- diphosphorus trisulfide A.) Phosphorus (non metal) B.) Sulfur (non metal) C.) Covalent Bond D.) Prefix (covalent only) – use “di” which means 2 Use “tri” which means 3 E.) Suffix – use “ide” with sulfur (because it is a single element) Examples: CaCO3– Calcium Carbonate A.) Calcium – metal, do not use a prefix because it is an ionic bond. B.) Carbonate is Carbon and Oxygen bonded together. They are both non metals and are a polyatomic bond. C.) Ionic Compound D.) Suffix - use “ate” because of the polyatomic bond. Directions: Name these compounds. List if they are either ionic or covalent. PBr3 – P (phosphorus) + Br (bromine) This is a Covalent (2 nonmetals) Phosphorus tribromide Na2SO4 – Sodium Sulfate Na – Sodium, metal, 2 atoms of sodium S – Sulfur, nonmetal, 1 atom of sulfur O – Oxygen, nonmetal, 4 atoms of oxygen “ATE” – suffix use this suffix because it is a polyatomic 3. CF4 Directions: Write the formula for the following compounds. 1. carbon monoxide - CO 2. sulfur dichloride - SCl2 3. diboron dihydride - B2H2