The Industrial Revolution

BELL WORK: GET PAPER
FROM FRONT!
What do you think it means to be industrialized?
Can you give an example of a country that is, and one that is not?
THE INDUSTRIAL
REVOLUTION
1750-1850
(But really ongoing)
MAP OF LDCS- MDCS
LEARNING TARGETS
I can explain the causes of the
Industrial Revolution and why it began in Britain.
I can analyze the social, political and economic effects of the
Industrial Revolution.
INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
The slow shift in production from simple hand tools to complex machines.
A shift from an agricultural to a manufacturing economy
A shift from rural to urban
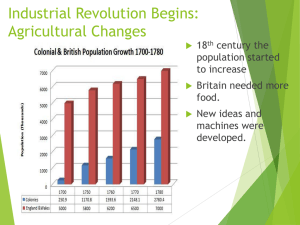
CAUSES
Improved farming methods
Crop rotation, turnips to restore soil, seed drill, crossbreeding of livestock
Enclosure: open farmlands enclosed into more productive fields.
New technology
James Watt – steam engine- became the key power source of the IR.
Improved iron- used for the construction of machines and steam engines
WHY IT BEGINS IN BRITAIN:
Using the text on pgs 250-253, make a concept web with the key factors that helped Britain take an early lead in industrialization. Explain them, don’t
JUST use one word!
WHY THIS REVOLUTION IS SO
IMPORTANT:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zhL5DCizj5c
THE SEED DRILL
THE STEAM ENGINE
WORLD’S FIRST IRON BRIDGE, 1779
THE TEXTILE INDUSTRY
“The Cottage Industry” – the world’s first mechanized industry
High demand for cloth – raw cotton was distributed to peasant families who spun it into thread and then wove thread into cloth in their homes.
Small wages for workers, big profits for entrepreneurs.
TEXTILE INDUSTRY INVENTIONS
John Kay – flying shuttle
James Hargreaves – spinning jenny
Richard Arkwright – water frame
Main Idea: New machines were too big for homes.
New buildings were built to house them.
“Factories” – located near rivers
Power, transportation
Production increased exponentially. Completely changed the economies and societies of Europe.
THE TRANSPORTATION REVOLUTION
First steam locomotive: 1804 – traveled
2.5 mph
1829-The Rocket – 16 mph, but still killed a member of the British Cabinet not paying attention on its debut
World’s first railroad: The Liverpool-to-
Manchester opened in 1830.
By 1860, trains were moving 60mph
.
THE EFFECTS OF
THE I.R.
https://www.flocabulary.com/industrial -revolution/
URBANIZATION
New farming techniques and mass production of goods put farmers and skilled craftsman out of work.
Migrated to factory towns in search of work.
City population exploded
Ex: Manchester: 17,000 in 1750; 70,000 by
1800
Living conditions horrible
Overcrowding, entire families slept in 1 room slums
No police, fire, health, water, or sanitation services
LIVING CONDITIONS
Sewage ran through the streets
“Londoners living near the Thames River kept their doors and windows closed year-round due to the smell of the river”
INDOOR BATHROOMS AKA EARTH CLOSETS
LIFE IN FACTORIES
12-16 hour workdays
No mandatory breaks
No safety devices on machines
No disability or workers comp or insurance…if you got sick or injured, you just lost your job
Employers preferred women and children workers:
Paid them less
Easier to manage
Smaller hands