Beginning of Industrial Revolution
advertisement

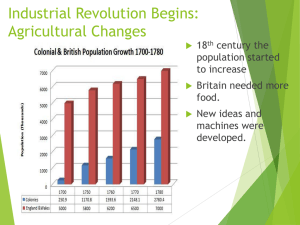
BEGINNING OF INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION REVIEW QUESTIONS What is the enclosure movement? Enclosing animals and land to increase production What is urbanization? Population shift from rural to urban What was the cottage system? Traditional form of manufacturing goods – self sufficient, “in house” What three new ideas allowed the agrarian revolution to happen? Enclosure movement, Seed Drill, Crop rotation Who unified Germany? Otto von Bismarck OBJECTIVE Students will identify the factors of production Students will identify why the industrial revolution began in great Britain as opposed to anywhere else ECONOMY Economist: studies scarcity Economy: act of allocating scarce items Scarcity: unlimited wants but limited resources Can’t have it all – not possible FACTORS OF PRODUCTION In order to produce goods, all of the factors of production must be present Land: natural resources Labor: workers Capital: Financial: start up money Physical:Tools to get the job done (hammer, nails) Human: knowledge and experience LAND What do we notice about the geography of Great Britain? Lots of coastline Lots of rivers LAND In addition to being geographically ideal, GB also had other natural resources Coal and Iron were abundant LABOR Urbanization: population shift from rural to urban areas Small farmers were out of work so they moved to the city seeking employment They were ready to do whatever they had to in support of their families This also increased the demand for goods and services in urban areas CAPITAL Financial: excess money was brought in by the colonies (remember this is 1750) Mercantilism Excess money will be invested into start ups of new businesses Human: people had experience with business practices, developed banking system Physical: People are going to invent new tools Jethro Tull (seed drill) Necessity is the mother of all invention SOOOO…. Great Britain was in possession of all the factors of production The timing was perfect for production to EXPLODE Industrial Revolution AGE OF IRON AND COAL Instead of manual labor (bulls, hand plows, etc…) *Hist. Circs* Factories were built on waterways (rivers) so they could use the water to produce steam The steam would power the machines Iron Ore was used to cast parts for machines Coal was used to heat the water to create steam TEXTILE INDUSTRY Textiles = cloth goods First major industry Reliant on colonies (mercantilism) Raw cotton from colonies were produced into clothing items New technologies As the industry took off, there was a need for more efficient technologies New technologies make production cheaper, faster, and better quality TECHNOLOGY ADVANCEMENTS IN TEXTILE INDUSTRY Flying shuttle Spinning Jenny Water Frame FLYING SHUTTLE Flying shuttle allowed a single person to weave faster using much wider fabrics John Kay Eventually will be mechanized All woven fabrics looked the same (uniformity) SPINNING JENNY James Hargreaves Produced yarn using 8-9 spools at once WATER FRAME Richard Arkwright First powered, automatic, continuous textile machine that enabled the rapid spinning of threads STEAM ENGINE James Watt Used water to generate power efficiently Will be used in trains, factory machines, etc… PACKET WORK Complete page 28 in your packet Identify how specifically GB had each of the factors of production HOMEWORK Recipie for Industrialization EXIT TICKET Define all the factors of production Identify how Great Britain had all the factors of production Identify two inventions of the early industrial revolution